A small thread on Enterprise Value (EV) - A measure of the total value of the company!! 🏦🏭
What does it mean, how do you calculate it and how to use it?
#EnterpriseValue #EVEBITDA
Like and retweet for maximum reach!!📈
What does it mean, how do you calculate it and how to use it?
#EnterpriseValue #EVEBITDA
Like and retweet for maximum reach!!📈
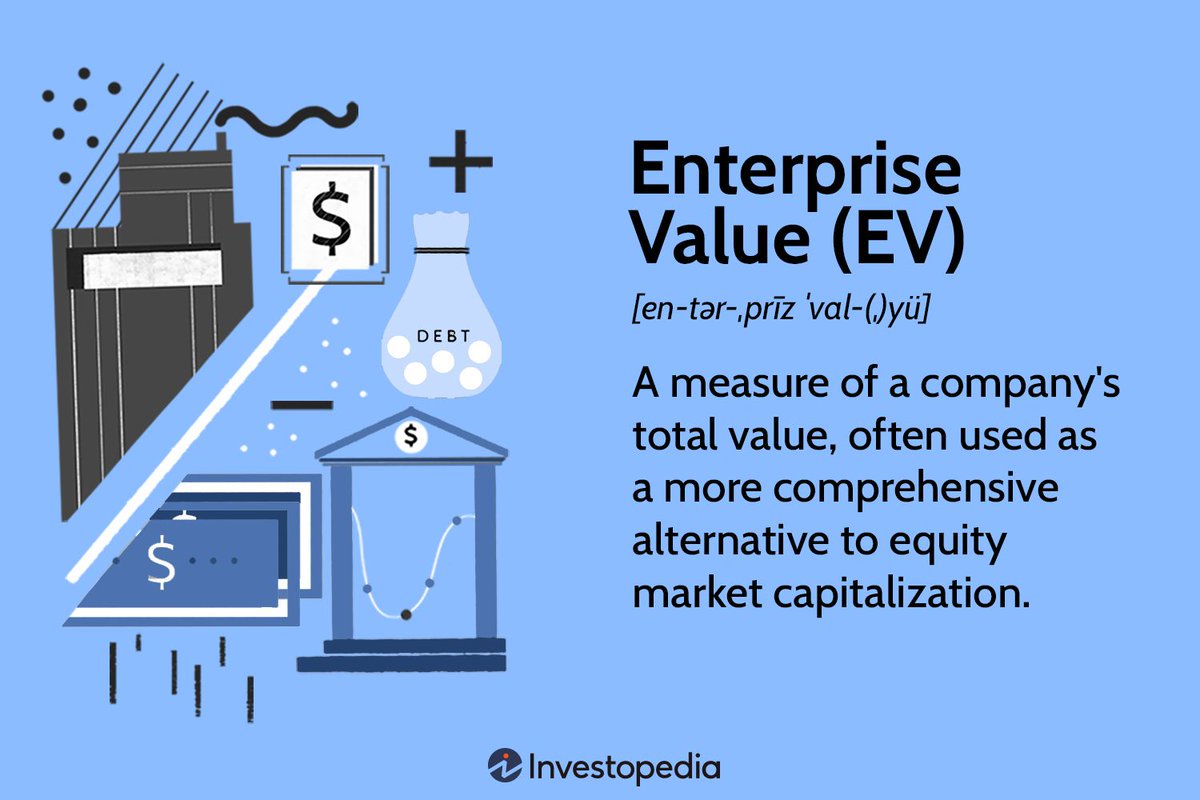
1. How to calculate it?
•The Enterprise Value of a firm is calculated by adding the value of the company’s debt and total outstanding equity and subtracting the amount of cash held by the company
•The Enterprise Value of a firm is calculated by adding the value of the company’s debt and total outstanding equity and subtracting the amount of cash held by the company

2. What does it mean?
•Enterprise Value gives us the total monetary value of all assets of the company. It is usually looked at when a company is being acquired and it signifies the amount you would need to pay all stakeholders that have a financial interest in the company.
•Enterprise Value gives us the total monetary value of all assets of the company. It is usually looked at when a company is being acquired and it signifies the amount you would need to pay all stakeholders that have a financial interest in the company.
•The value of debt is added to the value of equity as anyone who acquires the firm also assumes the debt liability. To look at it another way, EV gives us the value of all the assets that can be deployed by the company as the acquirer gets the benefit of the
assets being financed using debt.
•The cash is subtracted from the value of debt and equity as anyone who acquires the firm also gets the cash which the company holds, which effectively reduces his buying price.
•The cash is subtracted from the value of debt and equity as anyone who acquires the firm also gets the cash which the company holds, which effectively reduces his buying price.
•Another way to look at it would be that the cash would be used to pay down the debt. So in that case, we can also look at Enterprise Value as the Value of Equity and the Net Debt of the company 
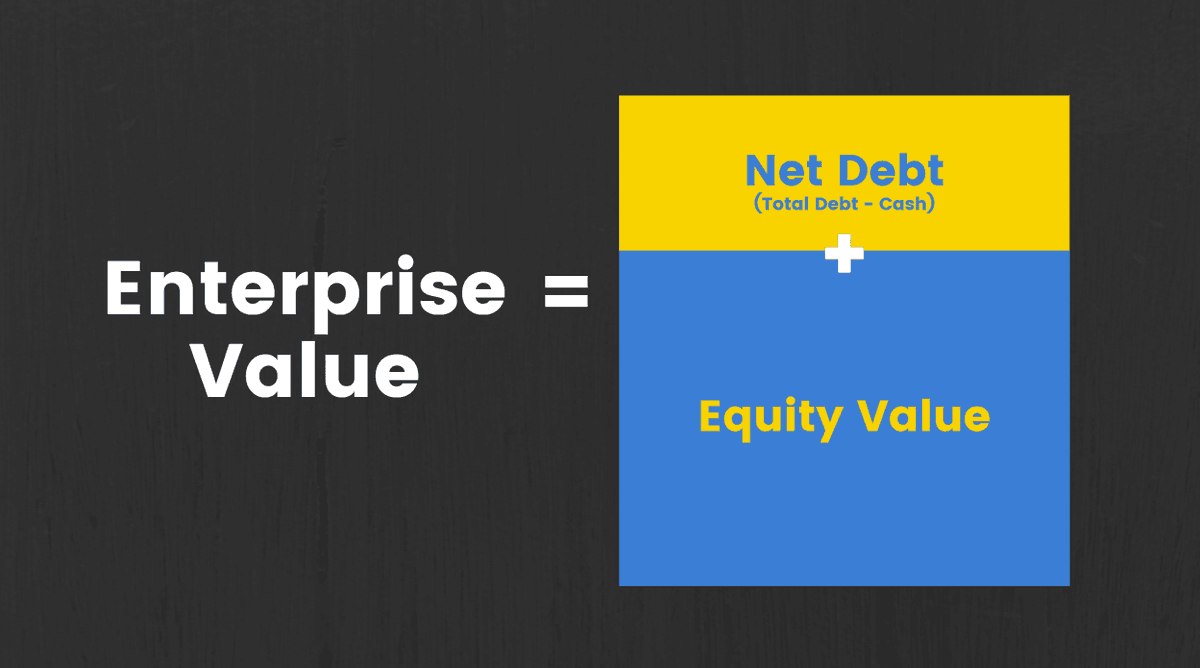
•Enterprise Value makes it easy to compare the size of 2 firms as it eliminates the differences in capital structure and looks at 2 businesses purely in terms of the assets they have.
3. When to use it?
•Minority investors usually look at the Market Capitalization of a company whereas Enterprise Value is used more for mergers and acquisitions.
•Enterprise Value is a good measure to use when the company is being acquired as it gives a better picture of
•Minority investors usually look at the Market Capitalization of a company whereas Enterprise Value is used more for mergers and acquisitions.
•Enterprise Value is a good measure to use when the company is being acquired as it gives a better picture of
what is the true cost to own that company. The acquirer of the company will only be paying for equity of the company upfront. But by becoming the new owner of the company they assume all the debts of the company as well.
•For example, suppose a company is evaluating whether they should buy Suven Pharma which has a Market Cap of ~₹12,000 Cr or Piramal Pharma which has a Market Cap of ~₹8,500 Cr
•On the face of it, it seems like the company would have a lesser cash outlay if they were to buy Piramal Pharma. But Piramal Pharma has ~₹5,000 Cr of debt whereas Suven Pharma has very minimal debt of ~₹91 Cr 

•This would make the Enterprise Value of Piramal Pharma higher than Suven Pharma, which means the acquirer will ultimately be paying more for Piramal Pharma.
•Enterprise Value is also a much better metric to use when valuing companies in capital intensive industries. Since these types of companies generally employ large amounts of debt, multiples based on price/market cap may not give the true picture.
4. Valuation Multiples based on EV
•Enterprise Value/EBITDA is one of the most commonly used valuation ratios when looking at capital intensive industries. It gives a true picture of the true value of the entire company, not just the value of the stock.
•Enterprise Value/EBITDA is one of the most commonly used valuation ratios when looking at capital intensive industries. It gives a true picture of the true value of the entire company, not just the value of the stock.
•When valuing a company based on EV/EBITDA, we use EBITDA as it signifies the return generated for all the stakeholders that have supplied capital to the company.
•Apart from that, we can also use other valuation metrics like EV/EBIT, EV/Sales, EV/CFO or EV/FCFF.
•Apart from that, we can also use other valuation metrics like EV/EBIT, EV/Sales, EV/CFO or EV/FCFF.
Join the Micro Cap Club:
bit.ly/3zYY8OS
bit.ly/3zYY8OS
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter










