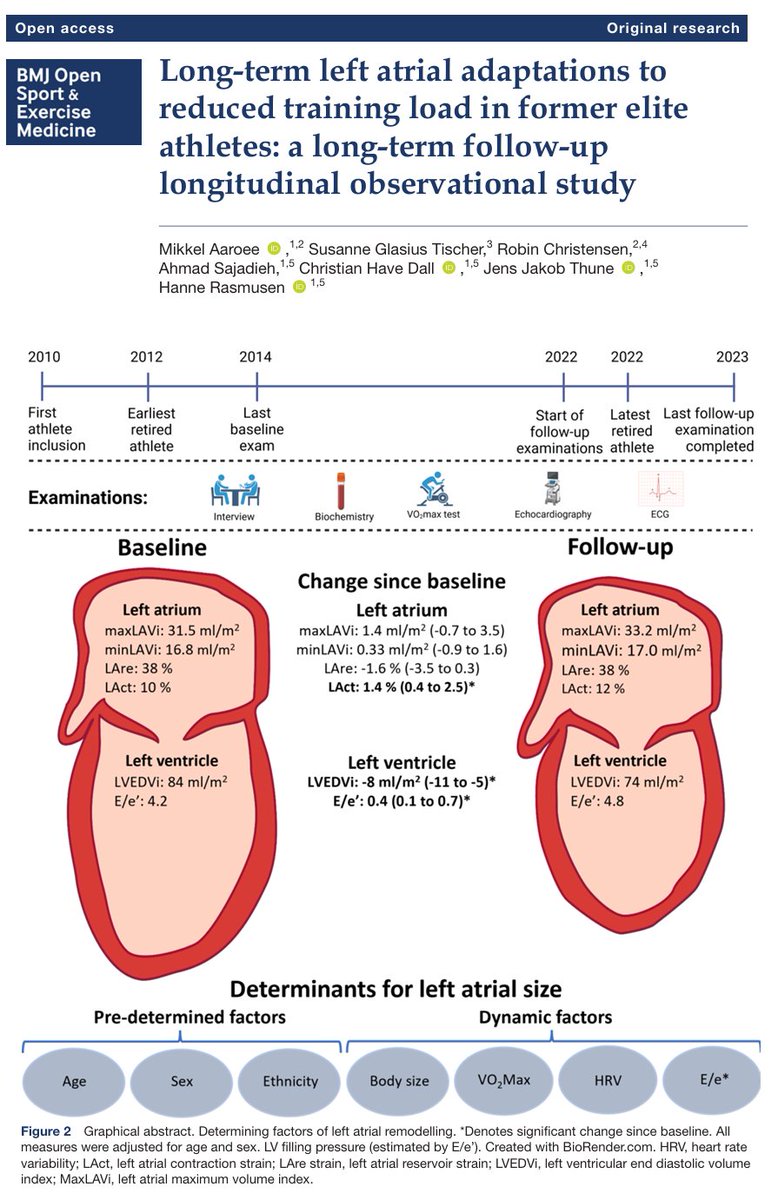
- Prolonged QT dispersion derived from electrocardiograms has been used as an indicator of abnormal ventricular repolarization for several cardiac diseases.
- An increased QT dispersion has been documented in patients with arterial hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy.
- In addition to clinical environments, left ventricular hypertrophy is observed in athletes completing regular training.
- This left ventricular hypertrophic cardiac response serves as a reactive mechanism to compensate for volume overload experienced during endurance training or pressure overload experienced during resistance training.
- Although athletes develop impressive left ventricular tissue growth, it is unknown whether this exercise-induced left ventricular hypertrophy is associated with increased QT dispersion as observed in patients with hypertensive myocardial hypertrophy.
- Despite evidence suggesting that cardiac remodeling varies in response to pressure overload (concentric hypertrophy) or volume overload (eccentric hypertrophy)...
...there is limited research on comparing QT dispersion and echocardiographic parameters across athletes competing in different sports varying in terms of the predominant type of overload imposed.
- In this way, sports may be classified according to the mechanical demands they elicit based on the peak static components (expressed as relative intensity of voluntary muscular contraction across three levels [A, B, C])...
...and the peak dynamic components (expressed as percentage of maximal oxygen uptake across three levels [I, II, III]) undertaken by athletes.
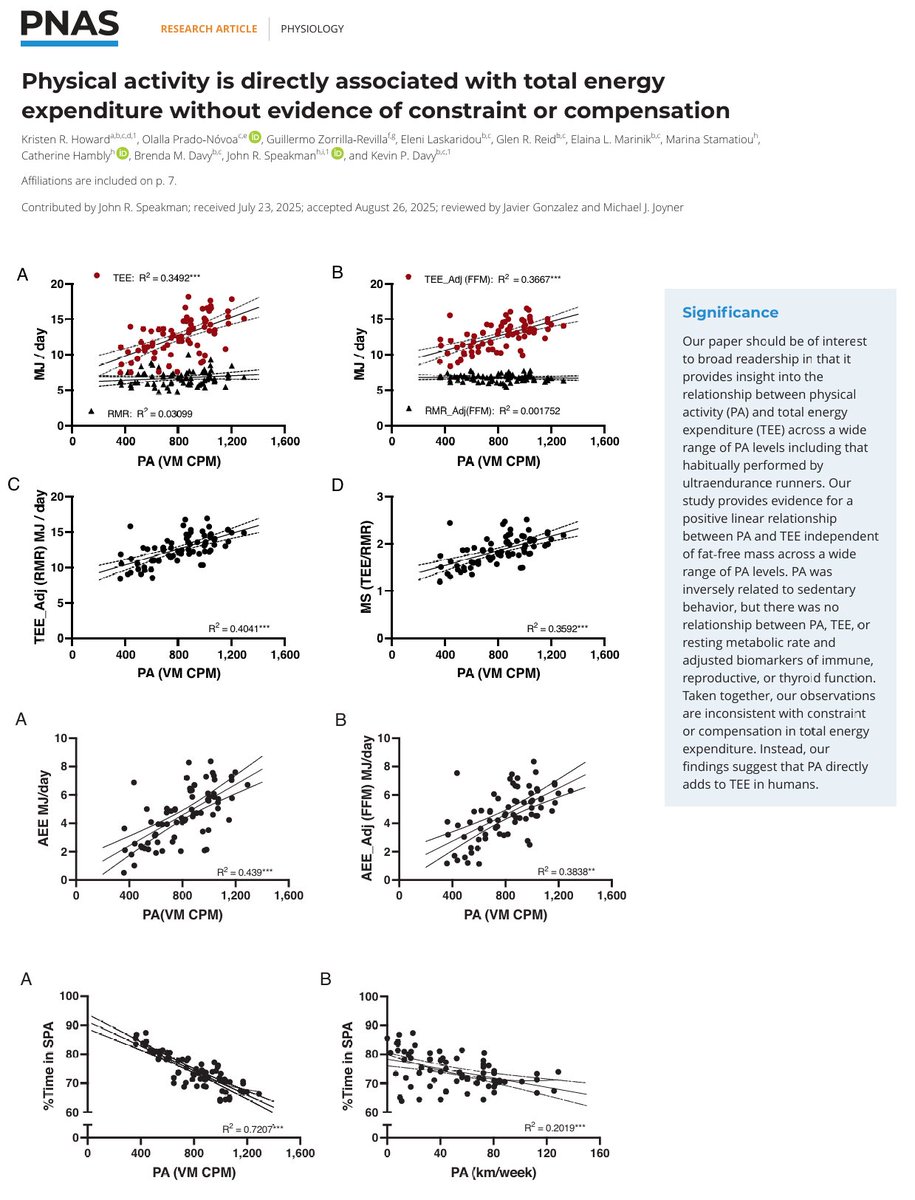
- This study aimed to compare QT dispersion and echocardiographic parameters between athletes competing in different sports and sedentary controls and assess the associations between QT dispersion and echocardiographic parameters among them.
- Advanced left ventricular hypertrophy, predominantly concentric in nature, induced by pressure overload, accompanied with an increased QT dispersion was observed in athletes predominantly completing static exercise (powerlifters and bodybuilders).
"These structural parameters we observed in powerlifters and bodybuilders represent remodeling adaptations in response to training that fall within a 'grey zone'...
"...where extreme expressions of athlete’s heart and mild morphological forms of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy may overlap...
"...Although these likely remodeling adaptations in powerlifters and bodybuilders mimic pathological hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, their LV end-diastolic diameters (~ 52–53 mm) were within clinically accepted partition values for the general population (45–55 mm)...
"...which is a useful and sensitive marker in distinguishing an athletic heart from hypertrophic cardiomyopathy diagnosis."
- On the other hand, mild left ventricular hypertrophy (toward the upper threshold of the normal reference range) induced by volume overload that was accompanied with a reduced QT dispersion was observed in long-distance runners, volleyball athletes, and football athletes.
"In addition to LV structural parameters, LV systolic indicators were also within clinically accepted reference ranges for the general population...
"...further supporting adaptive (rather than maladaptive) physiological cardiac remodeling in athlete groups predominantly undertaking dynamic (long-distance runners, football athletes, and volleyball athletes) or static exercise (powerlifters and bodybuilders)."
Sport-related differences in QT dispersion and echocardiographic parameters in male athletes (open access)
doi.org/10.1038/s41598…
#exercise #fitness #fit #FitFam #FitLife #FitnessAddict #Workout #TrainHard #GymLife #GymTime #muscle #strength #lift #GetStrong #cardio #hiit
doi.org/10.1038/s41598…
#exercise #fitness #fit #FitFam #FitLife #FitnessAddict #Workout #TrainHard #GymLife #GymTime #muscle #strength #lift #GetStrong #cardio #hiit
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh