Leather jackets that are a style statement today (unfortunately!) may have been a trend from the Pleistocene era! Here’s how researchers from @MPIWG found evidence of early humans who wore leather clothes around 100,000 years ago!
Read: weather.com/en-IN/india/sc…
📸: E Y Hallett
Read: weather.com/en-IN/india/sc…
📸: E Y Hallett
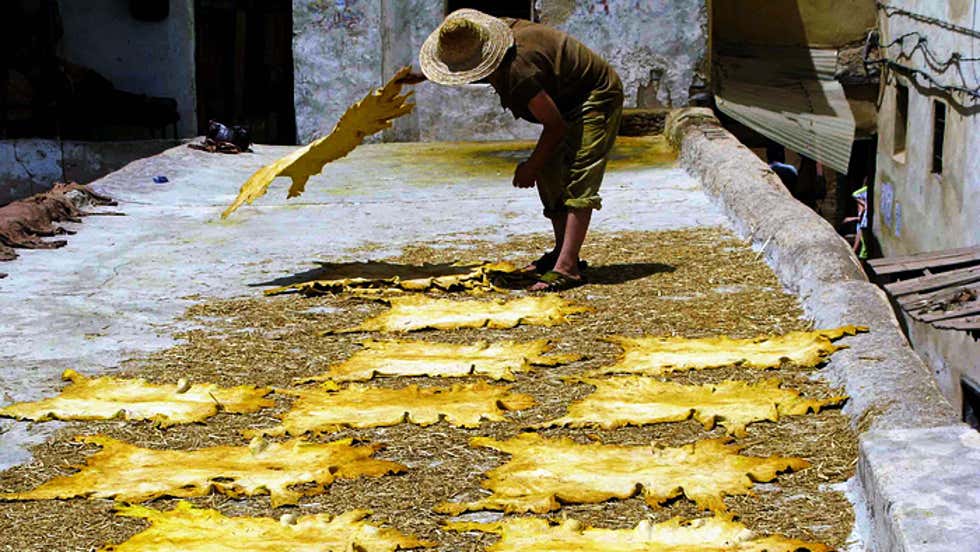

The researchers unearthed 62 bones from layers dating from the Pleistocene era that appeared to have been used as tools. Early humans made these specialised bone tools to skin animals and then processed these skins for fur and leather.
Researchers also found broad, rounded end objects called spatulates, ideal for scraping & removing internal connective tissues from leathers & pelts during the hide or fur-working process. A whale tooth was also retrieved, which appeared to have been used to flake stone.
Remains of sand foxes, golden jackals & wildcats were found with the bone tools, plainly displaying marks similar to those left during skinning. There were no signs of the butchery of these #Carnivore species, but merely the cuts required to remove the skin.
📸: J N Cerasoni
📸: J N Cerasoni

Before this, bone needles discovered in Siberia around 40,000 years ago were the earliest evidence for clothing among the Homo family. Scientists conclude that humans began wearing clothing 100,000 years ago since studies showed the #Evolution of cloth-loving lice to this period.
The scientists also found trinkets such as shell beads, which the early humans could have used as ornaments. With the current evidence, it does look like our Pleistocene ancestors found a way to blend practicality with a bit of whimsy.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh