What do we know about Vitamin C and #COVID19 so far?
The role of #VitaminC goes beyond immunity-boosting & the micronutrient at high dose is crucial to prevent severity.
Making a case with 14 studies, postulating Vitamin C to be an integral part of COVID treatment.
The role of #VitaminC goes beyond immunity-boosting & the micronutrient at high dose is crucial to prevent severity.
Making a case with 14 studies, postulating Vitamin C to be an integral part of COVID treatment.

Direct Association:
1. August 2020 case study in a 74 years old COVID 19 patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome treated with oral vitamin C 1 g twice a day along with antivirals was able to be taken off mechanical ventilation within 5 days.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
1. August 2020 case study in a 74 years old COVID 19 patient with acute respiratory distress syndrome treated with oral vitamin C 1 g twice a day along with antivirals was able to be taken off mechanical ventilation within 5 days.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
2. A single-center observational study identified a total of 17 patients who received IV vitamin C for COVID-19 & noted a significant decrease in inflammatory markers, including ferritin and D-dimer, and a trend to decreasing FiO2 requirements.
covid19.elsevierpure.com/en/publication…
covid19.elsevierpure.com/en/publication…
3. In a research letter, Camon L et al illustrated that 17 patients (94.4%) of a cohort with ARDS had undetectable vitamin C levels and 1 patient had low levels (2.4 mg/L). The reference value is 5 mg/dl.
link.springer.com/content/pdf/10…
link.springer.com/content/pdf/10…
Aid in Recovery:
4. A meta-analysis of 29 controlled trials with 11,306 participants, showed that regular vitamin C intake of around 1 g/day shortened URTIs by 8% in adults and in children by 14%.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23440782/
4. A meta-analysis of 29 controlled trials with 11,306 participants, showed that regular vitamin C intake of around 1 g/day shortened URTIs by 8% in adults and in children by 14%.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23440782/
5. A meta-analysis of 12 trials with 1,766 patients in ICU found that vitamin C shortened ICU stay by 8%.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30934660/
6. Another meta-analysis of 8 trials found that vitamin C shortened the duration of mechanical ventilation
in patients.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32047636/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30934660/
6. Another meta-analysis of 8 trials found that vitamin C shortened the duration of mechanical ventilation
in patients.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32047636/
7. There is evidence that Vitamin C declines drastically in critically ill patients. In a study with 44 such patients, Carr A et al showed that nearly 40% of the septic shock patients were deficient in Vit-C, compared with 25% of the non-septic patients.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29228951/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29228951/
8. An RCT with 20 critically ill patients with multiple organ dysfunction demonstrated 2 g/d dose was associated with normal plasma concentrations, and the 10 g/d dose was associated with supranormal plasma concentrations.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29522710/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29522710/
9. Treatment with vitamin C decreases IL-6 and blocks in vivo the release of IL-6 in the endothelium induced by endothelin-1 (ET-1) in humans.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
Prophylaxis & Prevention:
10. Feyaerts A et al proposed that Low dose (0.5–2 g/d) vitamin C may have benefits when used early in severe acute respiratory syndrome.
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…
10. Feyaerts A et al proposed that Low dose (0.5–2 g/d) vitamin C may have benefits when used early in severe acute respiratory syndrome.
sciencedirect.com/science/articl…

11. A total of 148 animal studies have indicated that a daily dose of a few grams of vitamin C may alleviate or prevent infections.
mdpi.com/2072-6643/9/4/…
mdpi.com/2072-6643/9/4/…
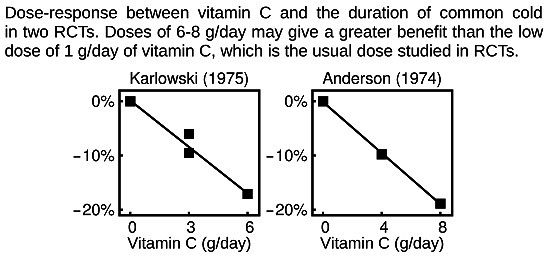
12. Vitamin C is known to support various cellular functions of both the innate and adaptive immune systems, including modifying susceptibility to various viral infections and by influencing inflammation.
portlandpress.com/biochemsoctran…
portlandpress.com/biochemsoctran…

13. During the outbreak of SARS‐CoV‐1 in 2003, the use of vitamin C, an essential micronutrient for humans and free radical scavenger, was suggested as a nonspecific treatment for severe viral respiratory tract infections.
academic.oup.com/jac/article/52…
academic.oup.com/jac/article/52…
14. A Cochrane systematic review concludes that 1 to 2 g vitamin C per day is safe, inexpensive, and has a consistent effect on the duration and severity of the common cold.
cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.10…
cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.10…
All this evidence makes a very strong case on why a high dosage of Vitamin C needs to be a crucial part of COVID 19. More RCTs are recommended to establish this hypothesis.
@PeterVermont @drdavidsamadi @deboraha_rd @AndrewJacksonV3 @AAPSonline please take a look at this thread and opine.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh