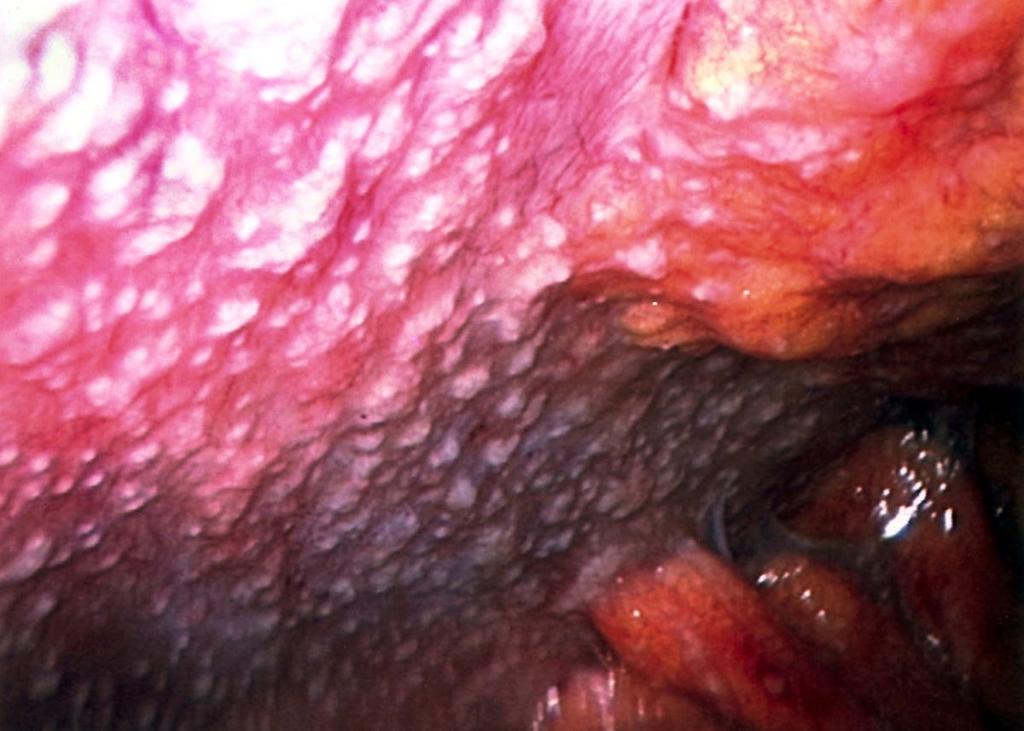
56M Mexico. Chronic abdominal pain, weight loss, anorexia.
Work up: elevated markers (CA19-9, CA-125, AFP). CXR normal. CT peritoneal carcinomatosis.
Laparoscopy (photo). Biopsy showed granuloma. What is your DDx? #MayoIDQ MCQ next...
Thank you for your responses.
Culture of tissue (peritoneal nodules) of this 56M (see prior tweet) with granuloma on biopsy: Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Resistant to pyrazinamide.
Which of these choices is the most likely mechanism of transmission?
Case diagnosis: Peritoneal #tuberculosis due to #Mycobacterium #bovis
Path: granuloma and positive #AFB stain
Culture: M tuberculosis complex
Clue: #PZA resistance —> THINK M. bovis
Reported by @GaboMotoa during his rotation in Mayo Clinic
doi.org/10.1002/ccr3.3…
#Mycobacterium #tuberculosis complex is a group:
- M tuberculosis: most common in human disease
- M #bovis (and BCG strain): mostly zoonotic but can cause human illness
- M africanum
- M microti
#Mycobacterium #bovis
- “zoonotic (e.g. bovine) TB”
- In humans: disease is most often “extrapulmonary TB” due to ingestion of infected cow’s milk products —> GI disease and enteric lymph nodes —> may disseminate
cdc.gov/tb/publication…
Transmission #Mycobacterium #bovis
1. Ingestion of animal products (most common): e.g., unpasteurized milk
- MCQ answer
2. Inhalation of airborne particle
3. Prolonged contact with infected animals/humans
4. Instillation: BCG Rx of bladder CA
cdc.gov/tb/publication…
Epidemiology #Mycobacterium #bovis
Variable geographic incidence
Mexico: study of TB cases 2000-2014
- 26% of TB cases due to M bovis
journals.plos.org/plosntds/artic…
Characteristics #Mycobacterium #bovis
1. Often extrapulmonary disease (remember: ingestion of infected milk and animal products is most common method of transmission)
2. PZA resistance: M bovis is INTRINSICALLY resistant
3. Risk: Hispanic ethnicity (Mexico) and diabetes
Clinical / radiologic features of #Mycobacterium bovis is similar for TB
- primary, reactivation
- pulmonary, extrapulmonary, disseminated disease
Distinguishing TB vs M bovis is not done routinely in US laboratories
- PZA mono-resistance
- Genomic / Biochemical assays
Treatment of #Mycobacterium #bovis is similar to PZA-resistant TB
(Remember: M bovis always resistant to PZA)
Example of Rx:
- 2 mo INH RIF EMB followed by 7 mo INH RIF
Guided by susceptibility tests
#Mycobacterium #bovis #Pearls
1. Zoonotic; may infect humans
2. Ingestion (unpasteurized milk) > inhalation / contact > instillation (BCG Rx)
3. Clinical, diagnostic - similar to TB
4. Hispanics / DM - higher risk
5. Rx: intrinsic PZA resistance
Thanks for participating!