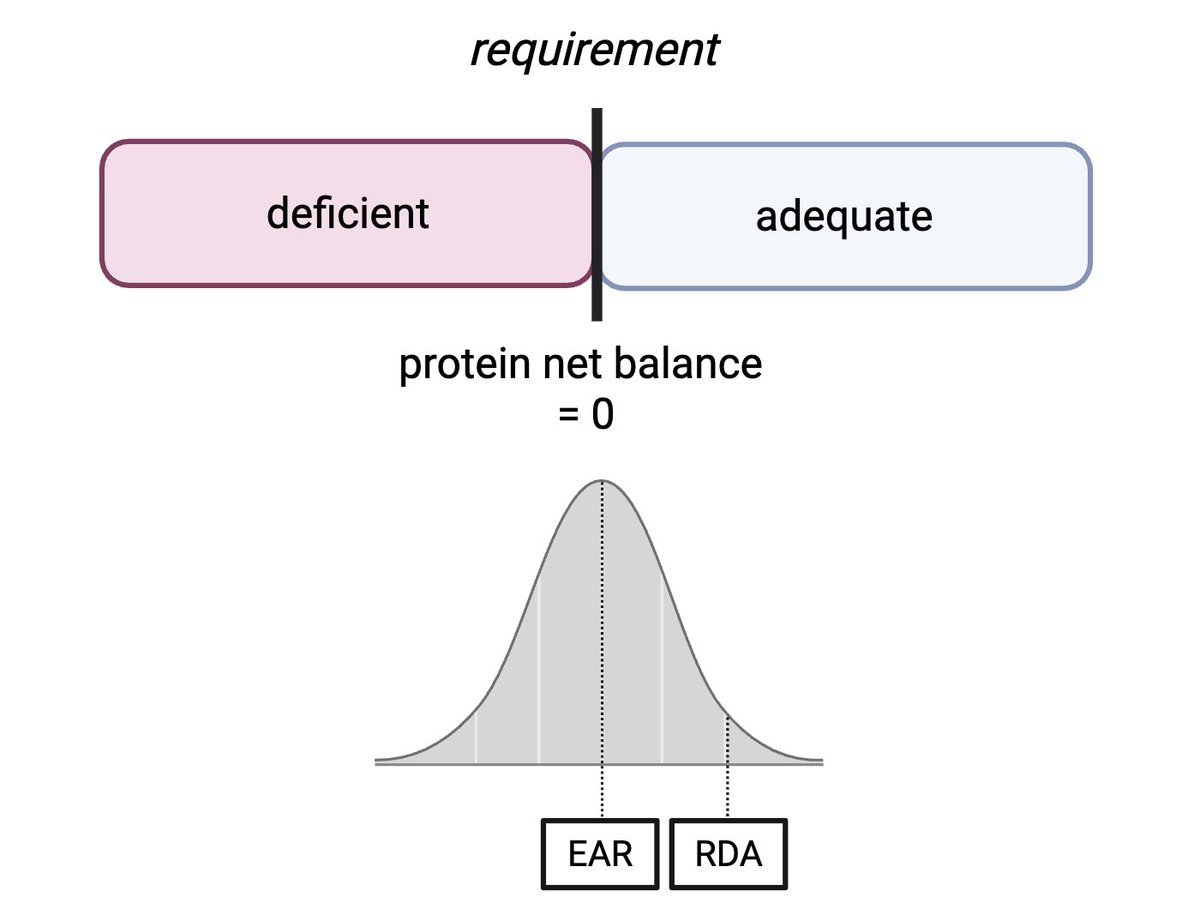
Mediterranean countries have lower cardiovascular mortality rates compared to northern Europe and the United States. It is often suggested that this is at least partly due to the Mediterranean diet.
2/
2/

The Mediterranean diet includes high intake of olive oil, fruit, nuts, vegetables, and cereals; a moderate intake of fish and poultry. In addition, it has a low intake of dairy products, red meat, processed meats, and sweets; and moderate wine consumption.
3/
3/

The current study investigated the effect of the Mediterranean diet on major cardiovascular events (myocardial infarction, stroke, or death from cardiovascular causes) compared to a control diet with an emphasis on low fat intake.
4/
4/

Subjects with cardiovascular risk were allocated to 1) a control diet (advice on a low fat-diet), 2) a Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra-virgin oil (≥4 tablespoons/d), or 3) a Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra nuts (≥30 g/d).
5/
5/

After 5 years of the diet, significantly more subjects in the control diet (4.4%) have had a major cardiovascular event compared to the olive oil (3.8%) or nut (3.4%) supplemented Mediterranean diets.
6/
6/
Strengths of the study include the relatively large sample size (n=7447) and duration for this type of research.
7/
7/
Despite being advised to reduce fat intake, changes in fat intake were small. The Mediterranean diets groups were advised to make many changes, but the consumption of the supplemental items turned out to be the main difference between the groups.
8/
8/
In conclusion, the Mediterranean diet can reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events in people with cardiovascular risk.
Study:
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29897866/
10/10
Did you find this useful? Please help promote the first tweet of the thread:
Study:
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29897866/
10/10
Did you find this useful? Please help promote the first tweet of the thread:
https://twitter.com/JornTrommelen/status/1593279550334582784?s=20&t=WY37oBFJTuLZZHd4SctGsw
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh