⭐️Everything you need to know about H. pylori: the Maastricht V/Florence Consensus Report summarized❗️ 🧵
🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠
#MedTwitter #GITwitter #IDTwitter #microbiome
gut.bmj.com/content/71/9/1…
🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠🦠
#MedTwitter #GITwitter #IDTwitter #microbiome
gut.bmj.com/content/71/9/1…
INDICATIONS/ASSOCIATIONS
🦠HP gastritis is an infectious disease irrespective of symptoms/complications
⚠️HP▶️chronic active gastritis in ALL colonized individuals. This can▶️peptic ulcer disease, atrophic gastritis, gastric adenocarcinoma, MALT. Eradication prevents all of this
🦠HP gastritis is an infectious disease irrespective of symptoms/complications
⚠️HP▶️chronic active gastritis in ALL colonized individuals. This can▶️peptic ulcer disease, atrophic gastritis, gastric adenocarcinoma, MALT. Eradication prevents all of this
🦠Test-and-treat (versus endoscopy or empiric PPI) for uninvestigated dyspepsia. Subject to regional HP prevalence and 💰considerations. This does NOT apply to patients with 🚩symptoms or older patients.
⚠️Need EGD if🚩. Can also consider🔦in patients where HP prevalence is ⬇️
⚠️Need EGD if🚩. Can also consider🔦in patients where HP prevalence is ⬇️
🦠Consider endoscopy 🔦 in patients with dyspeptic symptoms, especially in populations with ⬇️ HP prevalence
💡For good 🔦, need visualization of esophagus, cardia, fundus, corpus, antrum, duodenal bulb, descending duodenum; biopsies per standard protocol
💡For good 🔦, need visualization of esophagus, cardia, fundus, corpus, antrum, duodenal bulb, descending duodenum; biopsies per standard protocol
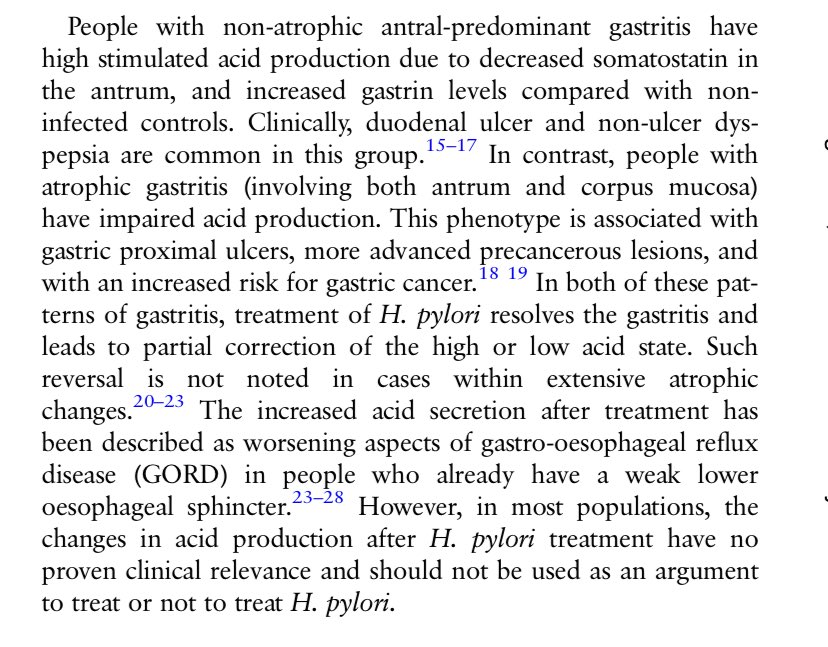
🦠HP gastritis may ⬆️ or ⬇️ acid secretion. Treatment may reverse or partially reverse these effects.
🗺Location location location 👇🏽
🗺Location location location 👇🏽
🦠HP gastritis is a distinct entity and causes dyspeptic symptoms in some patients. HP eradication▶️long-term relief of dyspepsia in ~10% of patients
💊In uninvestigated or functional dyspepsia, NNT = 14 for eradication improving sx
⚠️Many HP➕ patients do NOT have any symptoms
💊In uninvestigated or functional dyspepsia, NNT = 14 for eradication improving sx
⚠️Many HP➕ patients do NOT have any symptoms
🦠HP gastritis has to be excluded before diagnosing functional dyspepsia
🦠Aspirin & NSAIDs ⬆️ ulcer risk in HP infected subjects. Anticoagulants ⬆️ bleeding risk in those with ulcers.
🦠Test for HP in aspirin & NSAID users with a history of peptic ulcer
🦠Aspirin & NSAIDs ⬆️ ulcer risk in HP infected subjects. Anticoagulants ⬆️ bleeding risk in those with ulcers.
🦠Test for HP in aspirin & NSAID users with a history of peptic ulcer
🦠Long term PPI alters the topography of HP gastritis. Eradication heals gastritis in long term PPI users
💡HP & #GERD = inversely associated. Eradication does not cause or exacerbate GERD
⚠️The presence of GERD should not dissuade against treating HP!
💡HP & #GERD = inversely associated. Eradication does not cause or exacerbate GERD
⚠️The presence of GERD should not dissuade against treating HP!
⚠️Some HP➕ patients experience sudden-onset transient epigastric pain after starting PPI treatment for reflux
🦠HP is🔗with unexplained iron deficiency anemia, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, and B12 deficiency. 👀HP in these cases!
🦠HP has also been🔗with ⬆️ atherosclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer disease, Parkinson disease and ⬇️ obesity and asthma, but causality has not been proven
🦠HP has also been🔗with ⬆️ atherosclerosis, stroke, Alzheimer disease, Parkinson disease and ⬇️ obesity and asthma, but causality has not been proven
🦠HP eradication is the first line treatment for localized stage gastric MALToma
💡This cures up to 80% of cases
⚠️if t(11;18) translocation, HP eradication is usually not effective, so these patients need other treatments
⚠️gastric MALToma is a risk factor for adenocarcinoma
💡This cures up to 80% of cases
⚠️if t(11;18) translocation, HP eradication is usually not effective, so these patients need other treatments
⚠️gastric MALToma is a risk factor for adenocarcinoma
DIAGNOSIS
🦠Urease breath test (13C) is the best non-invasive test for test-and-treat strategy. Monoclonal 💩 antigen test can also be used. Serological tests can be used only after validation. Rapid serologic testing should not be used.
🦠Urease breath test (13C) is the best non-invasive test for test-and-treat strategy. Monoclonal 💩 antigen test can also be used. Serological tests can be used only after validation. Rapid serologic testing should not be used.
🦠🛑PPI 2 weeks before testing, antibiotics and bismuth 4 weeks before
💡H2RAs have minimal effect on 🌬sensitivity; antacids do not impair sensitivity of 🌬 or 💩
💡H2RAs have minimal effect on 🌬sensitivity; antacids do not impair sensitivity of 🌬 or 💩
🦠When there is indication for 🔦, rapid urease test is 1st line. If positive: immediate treatment. Take one biopsy from corpus and one from antrum. RUT should NOT be used to confirm eradication.
🦠To assess gastritis: minimum 2 biopsies from antrum and two from middle of body. Additional from incisura can be considered for detection of precancerous lesions.
⚠️Suspicious or ulcerated lesions need more biopsies. Can also use enhanced 🔦
⚠️Suspicious or ulcerated lesions need more biopsies. Can also use enhanced 🔦
🦠Most cases of HP can be diagnosed from biopsies using histochemical staining alone. In chronic active gastritis with negative HP, can use ancillary immunohistochemical testing. If normal histology, do not perform any immunohistochemical testing. 🔬
🦠Perform clarithromycin susceptibility testing when clarithromycin-based treatment is considered as the first-line therapy, except where resistance is <15%. Use antibiogram or molecular test
🦠After 1st failure, if🔦- culture and susceptibility testing (except if using quad rx)
🦠After 1st failure, if🔦- culture and susceptibility testing (except if using quad rx)
🦠Serologic testing with high accuracy and locally validated can be used for non-invasive diagnosis
⚠️Can detect past infection, so do not use to confirm eradication.
⚠️Do not use saliva or urine
⚠️Can detect past infection, so do not use to confirm eradication.
⚠️Do not use saliva or urine
🦠Pepsinogen serology is the most useful non-invasive test to determine non-atrophic vs atrophic gastric mucosa. PgI/PgII ratio can never be assumed as a biomarker of gastric neoplasia.
⚠️Limited value in antrum-restricted atrophy
👀 will serologic biopsies be the future? 🔮
⚠️Limited value in antrum-restricted atrophy
👀 will serologic biopsies be the future? 🔮
🦠UBT 🌬 is the best test to confirm HP eradication. SAT 💩 is an alternative. Should be done at least 4 weeks after completion of treatment.
⚠️ 🛑PPI for at least 2 weeks
🦠HP eradication improves gastritis and gastric atrophy but NOT intestinal metaplasia
⚠️ 🛑PPI for at least 2 weeks
🦠HP eradication improves gastritis and gastric atrophy but NOT intestinal metaplasia
TREATMENT
🦠🌎HP resistance to antibiotics is 📈
⚠️Clarithromycin resistance is up to 50% in some regions
🦠PPI-clarithromycin-containing triple therapy w/o prior susceptibility testing should be abandoned when the clarithromycin resistance rate in the region >15%
🦠🌎HP resistance to antibiotics is 📈
⚠️Clarithromycin resistance is up to 50% in some regions
🦠PPI-clarithromycin-containing triple therapy w/o prior susceptibility testing should be abandoned when the clarithromycin resistance rate in the region >15%
🦠Eradication rate can be predicted if cure rates are known for susceptible&resistant strains & prevalence of resistance.For individual patient,h/o prior🔑abx will predict abx resistance despite⬇️res in the pop.Susceptibility based results provide pop&individual-based results
🦠If⬆️(>15%) clarithromycin resistance, bismuth quadruple or non-bismuth quadruple, concomitant (PPI, amoxicillin, clarithromycin & a nitroimidazole) therapies are recommended.
If⬆️dual clarithromycin/metronidazole resistance, bismuth quadruple therapy is the recommended 1st-line
If⬆️dual clarithromycin/metronidazole resistance, bismuth quadruple therapy is the recommended 1st-line

💡If bismuth not available in ⬆️ dual clarithromycin/metronidazole resistance areas, levofloxacin, rifabutin, and ⬆️ dose dual (PPI+amoxicillin) treatments can be considered.
💡If tetracycline not available in high dual resistance areas, bismuth-containing quad therapy combining furazolidone ➕ metronidazole or amoxicillin ➕ metronidazole can be considered as well as bismuth ➕ triple therapy—PPI, amoxicillin, & either clarithromycin or levofloxacin)
🦠Treatment duration of bismuth quadruple therapy should be extended to 14 days, unless 10d therapies are proven effective locally.
🦠Clarithromycin resistance undermines the efficacy of triple & sequential Rx; metronidazole res undermines efficacy of sequential therapy; dual clarithromycin/metronidazole res undermines efficacy of sequential, hybrid & concomitant therapy.
🦠Concomitant therapy (PPI, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, & a nitroimidazole concurrently) should be the preferred non-bismuth quad therapy—has shown to be the most effective to overcome antibiotic resistance.
💡Concomitant therapy is the simplest (over sequential & hybrid)
💡Concomitant therapy is the simplest (over sequential & hybrid)
🦠Treatment duration of non-bismuth quadruple therapy (concomitant) is 14 days unless 10 day therapies are proven effective locally
🦠If⬇️clarithromycin resistance, triple therapy is recommended as first-line empirical treatment. Bismuth-containing quad therapy is an alternative
🦠⬆️dose PPI 2x/d ⬆️ the efficacy of triple therapy. Esomeprazole and rabeprazole may be preferred in Europe and N America where the prevalence of PPI extensive metabolizers is ⬆️.
⚠️cytochrome 2C19 & MDR polymorphisms determine response to PPI. >80% Caucasian are⬆️metabolizers
⚠️cytochrome 2C19 & MDR polymorphisms determine response to PPI. >80% Caucasian are⬆️metabolizers
🦠Duration of PPI-clarithromycin based triple therapy should be extended to 14 days, unless shorter therapies are proven effective locally.
🦠After failure of bismuth-containing quadruple therapy, a fluoroquinolone-containing triple or quadruple therapy may be recommended. In cases of high quinolone resistance, the combination of bismuth with other antibiotics, or rifabutin, may be an option.
🦠After failure of PPI-clarithromycin-amoxicillin triple therapy, a bismuth-containing quadruple therapy or a fluoroquinolone-containing triple or quadruple therapy are recommended as a second-line treatment.
🦠After failure of a non-bismuth quadruple therapy, either a bismuth quadruple therapy or a fluoroquinolone-containing triple or quadruple therapy are recommended.
🦠After failure of second-line treatment, culture with susceptibility testing or molecular determination of genotype resistance is recommended in order to guide treatment.
🦠After failure of 1st-line Rx (clarithromycin based) & 2nd-line Rx (w bismuth-containing quad), recommended to use fluoroquinolone-containing regimen. If⬆️fluoroquinolones resistance, a combo of bismuth➕different abx or rifabutin-containing rescue therapy should be considered
🦠After failure of the first-line treatment (triple or non-bismuth quadruple) and second-line treatment (fluoroquinolone-containing therapy), it is recommended to use the bismuth-based quadruple therapy.
🦠After failure of first-line treatment with bismuth quadruple and second-line treatment (fluoroquinolone-containing therapy), it is recommended to use a clarithromycin-based triple or quadruple therapy. A combination of bismuth with different antibiotics may be another option.
🦠In patients with penicillin allergy: in areas of low clarithromycin resistance, for a first-line treatment, a PPI-clarithromycin-metronidazole combination may be prescribed, and in areas of high clarithromycin resistance, bismuth quadruple therapy should be preferred.
🦠Rescue regimen: A fluoroquinolone-containing regimen may represent an empirical second-line rescue option in the presence of penicillin allergy.
PREVENTION/PUBLIC HEALTH
🦠HP is the major etiological factor for gastric cancer
🦠HP is also a risk factor for proximal gastric cancer (exclude esophageal & junctional adenocarcinoma)
⚠️>90% of gastric cancer attributable to HP
🦠HP eradication ⬇️ the risk of gastric cancer
🦠HP is the major etiological factor for gastric cancer
🦠HP is also a risk factor for proximal gastric cancer (exclude esophageal & junctional adenocarcinoma)
⚠️>90% of gastric cancer attributable to HP
🦠HP eradication ⬇️ the risk of gastric cancer
🦠The influence of environmental factors is subordinate to the effect of HP
⚠️HP is class 1️⃣ carcinogen.
⚠️ 🚬 and 🧂 are also risk factors, though less important.
🦠HP eradication abolishes the inflammatory response; early Rx prevents progression to preneoplastic lesions
⚠️HP is class 1️⃣ carcinogen.
⚠️ 🚬 and 🧂 are also risk factors, though less important.
🦠HP eradication abolishes the inflammatory response; early Rx prevents progression to preneoplastic lesions
🦠HP eradication reverses gastric atrophy if intestinal metaplasia is not present and🛑progression of preneoplastic▶️neoplastic lesions in some
🦠Risk of gastric cancer can be⬇️more effectively by employing eradication Rx before the development of atrophy & intestinal metaplasia
🦠Risk of gastric cancer can be⬇️more effectively by employing eradication Rx before the development of atrophy & intestinal metaplasia
🦠HP eradication for gastric cancer prevention is cost-effective in communities with ⬆️ risk for gastric cancer.
🦠Eradication offers clinical & economic benefits other than gastric cancer prevention and should be considered in all communities.
🦠Eradication offers clinical & economic benefits other than gastric cancer prevention and should be considered in all communities.
🦠Screen-and-treat strategies are recommended in communities at ⬆️ risk of gastric cancer.
🦠Consider screen-and-treat in communities with intermediate to ⬇️ risk for gastric cancer
💡This is cost effective, especially if we consider the effects on PUD and dyspepsia
🦠Consider screen-and-treat in communities with intermediate to ⬇️ risk for gastric cancer
💡This is cost effective, especially if we consider the effects on PUD and dyspepsia
🦠Screen-and-treat is recommended in individuals at increased risk for gastric cancer.
💡RFs: corpus predominant gastritis, gastric atrophy/intestinal metaplasia, hypochlorhydria, evidence of current or past HP, high risk populations, family history
💡RFs: corpus predominant gastritis, gastric atrophy/intestinal metaplasia, hypochlorhydria, evidence of current or past HP, high risk populations, family history
🦠Consider 🔦-based screening in those with ⬆️ risk of gastric cancer.
🦠Advanced preneoplastic lesions (atrophy/intestinal metaplasia) require follow-up by 🔦 staging
🦠Public awareness campaigns for prevention of gastric cancer should be encouraged.
🦠Advanced preneoplastic lesions (atrophy/intestinal metaplasia) require follow-up by 🔦 staging
🦠Public awareness campaigns for prevention of gastric cancer should be encouraged.
🦠Mass eradication using a screen-and-treat strategy with commonly used antibiotics may create additional resistance selection pressure on pathogens other than HP
⚠️Streptococci, E. coli, C. difficile
🦠An effective vaccine would be the best public health measure against HP 💉
⚠️Streptococci, E. coli, C. difficile
🦠An effective vaccine would be the best public health measure against HP 💉
HP AND THE GASTRIC MICROBIOTA
🦠Gastric microbiota include other🦠apart from HP
💡Healthy: Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria; the most commonly found genus in the stomach is Streptococcus. These are NOT just from the oral and throat microbiota!
🦠Gastric microbiota include other🦠apart from HP
💡Healthy: Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria; the most commonly found genus in the stomach is Streptococcus. These are NOT just from the oral and throat microbiota!
🦠Composition of a healthy gastric microbiota and how HP affects this have not yet been fully defined
💡HP⬇️diversity and predominates over other🦠
🦠Components of the gastric microbiota may play a role in the development of HP-related diseases
💡HP = main but not only trigger
💡HP⬇️diversity and predominates over other🦠
🦠Components of the gastric microbiota may play a role in the development of HP-related diseases
💡HP = main but not only trigger
🦠Non-HP Helicobacter species can cause human gastric and systemic disease.
💡Gastric: H. bizzozeronii, H. felis, H. heilmannii s.s., H. salomonis, H. suis; enterohepatic: H. bilis, H. cinaedi, H. fennelliae
🔬Diagnosis of these can be difficult, in part d/t patchy colonization
💡Gastric: H. bizzozeronii, H. felis, H. heilmannii s.s., H. salomonis, H. suis; enterohepatic: H. bilis, H. cinaedi, H. fennelliae
🔬Diagnosis of these can be difficult, in part d/t patchy colonization
🦠HP eradication therapy can impair the healthy gut microbiota, leading to short-term clinical consequences.
⚠️Antibiotics are the main risk factor for Clostridioides difficile infection
💡 #Probiotics may counteract the harmful effects of antibiotics on the microbiota.
⚠️Antibiotics are the main risk factor for Clostridioides difficile infection
💡 #Probiotics may counteract the harmful effects of antibiotics on the microbiota.
🦠HP eradication should be used with care in subjects with undeveloped or unstable gut microbiota to avoid long-term clinical consequences.
⚠️Risks include metabolic and weight dysregulation and immune dysfunction
⚠️Risks include metabolic and weight dysregulation and immune dysfunction
🦠Antibiotic-based HP eradication therapy can select antibiotic-resistant components of gut microbiota.
⚠️⬆️resistant streptococci, staphylococci, Enterococcus, Enterobacteriaceae, Bacteroides, MRSA, ESBL E. coli and Klebsiella– can last years after completion of therapy
⚠️⬆️resistant streptococci, staphylococci, Enterococcus, Enterobacteriaceae, Bacteroides, MRSA, ESBL E. coli and Klebsiella– can last years after completion of therapy
🦠Additional studies are required to address the long-lasting impact of HP eradication on the composition of gut microbiota.
🧪This is an important research opportunity!
🧪This is an important research opportunity!
🦠Certain #probiotics have been shown to be effective in ⬇️ GI side effects caused by HP eradication therapies. Specific strains should be chosen only upon the basis of a demonstrated clinical efficacy.
💡Lactobacillus genus, Saccharomyces boulardii, Bacillus clausii; >2 wks
💡Lactobacillus genus, Saccharomyces boulardii, Bacillus clausii; >2 wks
🦠Certain #probiotics may have a beneficial effect on HP eradication.
💡Data for Lactobacillus strains, Bifidobacterium strains, and S. boulardii
⭐️(My personal practice: prescribe S. boulardii during eradication therapy)
💡Data for Lactobacillus strains, Bifidobacterium strains, and S. boulardii
⭐️(My personal practice: prescribe S. boulardii during eradication therapy)
Bonus fun fact: I ✍️ this 🧵 from the island of Chios in 🇬🇷, unique home to the μαστίχα (mastic) 🌳. The resin produced by the 🌳 has anti-H. pylori activity. See here from the New England Journal of Medicine @NEJM: nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.105…
It’s also DELICIOUS!
#EatGREEK
It’s also DELICIOUS!
#EatGREEK

NB: The @aeprobio Clinical Guide to Probiotic Products contains recommendations for #probiotics as adjunctive treatment for H. pylori eradication. 👇🏽
usprobioticguide.com/?utm_source=in…
usprobioticguide.com/?utm_source=in…
Beautiful summary:
https://twitter.com/demadaria/status/1558542813410873351
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh