Thank you all for your support this week. It's been a blast! If you missed anything, here's a "thread of threads" of everything I talked about this week.
Please follow me at @IranChinaGuy for more posts like this! Also please check out my other project, @iranstudiesUS
Please follow me at @IranChinaGuy for more posts like this! Also please check out my other project, @iranstudiesUS
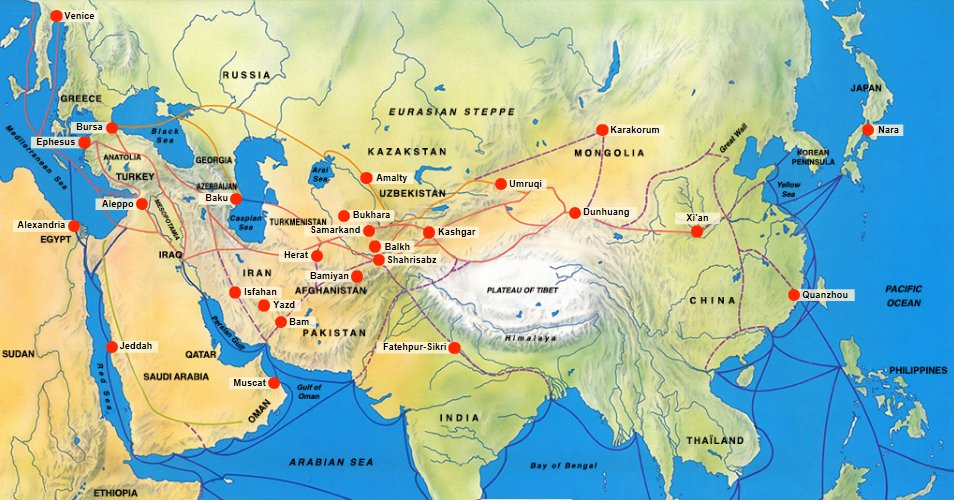
1/ How far back can ties between ancient China and early Iranian societies in Central Asia be traced?
https://twitter.com/HistorianofIran/status/1346143406741987329
2/ On Sassanian-Tang relations, especially after the Muslim conquest of Persia.
https://twitter.com/HistorianofIran/status/1346184296428613639
A brief but important intervention by @sasanianshah!
https://twitter.com/HistorianofIran/status/1346553494745059329
3/ On important figures in Chinese history from Parthian or Sassanian backgrounds.
https://twitter.com/HistorianofIran/status/1346547358839005185
4/ On the "Li" family and a famous pair of siblings of Iranian descent, Li Xun and Li Shunxian.
https://twitter.com/HistorianofIran/status/1346896945101627392
5/ The history of Persian, Arab, and African pirates, slaves, and merchants in ancient and medieval China.
https://twitter.com/HistorianofIran/status/1347324741313556480
6/ On the history of the consumption of Chinese ceramics and blue-and-white wares in Iran and the Middle East.
https://twitter.com/HistorianofIran/status/1347602202647547905
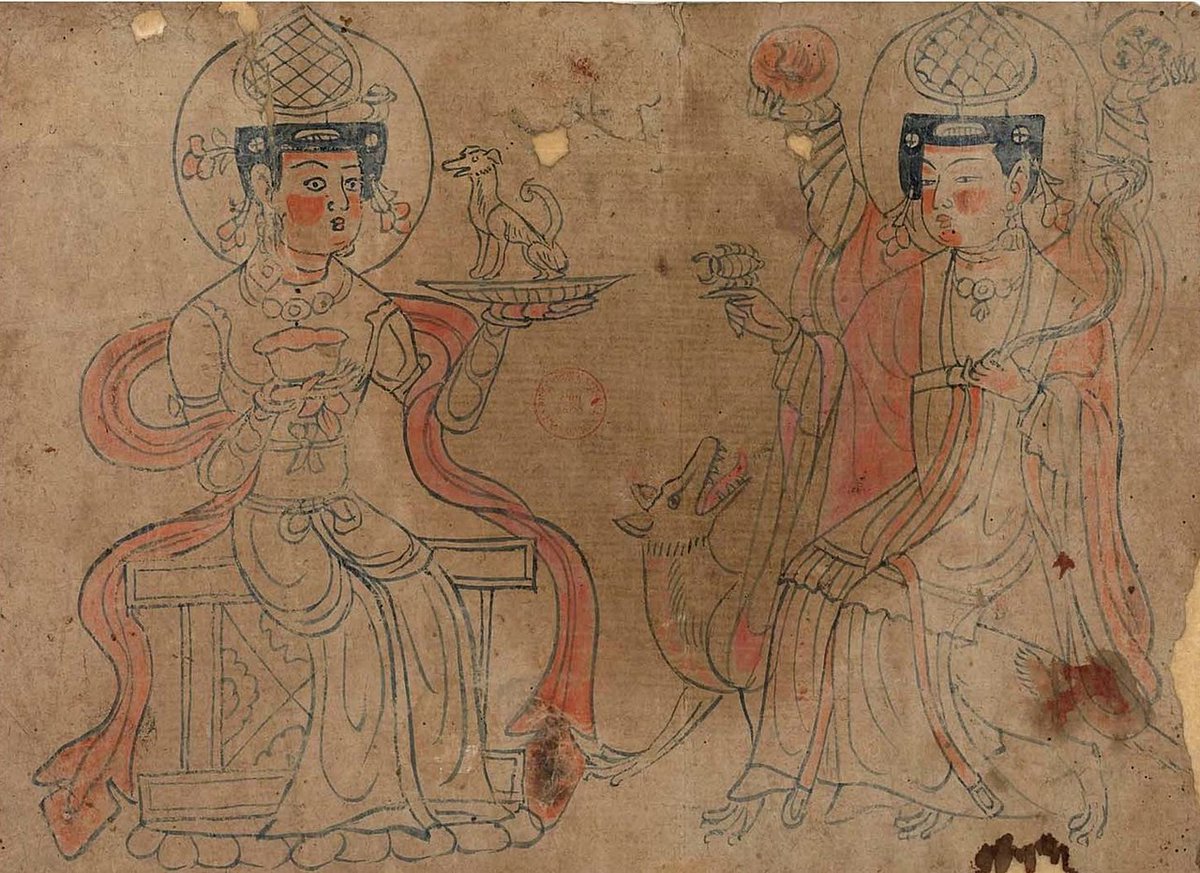
7/ On the spread of Buddhism, Zoroastrianism, and Persian Islamic texts in China.
https://twitter.com/HistorianofIran/status/1347972602397143041
8/ On Persian as an administrative and religious language during the Yuan and Ming.
https://twitter.com/HistorianofIran/status/1348022752406622210
9/ On the story of the competition between the Greek and Chinese painters, as told by Rumi.
https://twitter.com/IranChinaGuy/status/1328386077284065298
10/ On a new shared discourse of anti-colonial, Pan-Asian Sino-Iranian solidarity in the early 20th century...
https://twitter.com/HistorianofIran/status/1348293454573531138
11/ On the impact of the Iranian Constitution on Chinese intellectuals...
https://twitter.com/HistorianofIran/status/1348362188747116544
12/ On Sino-Iranian relations in the 1950s: Anti-Communism vs Socialist Solidarity
https://twitter.com/HistorianofIran/status/1348660331590148098
Thanks again and I hope you enjoyed! - B.F @IranChinaGuy
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh