🧵Continuing the tweet 
https://twitter.com/strain_rate/status/1449751850543165444?s=20fromthe paper pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34620522/ into the diastasis: At end of early filling, the vortex fills most of the ventricle.

1/ The intraventricular vortex fills the ventricle, and the downwards flow in the septal part, will close the anterior MV leaflet. This also isolates the vortex in the ventricle, which may conserve the kinetic energy in the vortex 

2/ At the end of diastasis, the lateral part of the vortex, with apical flow, is aligned with the incoming inflow in atrial systole, adding momentum and kinetic energy to the inflow during atrial systole. 

3/At the start of late inflow, simultaneous with mitral re opening, there is onset of a new phase of basal AV-plane motion. 

4/ The basal motion of the AV-plane again will expand the LVOT, diverting blood towards the septum and downwards, creating a new vortex similarly to the early filling, which also originates near the ventricular base. 

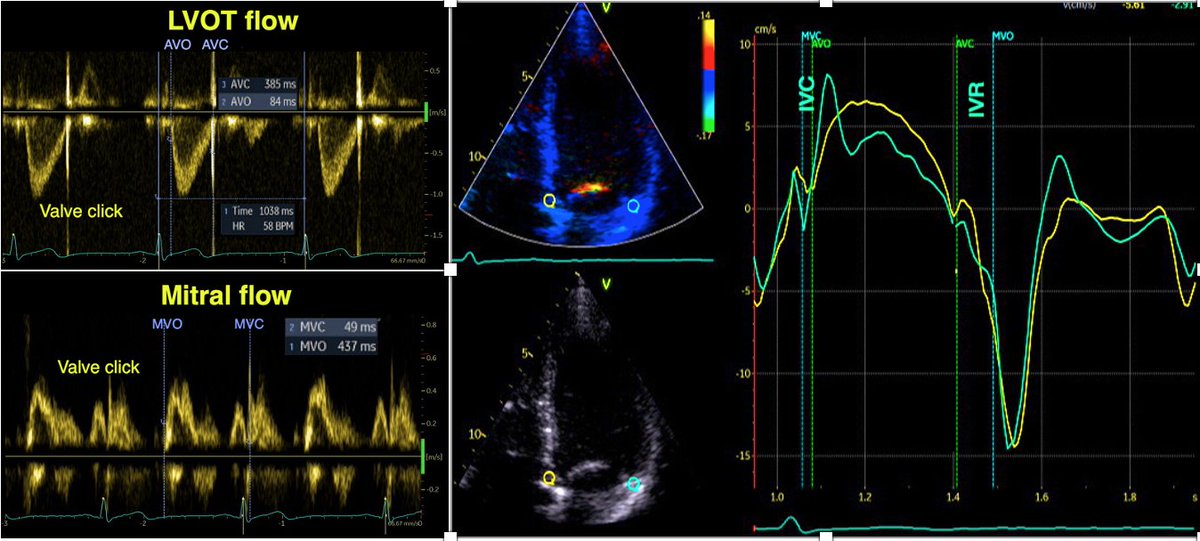
5/ This again creates into the LVOT, immediately before ejection. Earlier described as the “J-wave” pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2372400/, though incorrectly taken as return of the E-wave via apex, it was correctly, but inconsistently related the peak of the signal as related to the A-wave. 

6/ It was later ascribed to early return of the A-wave, with a transit time of 20 - 80 ms, compared to 80 - 200 ms for the E_LVOT. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8160627/ Although not evaluated in our study, it seems to be reasonable that the E_LVOT/A_LVOT ratio is related to the E/A ratio. 

7a/ In a recent publication the A_LVOT was described as “pre systolic flow”, , reported in only a fraction of patents, irrespective of EF, but presence associated with worse prognosis. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25440501/
7b As the amplitude of the A_LVOT is associated with the E/A ratio, low detection of A_LVOT may be related to the amplitude, creating a bias in detection towards a high E/A ratio, and thus being a confounder
8/ While the septal part of the early vortex seems to weaken, inflow in the A wave aligns with the lateral part, as the same time as the new vortex expands towards the apex. 

9/ At the end of late filling, electromechanical activation creates a short duration apical motion before MVC, as published pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34184410/ and tweeted earlier 
https://twitter.com/strain_rate/status/1417429145903157258?s=20

10/ At the same time, the vortex from the late inflow has a basal flow along the septum, directed towards the anterior mitral leaflet, that also may assist in MVC, as suggested previously. 

unroll @threadreaderapp
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh