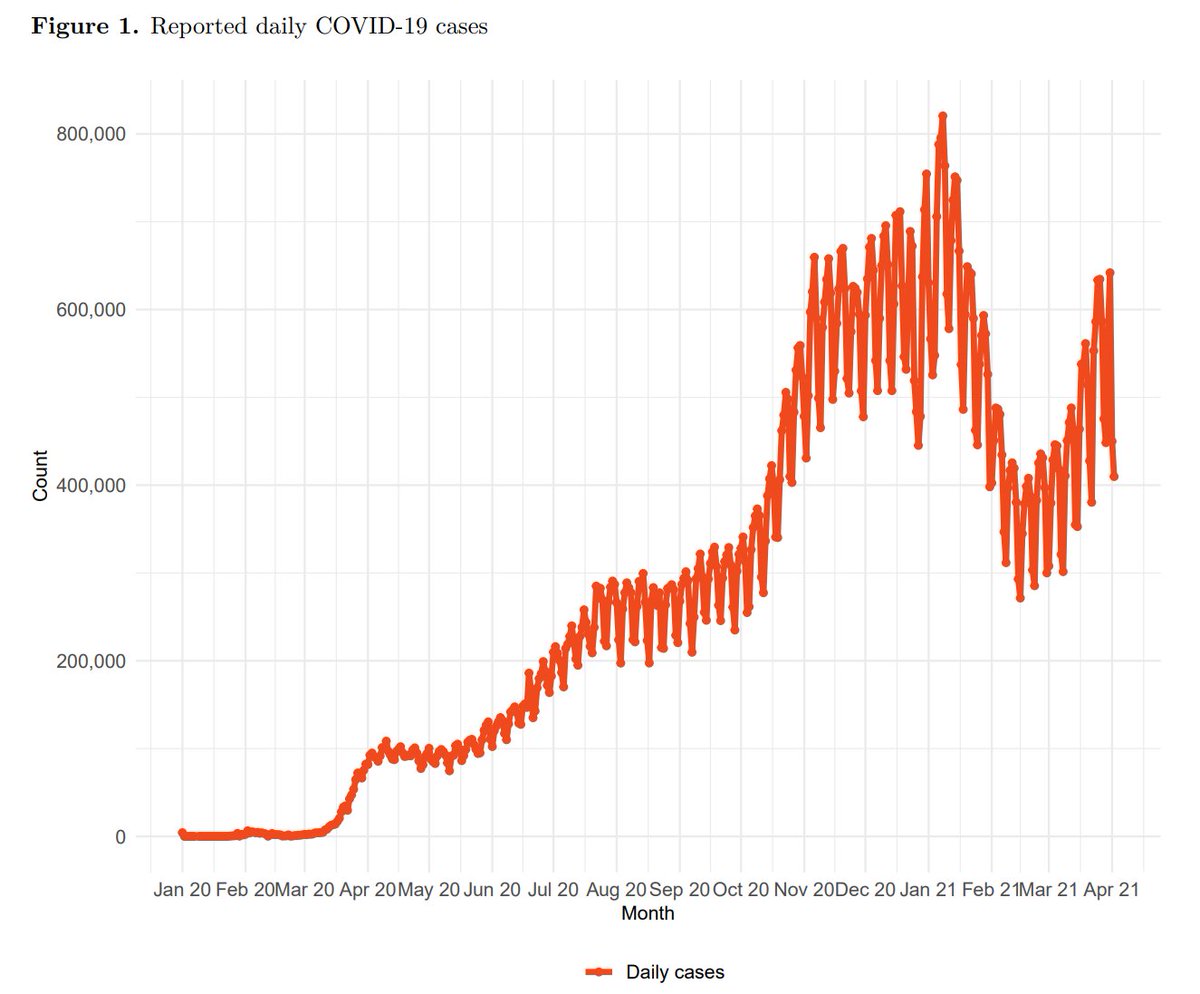
.@IHME_UW projects that daily infections will begin increasing in late August, and daily deaths corrected for under-reporting, will drop below 250 by mid-August, but then begin to increase slowly. 1/8 

Despite increasing vaccination and declining seasonality, five states have increasing transmission, based on hospitalization data. 2/8 

Given over one third of the population has been previously infected with COVID-19, vaccination with two doses is nearing 55% of adults, and seasonality is declining, the increases in transmission in these states is surprising. 3/8
It is likely this increased transmission can be traced to B.1.617.2 or P.1 spread, although it could be just increased interaction in these states. 4/8
Given CDC guidance to not test asymptomatic vaccinated individuals, hospitalization data are likely the best metric currently to track transmission. 5/8
Mask use continues to decline rapidly and mobility is nearly back to pre-COVID-19 baseline levels. 6/8 

Given that vaccination will likely run up against the limit of demand by early July, we expect there will be enough individuals who are susceptible to B.1.617.2 or P.1 infection to drive a late fall/winter surge which will slowly begin by late September. 7/8 

The most important strategy for the US in the next weeks will be to target the individuals who are unconvinced to get vaccinated. If B.1.617.2 drives more substantial increases in some states, as seen in Scotland, other measures to reduce transmission should be considered. 8/8 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh