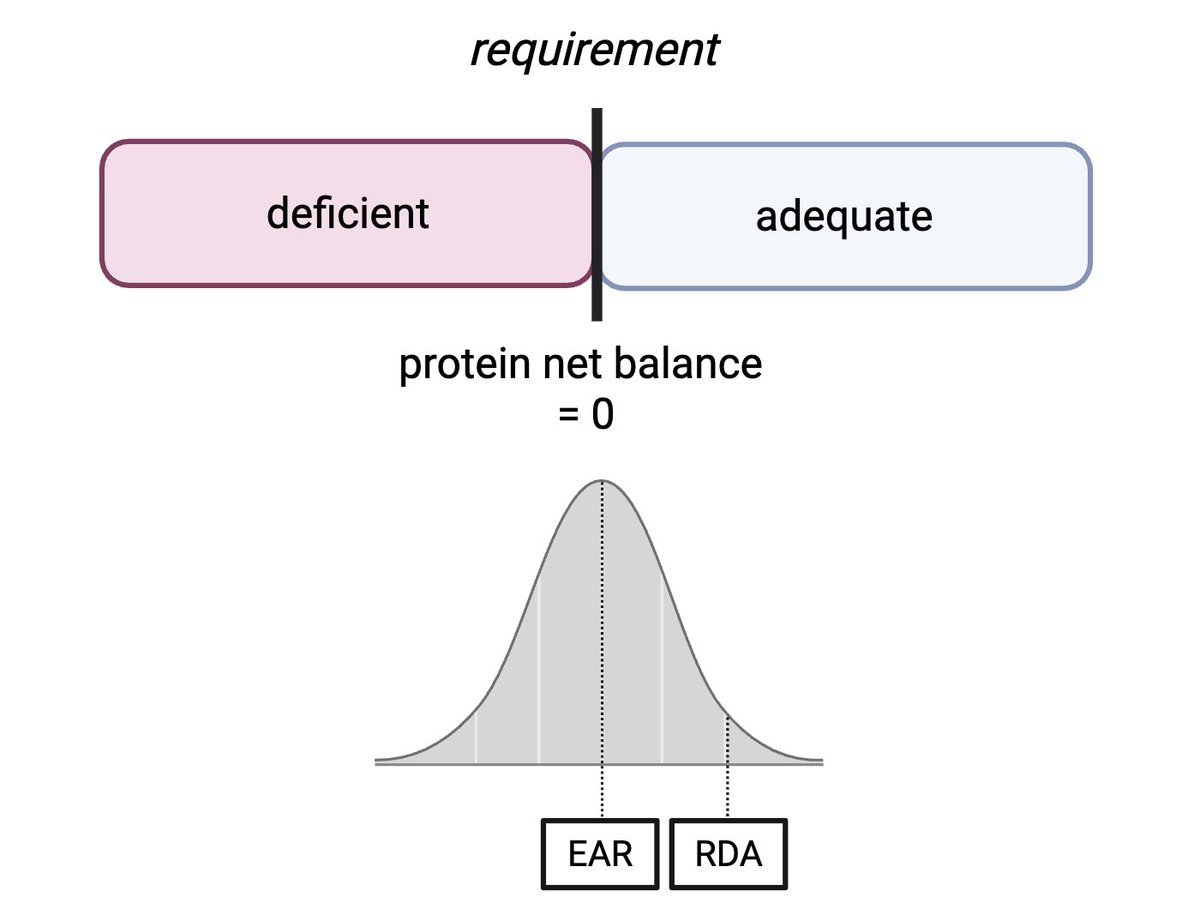
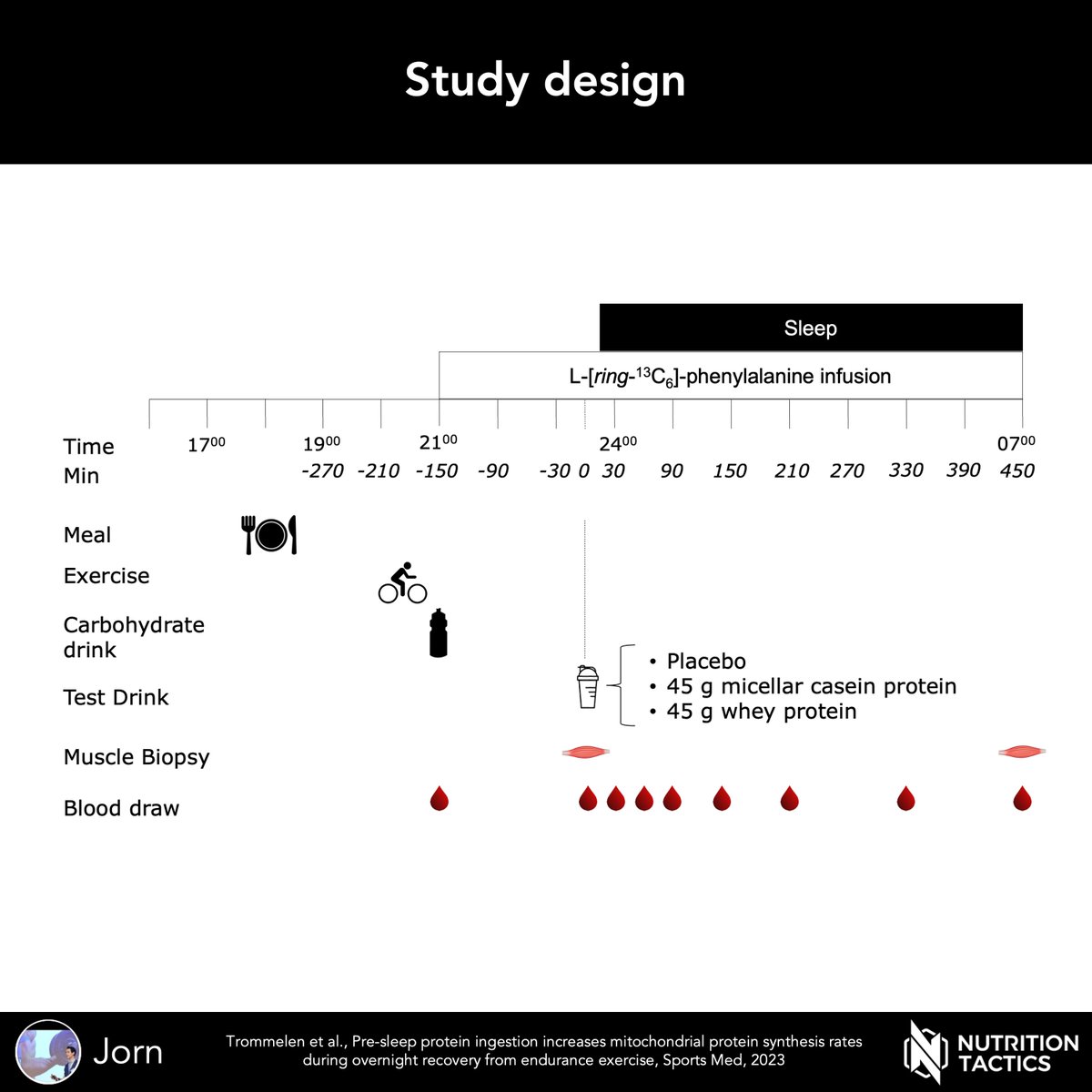
Many supplements claim to improve body composition or exercise performance. Some supplements seem promising, while others don’t seem to do anything, and some can even be counterproductive.
Here’s a thread of some of our supplements infographics 🧵👇
#supplements #performance
Here’s a thread of some of our supplements infographics 🧵👇
#supplements #performance

Creatine is an organic compound which is naturally present in our bodies. Creatine supplementation increases muscle creatine levels, strength and muscle mass gains during resistance training.
2/
2/

Nitrate-rich beetroot juice has been shown to increase endurance performance because. Beetroot juice supplementation can also improve repeated sprint performance compared to nitrate-depleted beetroot juice.
3/
3/

Carnitine helps fats get into mitochondria. Prolonged carnitine supplementation can result in sparing of muscle glycogen during low intensity exercise, allows for more carbohydrates to be used during high-intensity exercise, and can improve endurance performance.
4/
4/

Caffeine has been shown to improve exercise performance. The effect of caffeine seems to differ between people. In most people, it improves or has no effect on exercise performance. In contrast, it decreases performance in some people.
5/
5/

Melatonin is a hormone that is mostly known for regulating sleep patterns. Melatonin supplementation may improve body composition.
6/
6/

HMB is a metabolite of the amino acid leucine. In contrast to some claims, HMB supplementation does not result in greater muscle mass gains as compared to leucine.
7/
7/

Anti-oxidants can reduce oxidative stress and are therefore often seen as ‘good’. However, high dose anti-oxidant supplementation may reduce the adaptive response to exercise.
8/
8/

See the infographic index on our website for an overview of all infographics and a more detailed discussion of each study.
Overview all infographics:
nutritiontactics.com/infographic-in…
Did you find this useful? Please help promote the first tweet of the thread:
Overview all infographics:
nutritiontactics.com/infographic-in…
Did you find this useful? Please help promote the first tweet of the thread:
https://twitter.com/JornTrommelen/status/1590743330274816001?s=20&t=3PqwoiZQ0ciZShrqryw4Qg
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh