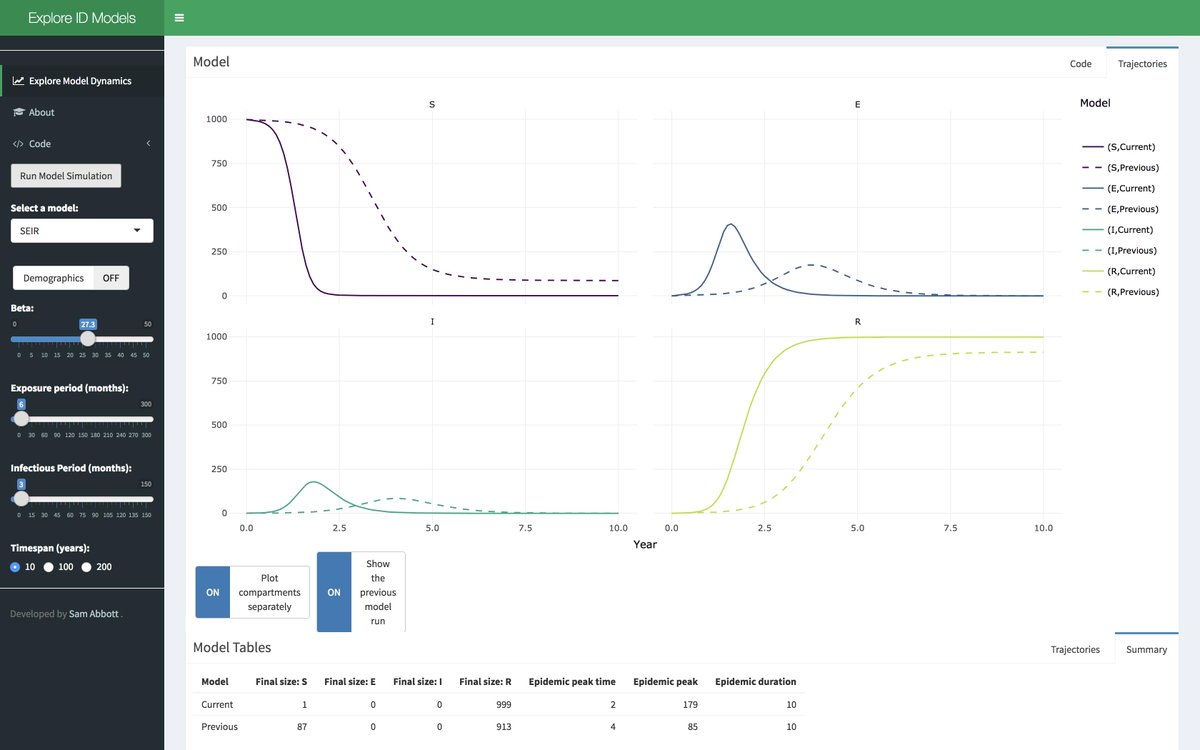
1/10 Since October @ftargument has been running a crowd forecasting project for #COVID19. First in Germany and Poland and now in all ECDC nations + the United Kingdom.
You can contribute your forecasts here: cmmid-lshtm.shinyapps.io/crowd-forecast/
You can contribute your forecasts here: cmmid-lshtm.shinyapps.io/crowd-forecast/

2/10 We submit an ensemble of these forecasts to the ECDC forecast hub where they are combined with many other models from other forecasters and evaluated.
covid19forecasthub.eu/visualisation
covid19forecasthub.eu/visualisation
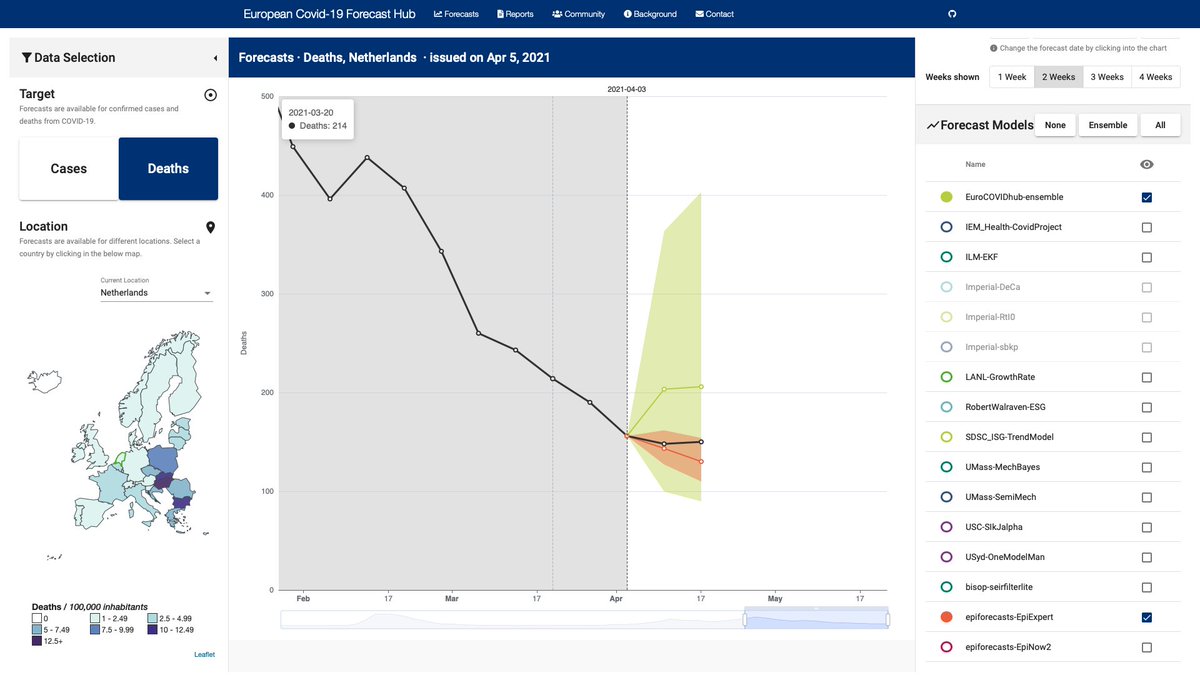
3/10 This crowd forecasting method has been found to perform well compared to models submitted by multiple groups and to be one of the only methods to produce useful forecasts at longer time horizons.
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
4/10 If you submit a forecast you can review your performance vs other forecasters (and several model based forecasts produced by our group) either in a weekly email or in this report.
epiforecasts.io/europe-covid-f…
epiforecasts.io/europe-covid-f…

5/10 For example, at the moment I am outperforming the ensemble but forecast deaths less well than cases. Importantly, I outperform @sbfnk and so look set for promotion (😅). 

6/10 You can also compare the performance of the combined crowd forecast vs all other submissions to the ECDC hub. The crowd forecast (EpiExpert) is currently performing quite well vs other forecasters.
covid19forecasthub.eu/reports
covid19forecasthub.eu/reports

7/10 @ftargument is currently working on new methods of crowd forecasting. One of these is an exciting combination of a model based forecast (using #EpiNow2) augmented with crowd opinion. This is a WIP but see more here:
cmmid-lshtm.shinyapps.io/crowd-rt-forec…
cmmid-lshtm.shinyapps.io/crowd-rt-forec…

9/10 This project is implemented in #rstats using #shiny and @mcmc_stan. All the backend code is #OpenSource and available here:
github.com/epiforecasts/e…
All the underlying code is packaged and available for use by other groups. #openscience
github.com/epiforecasts/e…
All the underlying code is packaged and available for use by other groups. #openscience
10/10 As a modeller I have found participating in this routinely extremely helpful as a way of evaluating my own assumptions about infectious disease transmission. I'm looking forward to building these insights into my next generation of tools.
We are currently writing up our evaluation of the forecasts submitted to German/Poland forecast hub but hope to use these insights to improve our ensembling of crowd forecasts going forwards.
kitmetricslab.github.io/forecasthub/fo…
kitmetricslab.github.io/forecasthub/fo…
@threadreaderapp unroll
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh