#Kolkata's trams are famous. The electric #trams were first introduced in 1902 and at their peak covered 40 lines carried commuters over a 70 km network. Today only 28 km of the network remains. Once upon a time other cities in India also had electric/mechanical trams.
Thread👇
Thread👇

#Karachi Tramway first opened for traffic in 1885 as a steam tramway. By 1909 the East India Tramwag Co, had an all petrol/diesel fleet of trams. In 1949 the whole tramway system was sold to the Mohamedali Tramways Company (MTC). All 4 lines closed in 1975. 



#Bombay Tramway Company Limited was established in 1873. Electrified service began in 1907 and double-deck tram service in 1920. At its peak in 1935, 433 trams ran on 47 km of track. The service closed in 1964. 





The #Madras Electric Tramway Co Ltd was formed in 1892. At its peak in 1921, there were 42 km of track and 97 cars running. The system went bankrupt due to low fares and was closed in 1953. 





Cawnpore Electric Tramways (CET) opened a tramway system in 1907. There were 7km of track and 20 single-deck open trams. The system closed in 1933. #Kanpur 


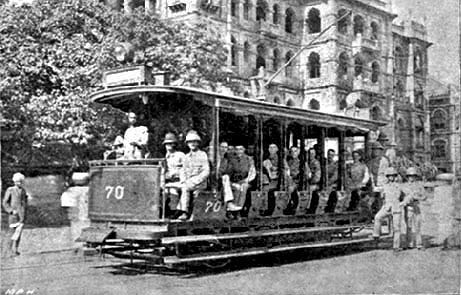
The #Delhi Electric Tramway and Lighting Company opened in March 1908 with 16km of track. By 1921 there were 24 convertible cars so as to meet summer and winter conditions of service. There were three main routes on the system with a hub at Fatehpuri. The system closed 1963. 





The #Baroda Tramway Company was established in 1908, from the BB&CI Railway Station at Raopura road to Goyagate (Pratapnagar Station). Converted to petrol in 1914, it functioned until 1925. 



In 1900 the #Ceylon Electric Tramways opened the country’s first tramway in #Colombo. At its height the 12 km line operated of 52 cars. Services were ended on on 30 June 1960. 





#Rangoon Electric Tramway (#Yangon, #Myanmar) began operations in 1906, and by 1921 there were 22 km of track and 77 cars in operation. Nationalized as part of the Rangoon Electricity Supply Board in 1953, the company was dissolved in 1961. 



#Mandalay Electric Company began operating trams in 1904. With a route length of 11 km, double track throughout, the company operated 24 electric cars. The track and overhead cables were severely damaged during the air raid of 3 April 1942 and subsequently were dismantled. 



• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





























