Neuroanatomy TOTD #14🧵
Got some requests to do one of the trickiest areas of human anatomy, the #temporalbone. So many named structures! #meded #FOAMed #FOAMrad #medtwitter #medstudents #radiology #neurorad #radres #neurosurgery #neuroanatomy #ENT #otolaryngology
1/21
Got some requests to do one of the trickiest areas of human anatomy, the #temporalbone. So many named structures! #meded #FOAMed #FOAMrad #medtwitter #medstudents #radiology #neurorad #radres #neurosurgery #neuroanatomy #ENT #otolaryngology
1/21
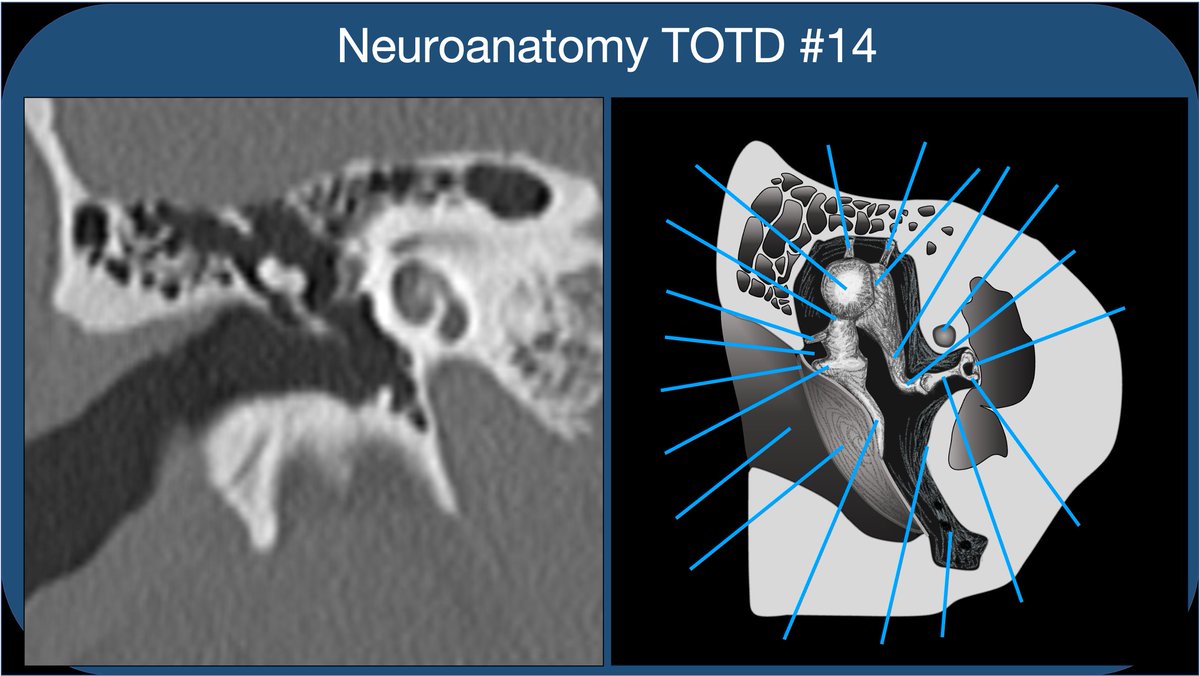
Whether learning t-bone anatomy as a medical student or evaluating a CT of the t-bone as a radres, it’s best to compartmentalize into external, middle, and inner ear. This thread🧵is on the middle ear: Inner ear to follow, some day:)
2/21
2/21

The external ear extends from the external meatus to the TM. The TM should be thin and *almost* imperceptible on CT. Thickened and retracted TM suggests prior pathology (usually otitis media) and scarring.
3/21
3/21

The middle ear is an air-filled cavity containing the middle ear ossicles, which transmit vibration from the tympanic membrane to the oval window. It can be further divided into epi-, meso-, and hypo-tympanum. Compartmentalize!
4/21

4/21


The ossicles reside in the mesotympanum. The ossicular chain acts as amplifier to sonic vibrations of TM. The malleus (hammer) has a head, neck, lateral process, anterior process, and manubrium. Both lateral process and manubrium are embedded in TM (best seen on coronalCT).
5/21


5/21



The head of the malleus articulates with the body of the incus (anvil) (incudomalleolar joint). The incus has short, long, and lenticular processes. The long and lenticular processes are slight and vulnerable to erosion in inflammatory dz.
6/21

6/21


The lenticular process articulates w/ the capitulum of the stapes (stirrup); stapes also has ant and post crus, as well as a footplate embedded in the annular ligament of the oval window. This is where the sonic vibrations are transmitted to the fluid of the inner ear.
7/21
7/21

Ossicles are supported by ligaments & 2 tiny muscles. Malleus is supported by sup,ant,&lat ligaments. (sup&lat➡️coronal, ant➡️axial). These may scar/ossify in chronic OM, contributing to conductive hearing loss (post-inflammatory ossicular fixation). pubs.rsna.org/doi/pdf/10.114…
8/21

8/21


The tensor tympani muscle (CN5 innervation) lies in a bony canal parallel & medial/superior to the Eustachian tube. The tendon courses laterally through the middle ear➡️neck of the malleus.
9/21
9/21

The stapedius muscle (CN7 innervation) is much smaller and not as well seen, attaching to the stapes. When contracted, these muscles tighten the tympanic membrane & annular ligament of oval window, dampening vibration and protecting cochlea from overly intense stimulation.
10/21
10/21
It’s helpful to understand bony landmarks and recesses of ME. Prussak’s space (best seen coronally) is bordered laterally by the bony scutum and pars flaccida of TM, and medially by the malleus. This space is the most common site of origin for acquired cholesteatoma.
11/21
11/21

The tegmen tympani is the roof of the epitympanum, and separates ME from middle cranial fossa. Dehiscence of the tegmen in inflammatory processes can lead to spread into the middle cranial fossa, as well as CSF leak. It's pretty thin!
12/21
12/21
The mastiod antrum is a large air cell posterolatteral to epitympanum, and connected to it by short passageway called the aditus ad antrum (hence continuity of ME and mastoid air cells).
13/21
13/21

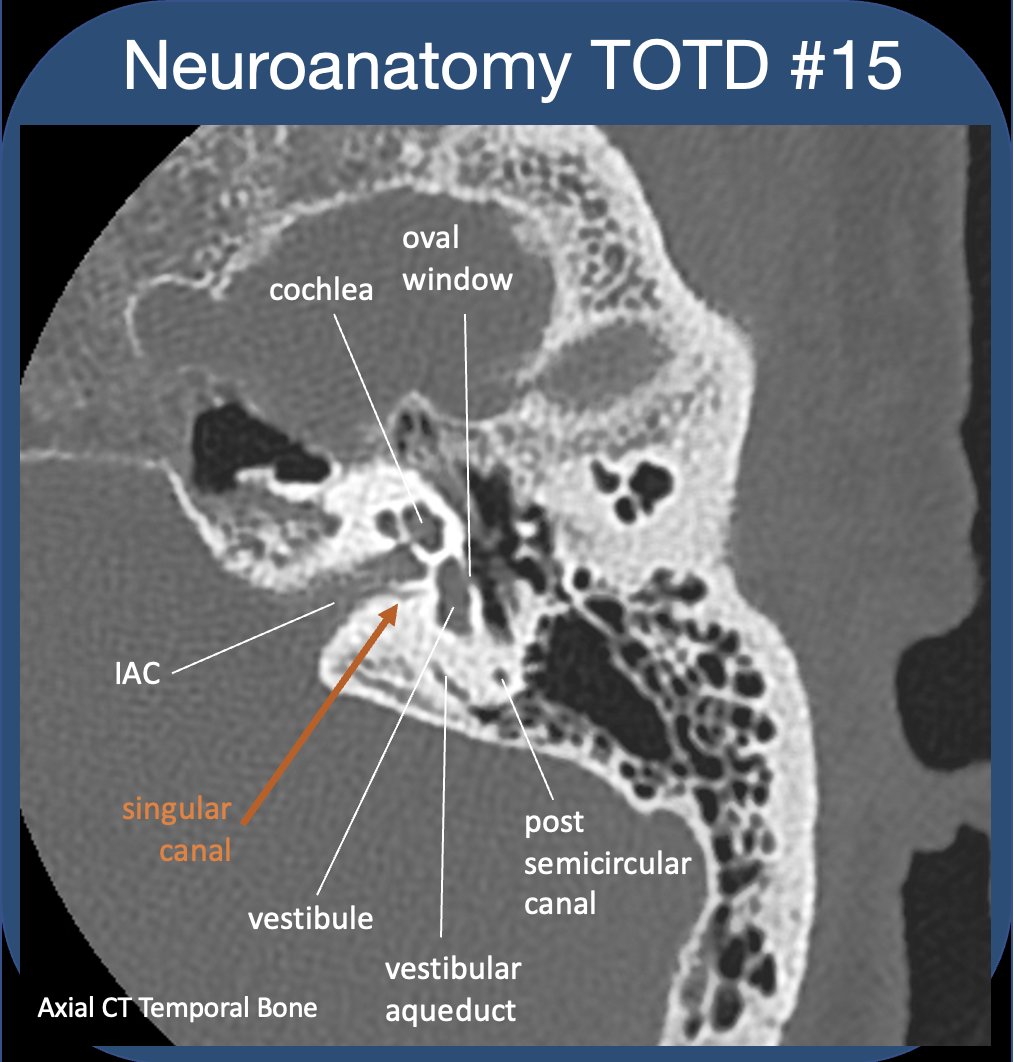
Along medial wall of ME, cochlear promontory is bone overlying the cochlea basal turn. Posterior is niche of the round window (RW separates the ME from the cochlea, allows for movement of inner ear fluid). Anteriorly is the carotid plate, and Eustacian tube/tensor tympani.
14/21
14/21

The tympanic segment of the facial nerve runs in a bony canal along the medial wall of the mesotympanum (above the oval window). Reaching the posterior wall, it turns vertically downward. (see prior thread on facial nerve
15/21
https://twitter.com/aaronrutman/status/1328082842258001920)
15/21

The bony prominence over the facial nerve at the posterior wall of the ME is the pyramidal eminence (PE). Medial to the PE is the sinus tympani, and lateral is the facial recess. Note the stapedius muscle arises from the pyramidal eminence (usually not well seen on CT).
16/21
16/21

Inferior to the cochlear promontory is the hypotympanum. The hypotympanum is separated by plates of bone from carotid canal (anteriorly) and internal jugular vein (posteriorly). Anteromedially (just ant to carotid plate), is the opening of the Eustachian tube.
17/21
17/21

So important for the radiologist to know T-bone anatomy--not only to confirm normal configuration and evaluate for typical pathologies affecting specific structures, but to properly describe findings for the ENT/oto docs.
18/21
18/21
Some pathology: trauma with longitudinal temporal bone fracture and hemotympanum. Ossicular injury can be subtle, as in this case of incudomalleolar separation. This would lead to conductive hearing loss.
19/21
19/21

Coronal CT shows a pars flaccida cholesteatoma filling Prussak’s space. Note blunting/erosion of the scutum (dashed arrow). Pathology of cholesteatomas is complicated, but they most often occur at pars flaccida (~80%) and expand into Prussak’s space.
ajnr.org/content/32/2/2…
20/21
ajnr.org/content/32/2/2…
20/21

s/p stapedectomy with stapes prosthesis for hearing loss/fenestral otosclerosis. Metallic piston is attached to either the incus or directly to TM (laterally), and through a hole in stapes footplate (medially), allowing vibrations to conduct into the fluid of the vestibule.
21/21
21/21

The goal was to simplify middle ear anatomy, but turns out that's hard to do in less than 20 tweets...
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh