Fructose Coingestion Does Not Accelerate Postexercise Muscle Glycogen Repletion
Our 2016 paper:
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26606271/
A thread with figures.
#fructose #glucose #glycogen
Our 2016 paper:
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26606271/
A thread with figures.
#fructose #glucose #glycogen

The gut absorption of the carbohydrate glucose is the limiting factor in using glucose drinks for energy during exercise (carbohydrate oxidation). Fructose is a carbohydrate that is absorbed differently in the gut than glucose. Sucrose consists out of glucose and fructose.
2/
2/

Therefore, a combined ingestion of glucose and fructose allows a higher total carbohydrate absorption rate, oxidation rate, and exercise performance. But does this combination also improve the recovery of the muscle carbohydrate stores (i.e. muscle glycogen) after exercise?
3/
3/
This study investigated whether the combination of fructose and glucose improves muscle glycogen recovery after exhaustive exercise.
4/
4/

Subjects were trained cyclists that performed high-intensity cycling exercise to deplete their muscle glycogen stores. Afterwards, subjects received either 1.5 g/kg/h of glucose or 1.2 g/kg/h glucose + 0.3 g/kg/h fructose during the 5 hours of recovery.
5/
5/

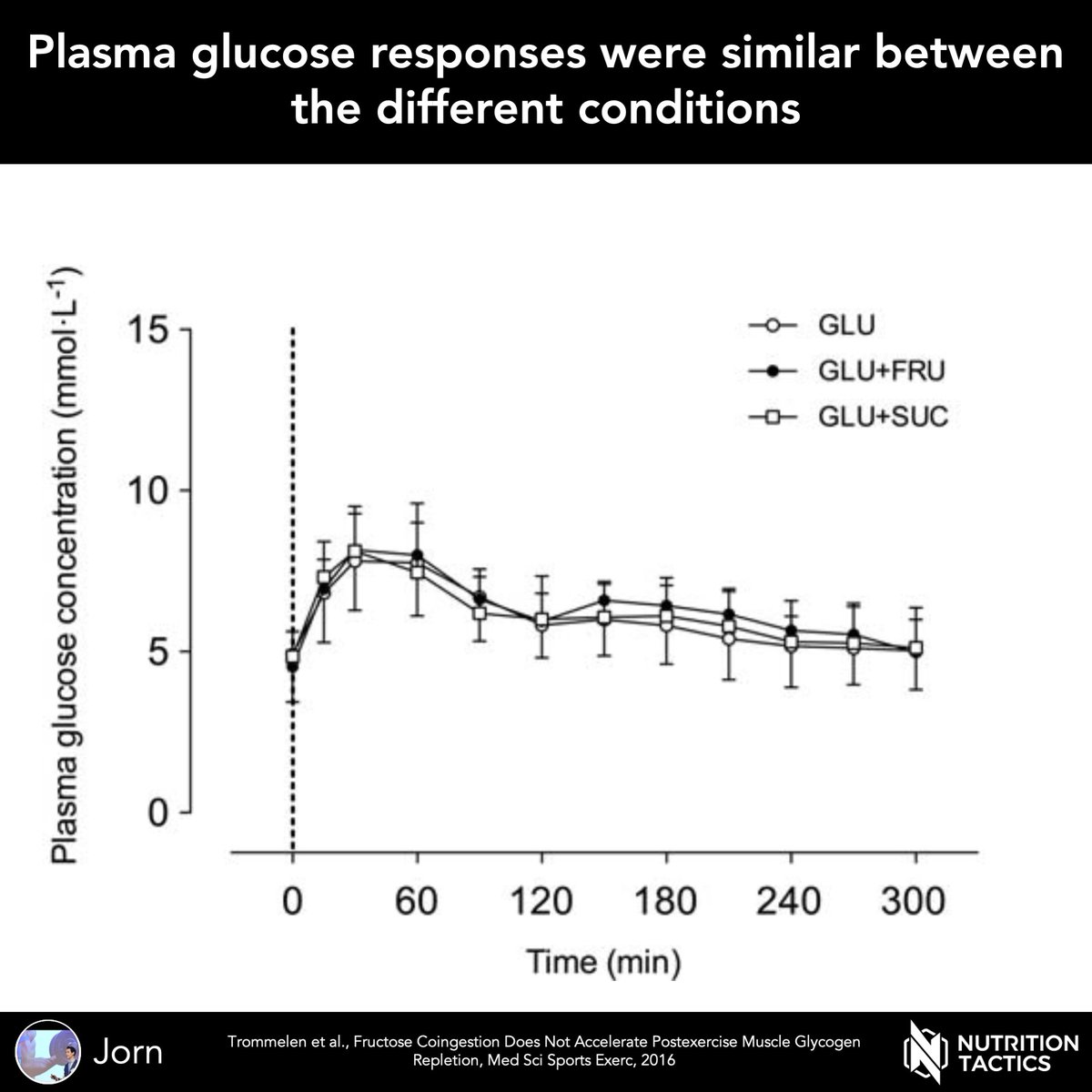
The glucose only, the glucose+fructose mix, and the glucose+sucrose mix increased muscle glycogen stores. However, there was no difference between the drinks.
7/
7/

However, the glucose/fructose mix resulted in less gastrointestinal complaints. In addition, the glucose/fructose mix is likely better for liver glycogen, but it was not measured in this study.
8/
8/

In conclusion, the combination of fructose and glucose does not enhance muscle glycogen recovery after exercise when compared to glucose only.
Paper:
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26606271/
Did you find this useful? Please help promote the first tweet of the thread:
Paper:
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26606271/
Did you find this useful? Please help promote the first tweet of the thread:
https://twitter.com/JornTrommelen/status/1572605302603935744?s=20&t=Ke4xKYE_-Mi1eHds8w6Eiw
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh