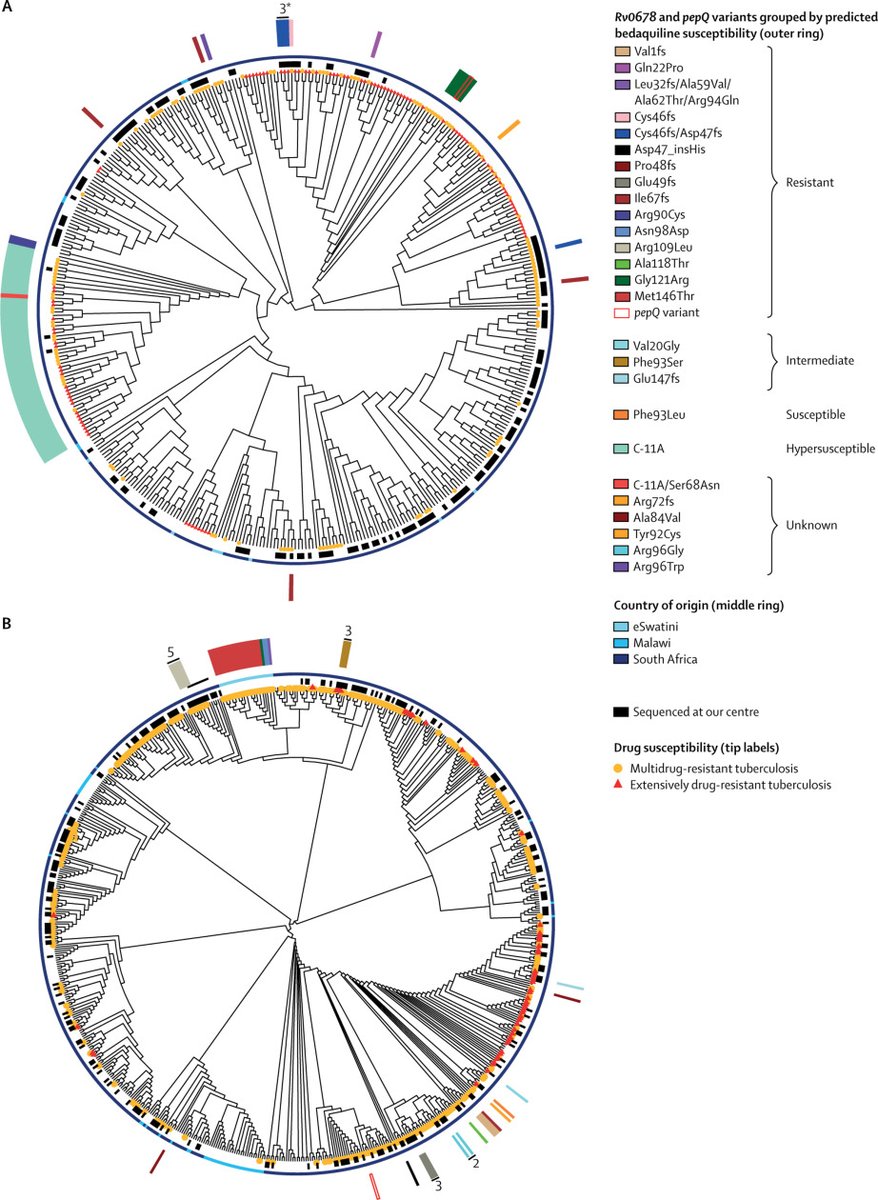
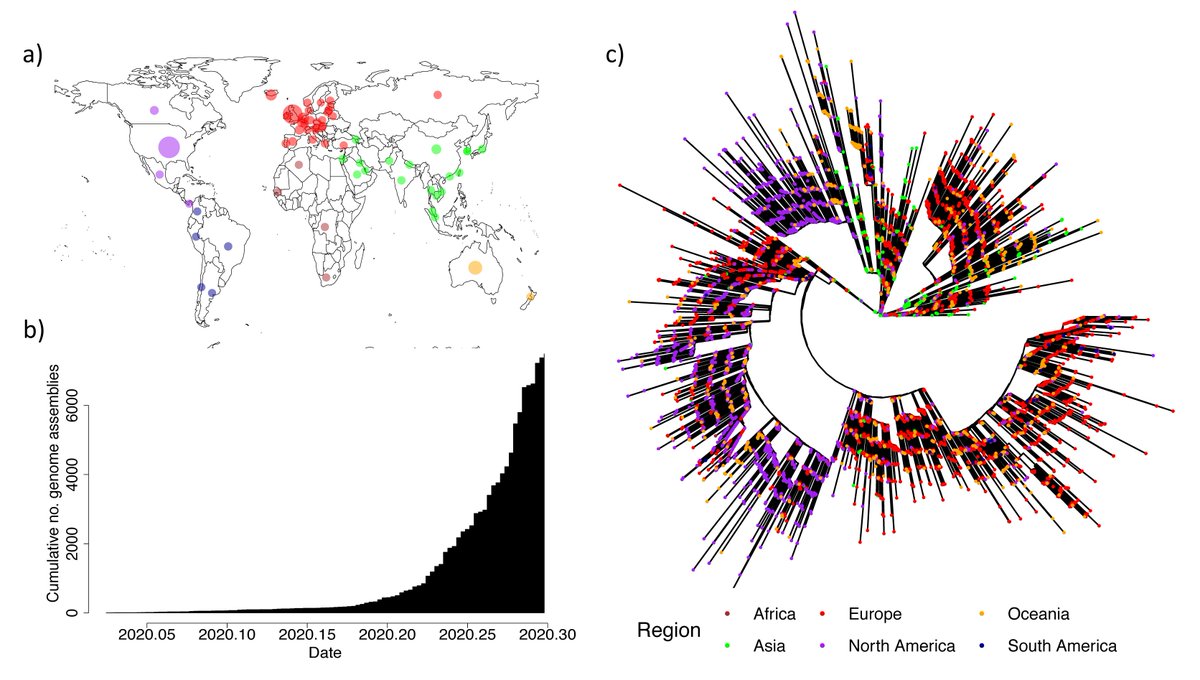
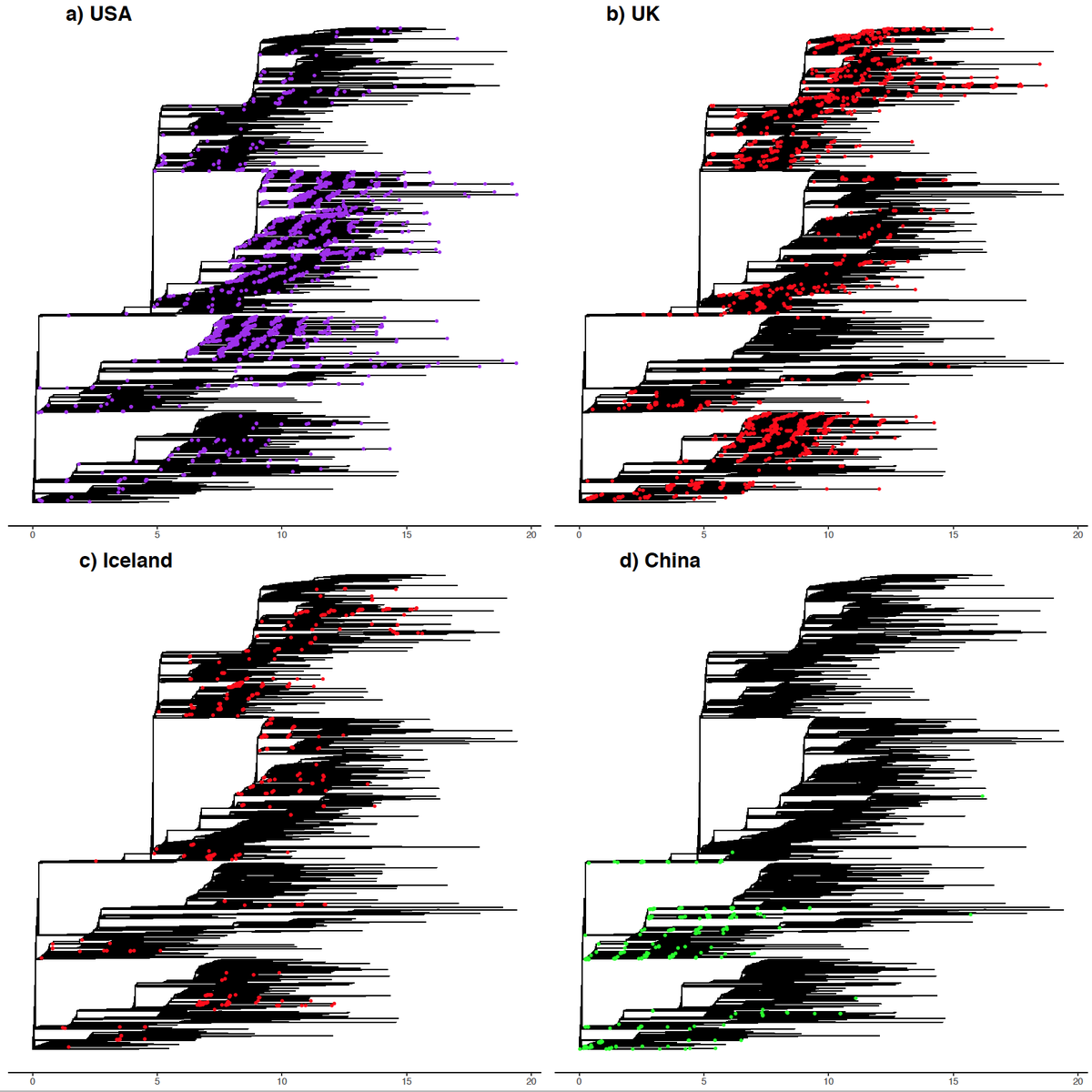
There are reports coming out in the Danish media of novel mutations emerging in #SARSCoV2 in #mink tinyurl.com/y5gbwype
SARS-CoV-2 can infect multiple mammalian carnivores and has now been detected in multiple mink farms to date 👇
SARS-CoV-2 can infect multiple mammalian carnivores and has now been detected in multiple mink farms to date 👇
Across high coverage #SARSCoV2 genomes isolated from mink @GISAID we pick up unique mutations including one in the #spike protein which has appeared at least five times in phylogenetically distant #mink lineages. 
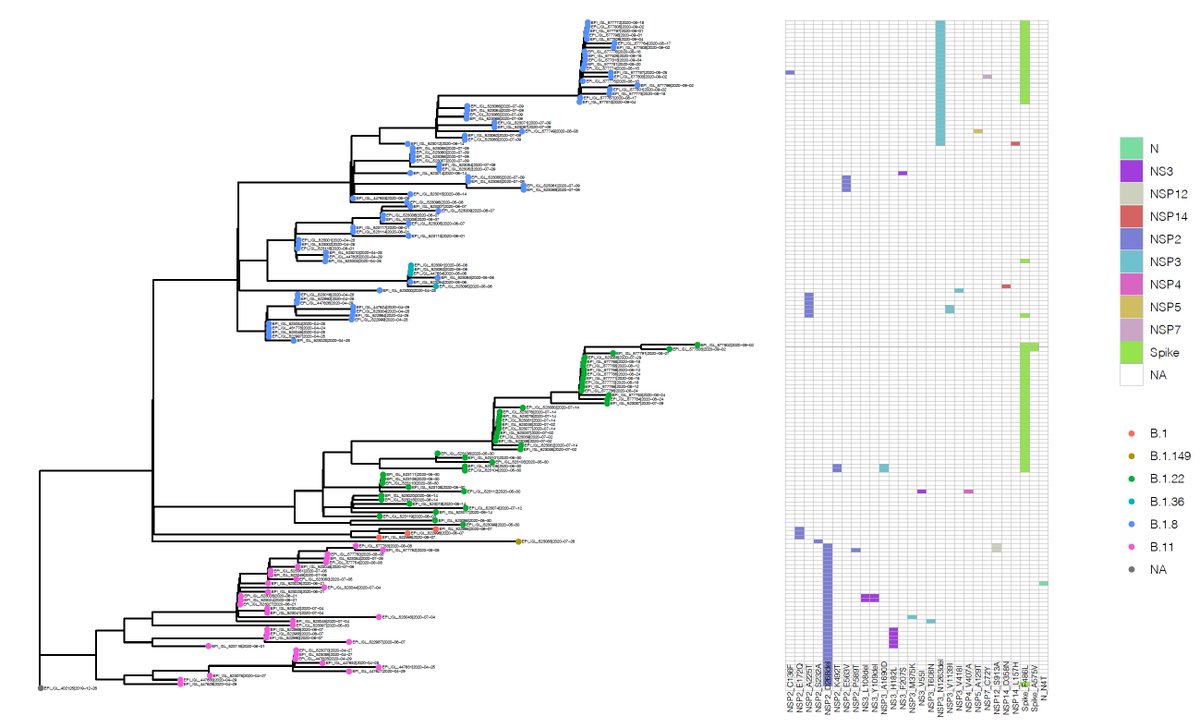
This mutation, falling within the receptor binding domain, may be a good candidate for adaptation of #SARSCoV2 to #mink hosts. While this mutation has been seen in #SARSCov2 in human circulation it is rare. Currently available mink genomes fall in the diversity of human #SARSCoV2
More information is required from the press release, including making the #genomes publicly available to the community, to allow better characterisation of the mutations present in Danish mink farms and their possible impact (if any).
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh