In this one, higher sedentary time was found associated with adverse cardiac structural measures, while higher light physical activity was associated with better cardiac function in adolescents. 

- This study examined the independent relationships of device-based measured sedentary time and physical activity in relation to cardiac structural and functional geometry among adolescents.
- Higher sedentary time was associated with higher left ventricular mass indexed for height, while higher moderate-to-physical activity was also paradoxically associated with higher left ventricular mass indexed for height.
Both these associations were not statistically significant among those with high fat mass and those with high lean mass.
The association between moderate-to-physical activity and higher left ventricular mass indexed for height was not observed among those with elevated blood pressure/hypertension.
- The sedentary time-associated left ventricular mass indexed for height increase was threefold higher than moderate-to-physical activity-associated left ventricular mass indexed for height increase.
- Higher moderate-to-physical activity was associated with lower higher left ventricular diastolic function and lower left ventricular filling pressure, but only among participants with high lean mass only.
"The paradoxical relationship between higher MVPA and higher LVMI in normotensive and optimal fat mass adolescent population may suggest physiological cardiac muscle increase which could complement the findings that higher MVPA was also associated with reduced LVDF and LVFP"
- Higher light physical activity was associated with higher left ventricular diastolic function in the total cohort and among participants who were normotensive & had high lean mass...
...and lower left ventricular filling pressure among participants with elevated systolic blood pressure/hypertension.
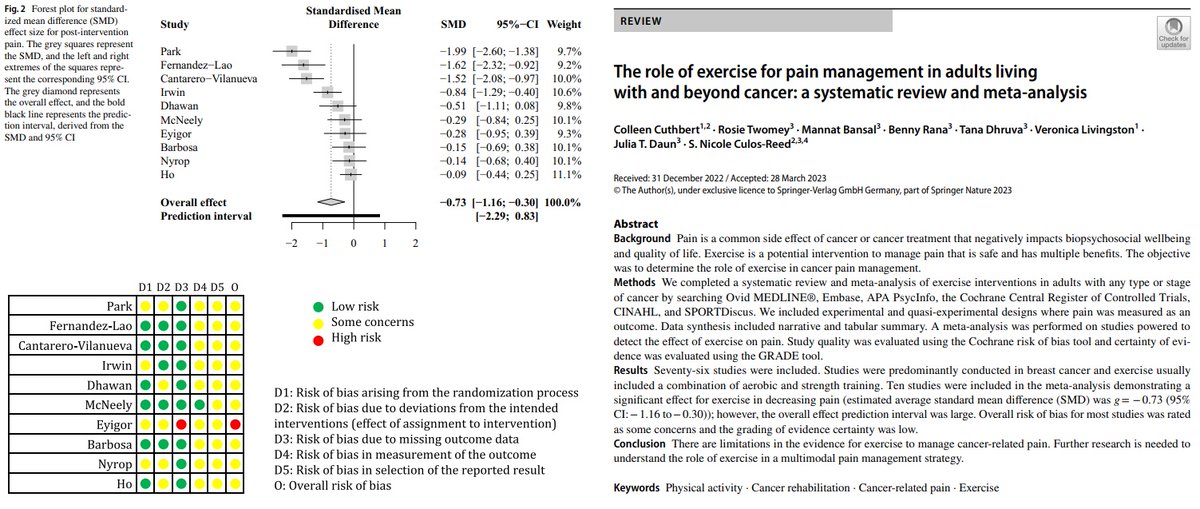
Associations of accelerometer-based sedentary time, light physical activity and moderate-to-vigorous physical activity with resting cardiac structure and function in adolescents according to sex, fat mass, lean mass, BMI, and hypertensive status (open access)
doi.org/10.1111/sms.14…
#exercise #fitness #fit #FitFam #FitLife #FitnessAddict #Workout #TrainHard #GymLife #GymTime #muscle #strength #lift #GetStrong #cardio #hiit
#exercise #fitness #fit #FitFam #FitLife #FitnessAddict #Workout #TrainHard #GymLife #GymTime #muscle #strength #lift #GetStrong #cardio #hiit
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter