Ever wonder why fever worsens brain injury after cardiac arrest?
I have diligently avoided fever in these patients for years but never knew the reason why.
#medthread #tweetorial #medtwitter
Let's review some of the early evidence that fever is actually harmful in this setting.
💥It was noted in the 1990s that hyperthermia after global ischemia in rats worsened neurological injury
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9065563…


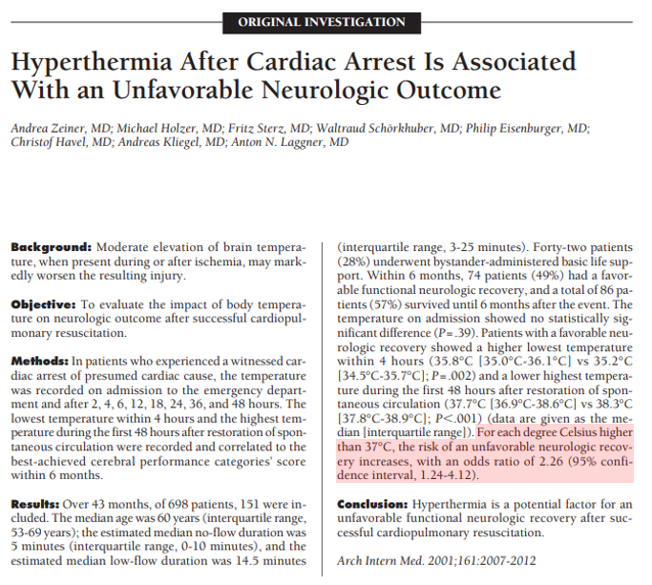
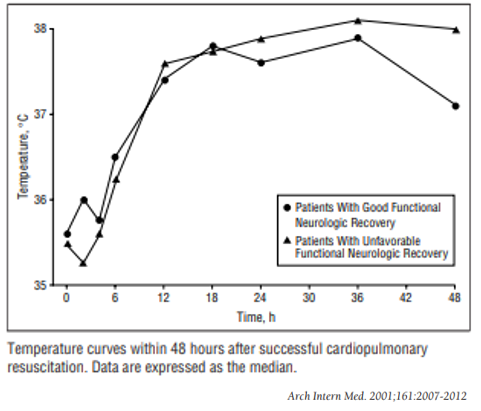
💥Shortly thereafter, a dose-response relationship between fevers and worsened neurological outcomes after cardiac arrest was observed.
The higher the fever, the worse the risk of poor outcomes, with an odds ratio of 2.26.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?term=11…
To understand why fevers worsen neurological outcomes, we need to understand the mechanisms of neurological injury after cardiac arrest.
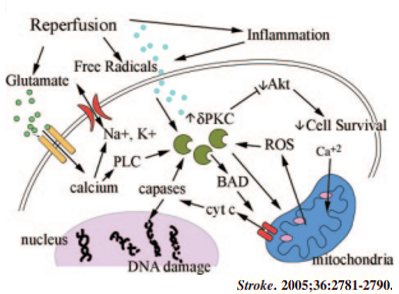
⚡️While there are multiple mechanisms, a sequence of events triggered by reperfusion is thought to predominate.
Reperfusion of ischemic neurons releases excitatory neurotransmitters, particularly glutamate.
💡Glutamate stimulates an intracellular cascade that interferes w/ mitochondrial function.
💡This ➡️ reactive oxygen species, DNA damage, cell death
bit.ly/30SnsnL
Returning to our original question, why does fever worsen brain injury after cardiac arrest?
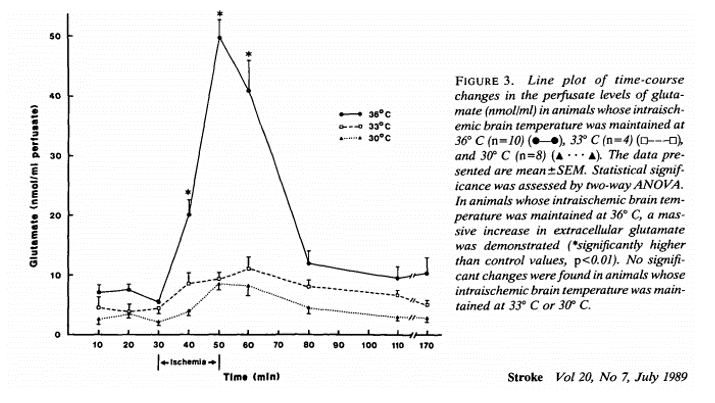
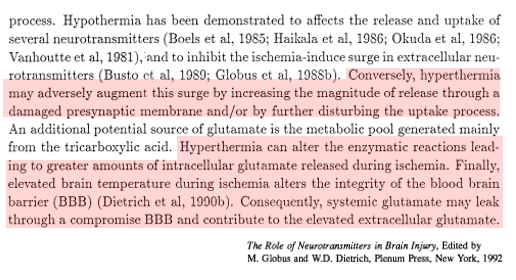
It turns out that glutamate release during and after ischemia is temperature-sensitive.
⚡️Higher temperatures = more glutamate release
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2568705
Exactly why ⬆️temperature induces release of glutamate isn't clear. 2 possibilities:
💡Stimulation of cellular enzymatic activity = more glutamate production/release
💡Inducing a leaky blood brain barrier allows systemic glutamate access to CNS
bit.ly/38F8pAS
Glutamate has even been shown to induce the release of neuron-specific enolase - which has been called the "brain troponin" as a marker of cerebral injury after cardiac arrest - in the absence of ischemia.
It is that neurotoxic when extracellular.
bit.ly/38DPw0O

Before closing, a caveat:
▪️ What temperature to maintain patients at after cardiac arrest is an open area of investigation and still somewhat controversial.
The need to avoid fevers is not.
To summarize:
💡Release of the neurotransmitter glutamate after reperfusion causes cerebral injury after cardiac arrest
💡Glutamate induces mitochondrial dysfunction, DNA damage, and neuronal death
💡Fevers induce release of glutamate, worsening neurological injury