Can Covid-19 lead to diabetes?
New from our team on risk and burden of diabetes in Long Covid at 1 year
In @TheLancetEndo
@VAResearch @vahsrd @WUSTLpubhealth @WUSTLmed @WUSTLnews @VREFSTL
@Biostayan
A thread 🧵
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
New from our team on risk and burden of diabetes in Long Covid at 1 year
In @TheLancetEndo
@VAResearch @vahsrd @WUSTLpubhealth @WUSTLmed @WUSTLnews @VREFSTL
@Biostayan
A thread 🧵
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
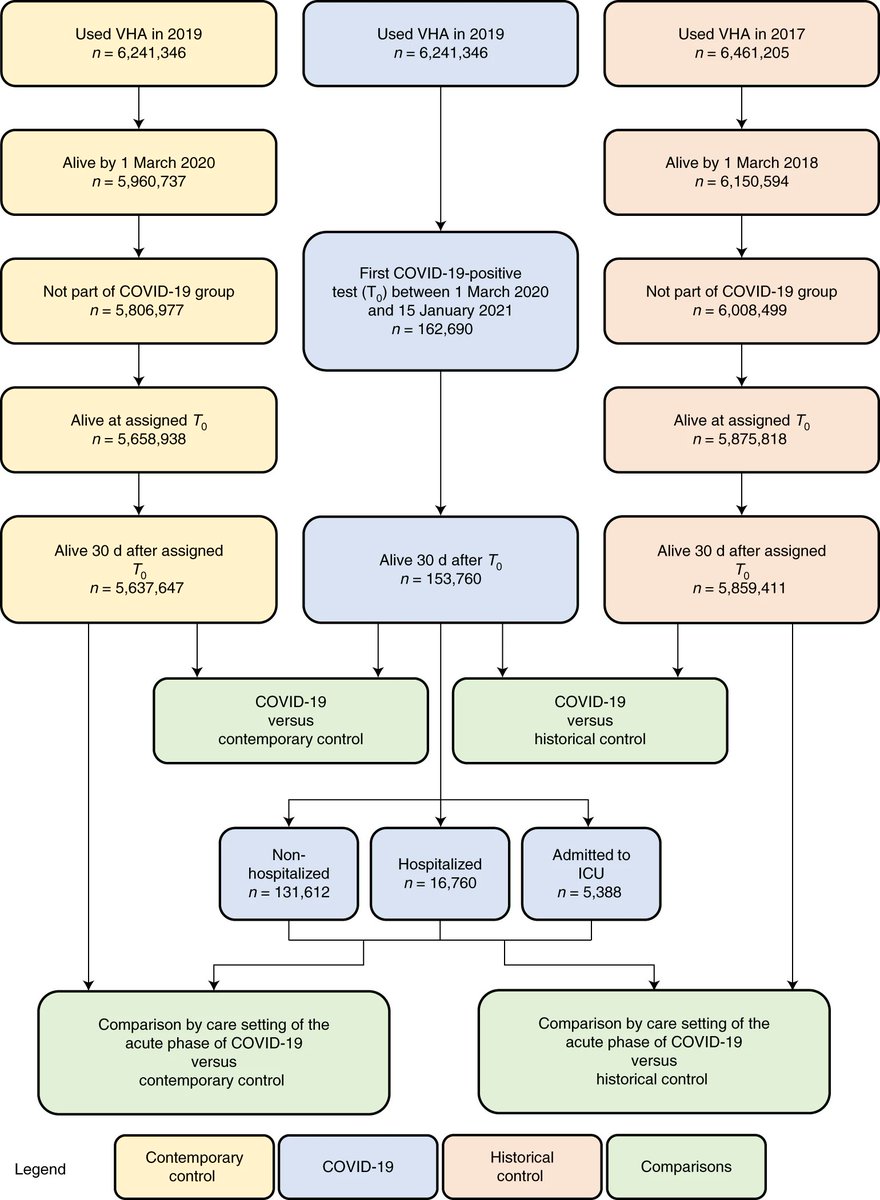
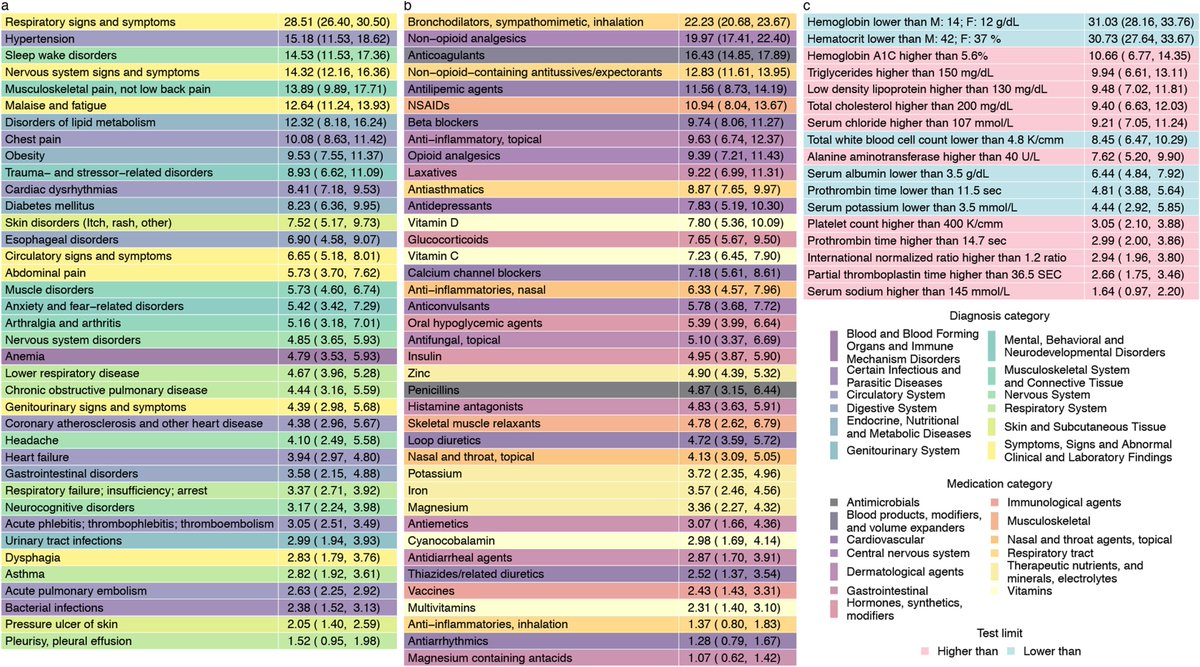
In this study of more than 8.5 million people: 181 k with COVID-19 and more than 8 million controls without evidence of infection
We show increased risk of new onset diabetes at 1 year
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
We show increased risk of new onset diabetes at 1 year
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
The risk was evident even among people who did not need hospitalization during the acute phase of SARS-CoV-2 infection — this group represents most people with COVID-19
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
The risk of diabetes was also evident even in people who had no risk factors for developing diabetes before they got COVID-19
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
2 out of 100 persons with COVID-19 developed new onset diabetes as a result of COVID-19
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
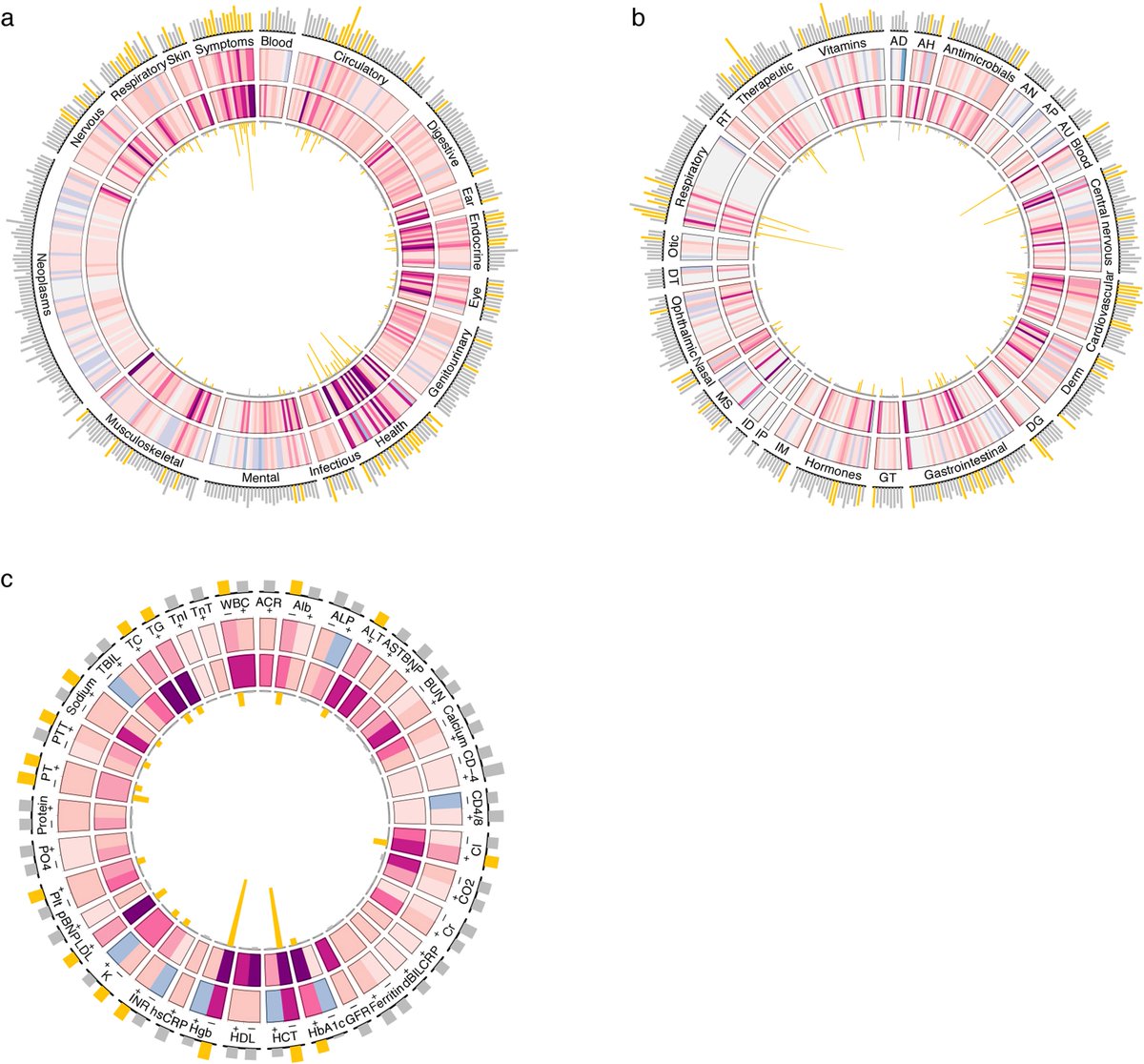
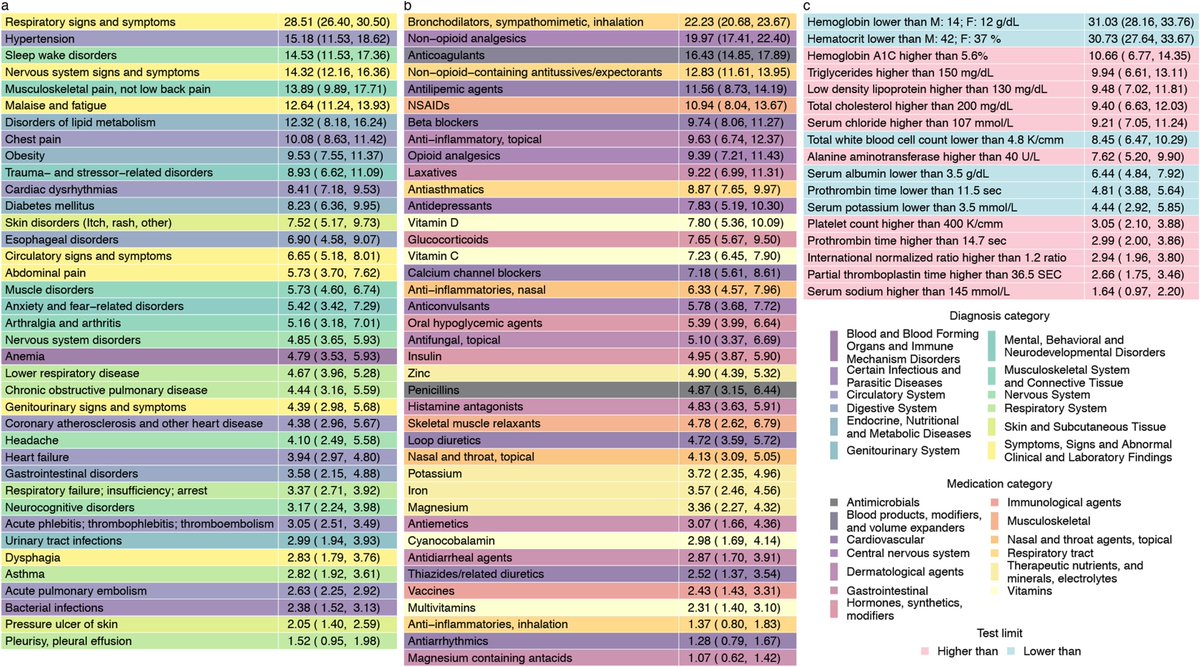
Given the large number of people with COVID-19, these absolute numbers might translate into substantial population-level burden and could further strain already overwhelmed health systems
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
Governments and health systems around the world should be prepared to screen and manage diabetes in people who had COVID-19.
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
And diabetes should be considered as a facet of the multifaceted Long COVID syndrome.
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
To place this in larger context:
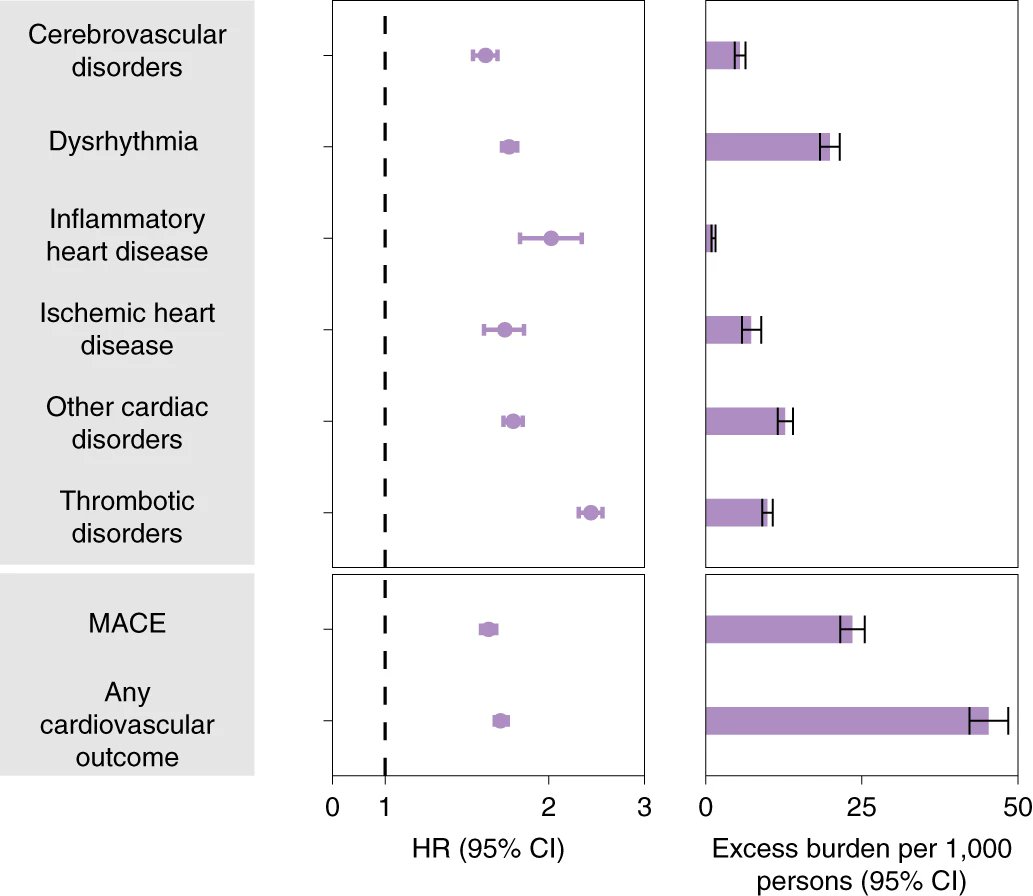
The long-term consequences of COVID-19 include increased risk of:
Heart disease nature.com/articles/s4159…
Kidney disease jasn.asnjournals.org/content/32/11/…
and now diabetes thelancet.com/journals/landi…
The long-term consequences of COVID-19 include increased risk of:
Heart disease nature.com/articles/s4159…
Kidney disease jasn.asnjournals.org/content/32/11/…
and now diabetes thelancet.com/journals/landi…
Clearly SARS-CoV-2 drives development of cardiometabolic disease
Heart disease nature.com/articles/s4159…
Kidney disease jasn.asnjournals.org/content/32/11/…
Diabetes thelancet.com/journals/landi…
Heart disease nature.com/articles/s4159…
Kidney disease jasn.asnjournals.org/content/32/11/…
Diabetes thelancet.com/journals/landi…
These are chronic diseases that last a lifetime – they can affect quality of life, lead to downstream health problems and reduce life expectancy
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
The absolute numbers may look small (1-4%), but they translate into millions of affected people in the US and many more around the world.
This will cause a rise in the burden of cardiometabolic disease globally
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
This will cause a rise in the burden of cardiometabolic disease globally
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
International bodies, national governments, and health systems must develop and implement strategies for early identification and treatment of affected individuals.
Millions of lives depend on this.
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
Millions of lives depend on this.
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
Thanks to the amazing first author @Biostayan, our funders @VAResearch @vahsrd , our Editors and Reviewers.
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
Thanks to the #LongCovid community!
You inspired us and continue to inspire everyday.
Thank you!
#LongCovidisfact
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
You inspired us and continue to inspire everyday.
Thank you!
#LongCovidisfact
thelancet.com/journals/landi…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh