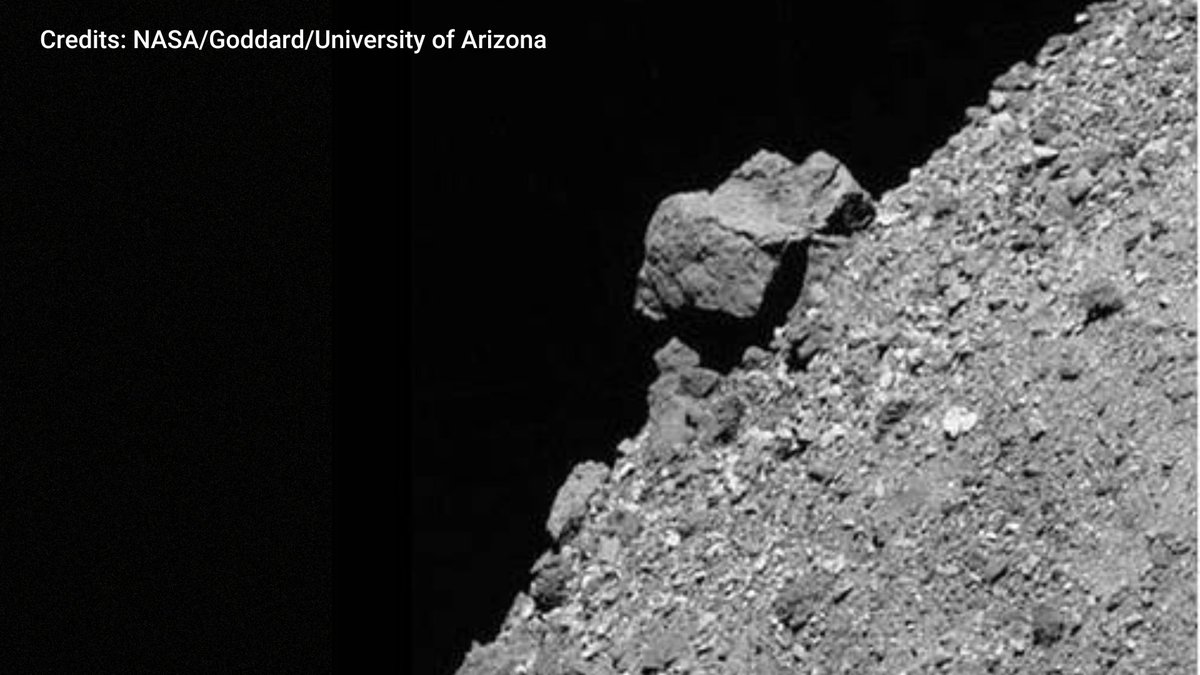
Two Asteroids of Over 19 Metre Diameter to Fly Past Earth This Tuesday; One to Approach Closer to #Earth Than #Moon - by @deekshith_np
weather.com/en-IN/india/sp…
(📸: NASA/JPL-Caltech)
weather.com/en-IN/india/sp…
(📸: NASA/JPL-Caltech)

Two #asteroids with an estimated diameter between 19 and 49 metres will pass by Earth on Tuesday, September 1. While both of them are relatively large, only one of them will be very close to Earth in terms of astronomical distances.
Both asteroids, officially named #2011ES4 and #2020QG5, are classified as near-Earth objects but are not expected to pose any harm to Earth on their approach.
2011 ES4
The 'potentially hazardous asteroid' 2011 ES4 will be 1.2 lakh km away from Earth at its closest approach on September 1. It means the asteroid will be closer to Earth than the Moon, which is 3.84 lakh km away from our home planet.
The 'potentially hazardous asteroid' 2011 ES4 will be 1.2 lakh km away from Earth at its closest approach on September 1. It means the asteroid will be closer to Earth than the Moon, which is 3.84 lakh km away from our home planet.
In fact, this is reportedly the closest approach of such a large asteroid over the next ten years.
Ruling out a possible threat, the US space agency said that the space rock would not hit Earth.
"Will #asteroid 2011 ES4 hit Earth? No! 2011 ES4's close approach is 'close' on an astronomical scale but poses no danger of actually hitting Earth," #NASAAsteroidWatch posted on #Twitter.
.@NASA estimates the asteroid's relative speed at around 8.16 km per second, Xinhua reported. The last time asteroid 2011 ES4 flew by Earth, it was visible from ground for four days.
This time, it will be closer to our planet than before, and the chances of spotting it, especially with a telescope will be very high.
The #asteroid was first discovered in the spring of 2011 and passed by Earth every nine years. A 'potentially hazardous asteroid' is currently defined based on parameters that measure the asteroid's potential to make threatening close approaches to the Earth, according to NASA.
2020 QG5
The asteroid 2020 QG5 is smaller than 2011 ES4 and is approaching Earth again after 16 years. On a relativistic coordinate time scale, this asteroid will approach around 5:30 TDB on September 1. The last time this asteroid approached Earth was on August 11, 2004.
The asteroid 2020 QG5 is smaller than 2011 ES4 and is approaching Earth again after 16 years. On a relativistic coordinate time scale, this asteroid will approach around 5:30 TDB on September 1. The last time this asteroid approached Earth was on August 11, 2004.
On its closest approach, #2020QG5 will be more than 29 lakh kilometre away from the #Earth and is not expected to pose any threat to Earth. Currently, it is in the constellation of Pegasus.
Near-Earth Objects are those that travel within the 50 million km of the Earth orbit. Just a fortnight ago, a car-sized space rock, named 2020 QG, passed by our planet on August 16.
Soon after its discovery, the asteroid was declared the closest asteroid to fly past Earth, without falling into the Earth. As per #NASA, it flew 2,950 kilometres above the southern Indian Ocean.
Two students from the Indian Institute of Technology-Bombay—Kunal Deshmukh and Kriti Sharma—have been credited with the discovery.
@iitbombay
@iitbombay
As per the estimates from @NASA, no large space rock is currently on a collision course with Earth. Therefore, the probability of a huge asteroid hitting Earth is quite slim.
In fact, no large object is likely to strike the #Earth any time in the next several hundred years as best as we can tell, says NASA.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh