Aardvarks and the dawn of tank-plinking, a thread. 1/8
#avgeeks #aviation #USAF #DesertStorm #History
#avgeeks #aviation #USAF #DesertStorm #History

On the night of Feb 5, 1991, Col. Tom Lennon, commander of #USAF's 48th FW, led a pair of F-111s on an experimental mission against dug-in units of the #Iraqi Republican Guard in the deserts north of Kuwait. 2/8 #avgeeks #aviation #DesertStorm #History 

For the experiment, each F-111 was armed with a Pave Track pod and four GBU-12 500 lb LGBs. The crews were to see if LGBs could be guided accurately enough to hit targets as small as an AFV. 3/8 #avgeeks #aviation #USAF #DesertStorm #History 

Cruising at 14,000ft, safely outside the reach of #Iraqi AAA, the two F-111 crews delivered a series of deliberate attacks against dug-in tanks and AFVs. 4/8 #avgeeks #aviationdaily #USAF #DesertStorm #History 

The mission was a resounding success: four tanks and one artillery piece were knocked out for an expenditure of eight GBU-12s. 5/8 #avgeeks #aviation #USAF #GulfWar #History 

Gen.Chuck Horner, Coalition Air Commander in #DesertStorm, immediately ordered all F-111Fs to shift from the strategic bombing campaign to attacking Iraqi AFVs in KTO. For the 48th TFW, tank-plinking (a term which irritated Schwarzkopf) became the order of the day. 6/8 #avgeeks 
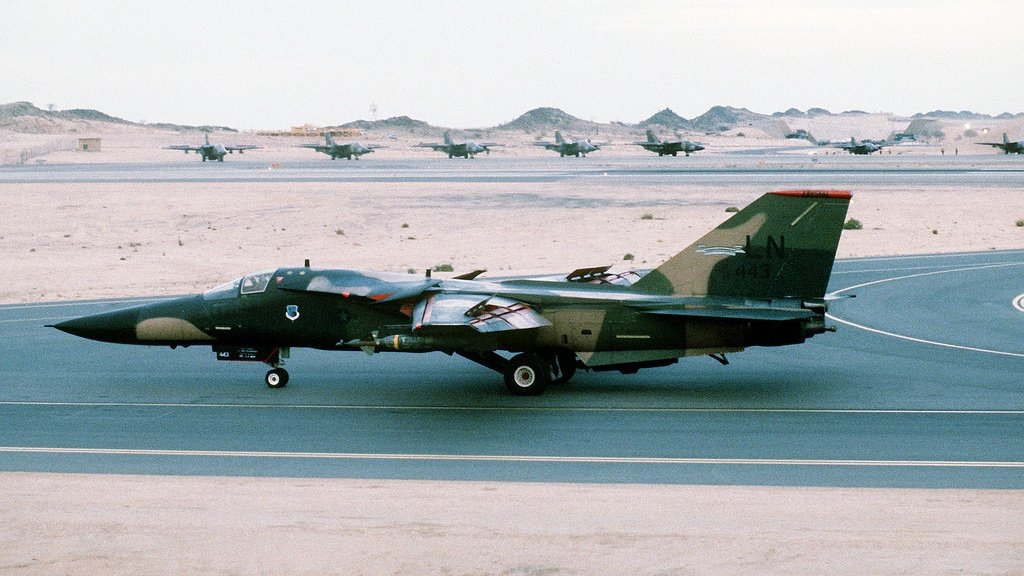

By February 28th, 1991, the 66 F-111Fs of the 48th TFW destroyed an estimated 920 tanks/APCs, 252 artillery pieces, and 12 bridges, and emerged as #USAF’s leading strike Wing of the war. 7/8 #avgeeks #aviationdaily #DesertStorm #History 

#FunFact: When it was discovered that the F-111Fs had destroyed 10x more tanks than the F-16s, the F-16s were directed to cease attacks by mid-afternoon each day to allow the dust to settle before the F-111s went to work at night! 8/8 #avgeeks #aviationdaily #USAF #DesertStorm 

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh