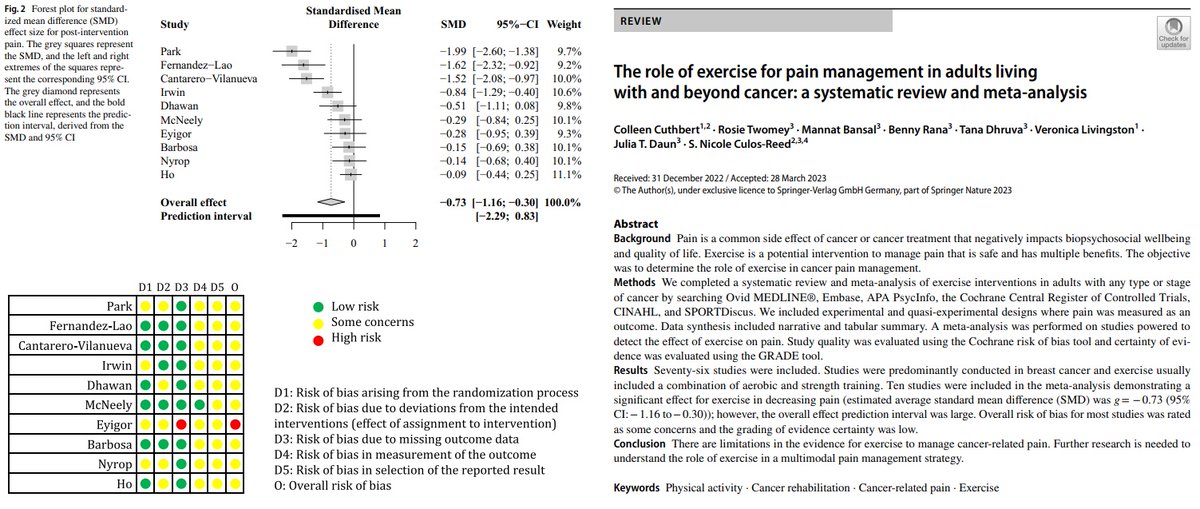
This systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that chronic exercise is likely to have a positive impact on markers of systemic inflammation in individuals with overweight/obesity and with or at risk of cardiometabolic diseases, as long as cardiorespiratory fitness is improved 

- Results suggested that aerobic, resistance, and combined (aerobic + resistance) training programs are likely to be an effective strategy to alleviate the inflammatory status in individuals with overweight or obesity, even in those with concomitant cardiometabolic diseases.
- The effects appeared to be at least modulated by the extent of increase in cardiorespiratory fitness (VO2max) with some impact of reducing body fat % on the levels of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10.
- The effect of each training intervention appeared to depend on the analyzed inflammatory marker and factors such as sex and age.
- "In conclusion, any exercise intervention should be aimed to increase cardiorespiratory fitness, a seemingly crucial factor in mediating any anti-inflammatory effect"
Long-term effects of different exercise training modes on cytokines and adipokines in individuals with overweight/obesity and cardiometabolic diseases: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression of randomized controlled trials
doi.org/10.1111/obr.13…
#exercise #fitness #fit #FitFam #FitLife #FitnessAddict #Workout #TrainHard #GymLife #GymTime #muscle #strength #lift #GetStrong #hypertrophy #gainz #gains #cardio #hiit
#exercise #fitness #fit #FitFam #FitLife #FitnessAddict #Workout #TrainHard #GymLife #GymTime #muscle #strength #lift #GetStrong #hypertrophy #gainz #gains #cardio #hiit
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh

 Read on Twitter
Read on Twitter