It is said that Distributed Validator Technology, or #DVT, could reshape @ethereum Liquid Staking. Why?
1) What is #DVT?
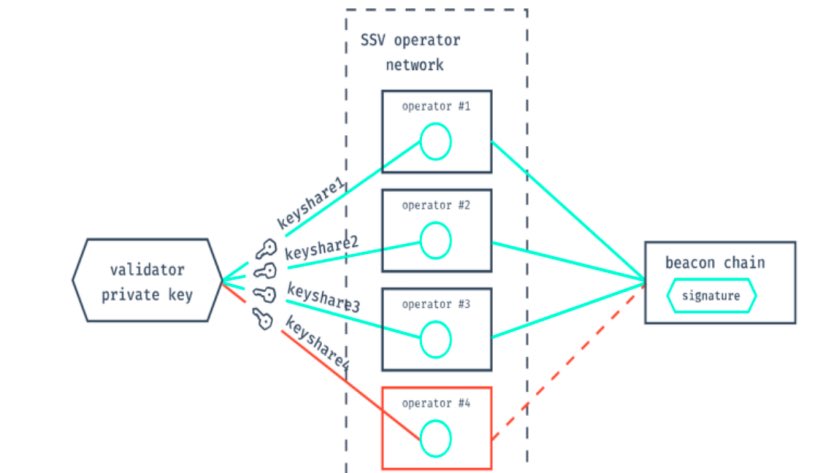
#DVT provides an open infrastructure for splitting and distributing validator keys into multiple KeyShares in order to run @ethereum validators on a cluster of nodes, allowing individuals, groups, or communities of operator to form as a single validator.
#DVT provides an open infrastructure for splitting and distributing validator keys into multiple KeyShares in order to run @ethereum validators on a cluster of nodes, allowing individuals, groups, or communities of operator to form as a single validator.
In the view of technology, #DVT consists of 4 key components: Distributed Key Generation, Shamir Secret Sharing of BLS Signatures, Secure Multi-Party Computation and the #DVT BFT Consensus Layer.
Among them, Multi-Party Computation is the most critical part for #DVT, which allows operators to share private key to sign transactions and perform computations without rebuilding on any other device.
2) Advantages of #DVT
First of all, #DVT introduces nodes of multiple parties to increase the robustness of the system and ensure that the system will not stagnate and the user's principal will not be slashed when some nodes go offline or misbehave.
First of all, #DVT introduces nodes of multiple parties to increase the robustness of the system and ensure that the system will not stagnate and the user's principal will not be slashed when some nodes go offline or misbehave.
In a #DVT cluster, even if some participating nodes go offline(<33%), the remaining nodes can still reach a consensus on what is signed. 

Secondly, with the help of #DVT, individuals or groups can participate in staking, making it possible to distribute the operations of @ethereum validators, improve security, increase inclusiveness, and decentralize the network.
Some popular Liquid Staking service providers such as @LidoFinance can also option #DVT as the bottom layer of their protocol to reduce the community's concerns over centralization.
Finally, under the mounting regulatory pressures, #DVT can make the @ethereum network more censorship-resistant.
3) #DVT-based projects
@ssv_network is a decentralized @ethereum Liquid Staking network developed based on #DVT. It provides an open infrastructure for anyone who wants to run an @ethereum validator, with a range from DIY users to staking pools or even staking institutions.
@ssv_network is a decentralized @ethereum Liquid Staking network developed based on #DVT. It provides an open infrastructure for anyone who wants to run an @ethereum validator, with a range from DIY users to staking pools or even staking institutions.
Obol Network is another #DVT pioneer. @ObolNetwork launched the plug-in client Charon to enable #DVT and ensure that the staking system can run in a decentralized way. Its ultimate goal is to build a "trust-minimized" @ethereum staking protocol. 

diva is also an @ethereum Liquid Staking protocol developed based on #DVT. Specifically, @divalabs is an ultra-light client that connects to existing @ethereum execution and consensus clients via standard API. 

Stakers can stake any amount of $ETH without a minimum requirement, and they don't need to run any nodes.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh