A 3-month-old ♂️, a dimple at the center of a lumbosacral hemangioma (a): fever & deteriorating condition.
CSF: ⬆️cell count 5717/µL;⬆️protein = 352 mg/dL; ⬇️glucose < 10 mg/dL.
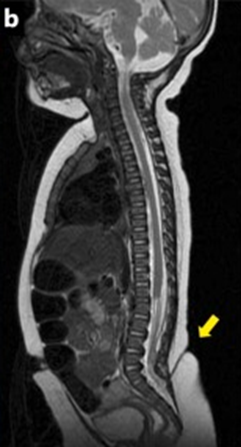
RM (b): ?
1/7
doi.org/10.1016/j.idcr…
#pediatric #IDtwitter #Neurology
CSF: ⬆️cell count 5717/µL;⬆️protein = 352 mg/dL; ⬇️glucose < 10 mg/dL.
RM (b): ?
1/7
doi.org/10.1016/j.idcr…
#pediatric #IDtwitter #Neurology

RM b): a congenital dermal sinus communicating with the spinal cord.
Enterobacter aerogenes was isolated from CSF and stool cultures
CONGENITAL DERMAL SINUS ASSOCIATED WITH MENINGITIS BY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES
2/7
#radiology #microbiology #pediatria
Enterobacter aerogenes was isolated from CSF and stool cultures
CONGENITAL DERMAL SINUS ASSOCIATED WITH MENINGITIS BY ENTEROBACTER AEROGENES
2/7
#radiology #microbiology #pediatria
Congenital dermal sinus is associated with meningitis caused by atypical pathogens.
Enterobacter aerogenes community-acquired infections associated with congenital dermal sinus are rarely observed.
3/7
#bacteriology #MedTwitter
Enterobacter aerogenes community-acquired infections associated with congenital dermal sinus are rarely observed.
3/7
#bacteriology #MedTwitter
Most sacral skin dimples are benign.
Some may be associated with spinal dysraphism (e.g., a congenital dermal sinus), which may lead to bacterial meningitis caused by atypical organisms (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Proteus species, and anaerobes)
4/7
Some may be associated with spinal dysraphism (e.g., a congenital dermal sinus), which may lead to bacterial meningitis caused by atypical organisms (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Proteus species, and anaerobes)
4/7
The presence of atypical pathogens, rather than typical pathogens such as Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae, suggests the presence of causative complications.
5/7
#Doctor #MedStudentTwitter
5/7
#Doctor #MedStudentTwitter
Initial antimicrobial therapy was adjusted to cefotaxime (CTX) based on susceptibility testing.
The response to treatment with CTX was partial (the CSF culture remained➕), and a switch to meropenem was required to achieve negative CSF cultures.
6/7
#resident #medicine
The response to treatment with CTX was partial (the CSF culture remained➕), and a switch to meropenem was required to achieve negative CSF cultures.
6/7
#resident #medicine
In febrile infants, a full physical examination, including back examination, is important.
Physicians should consider meningitis as differential diagnosis for febrile infant patients with dimples and other skin findings.
7/7
#MedicalStudents #MedEd
Physicians should consider meningitis as differential diagnosis for febrile infant patients with dimples and other skin findings.
7/7
#MedicalStudents #MedEd
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh