
WHAT'S THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN SHARDING AND SUBNET
A deep dive thread 🧵
1) What are they?
• Sharding technology is a form of dividing a database into smaller parts, called "shards", and storing them on different computers.
#Blockchain $AVAX #cryptocurrency #Crypto #subnet
A deep dive thread 🧵
1) What are they?
• Sharding technology is a form of dividing a database into smaller parts, called "shards", and storing them on different computers.
#Blockchain $AVAX #cryptocurrency #Crypto #subnet
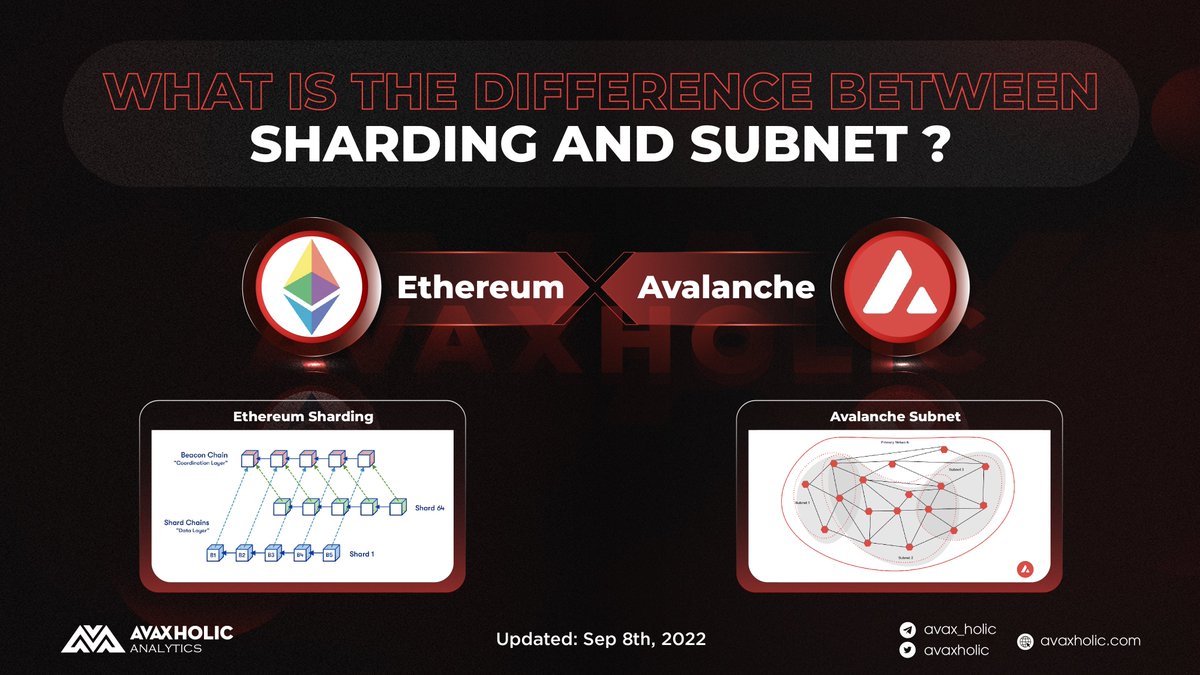
In the #Blockchain network, Sharding refers to the division of nodes in the network into groups responsible for a piece of chain data, these small groups can process many transactions at the same time.
• Subnets are a feature on #Avalanche Network that allows anyone to create their own L1 blockchain which can also operate as a L2 for new use cases.
A subnetwork can be a single customized blockchain or a group of customized blockchains that are validated together.
A subnetwork can be a single customized blockchain or a group of customized blockchains that are validated together.
👉 Subnetworks are also similar to sharding, as they create new separate but connected instances of the same blockchain.
However, the important difference here is that the subnet allows customizing the public or private blockchain as needed while Ethereum sharding is just a solution to handle transactions there instead of on Ethereum.
2) Technology
2.1) Ethereum sharding:
Unlike the block2block PoW chain, the PoS sharding chain of ETH 2.0 will be understood as Epoch2Epoch.
Each epoch consists of 32 slots which can be understood as 32 slots for blocks.
2.1) Ethereum sharding:
Unlike the block2block PoW chain, the PoS sharding chain of ETH 2.0 will be understood as Epoch2Epoch.
Each epoch consists of 32 slots which can be understood as 32 slots for blocks.

Validators will be automatically allocated to committees or become block proposers as each new epoch is formed.
👉 A committee is a group of validators.
👉 A committee is a group of validators.
For security, each location (in the Signaling Chain and each shard) has at least 128 committee validators.
An attacker has less than one in a trillion probability of controlling ⅔ of a committee.
An attacker has less than one in a trillion probability of controlling ⅔ of a committee.
2.2) Avalanche subnet:
Each blockchain is validated by exactly one Subnet, and a Subnet can have many blockchains. The number of validators inside a subnet is infinite, with a minimum of 5.
Each blockchain is validated by exactly one Subnet, and a Subnet can have many blockchains. The number of validators inside a subnet is infinite, with a minimum of 5.

A validator may be a member of many Subnets. Subnets are independent, they specify their own execution logic, determine their own fee regime, maintain their own state, facilitate their own networking, and provide their own security.
3) Ability of extension
Ignoring the technology issue of the two solutions, Avalanche's model does not limit the number of subnets that can be built.
Ignoring the technology issue of the two solutions, Avalanche's model does not limit the number of subnets that can be built.
Although it is expected that Ethereum will split into 64 shards to handle concurrent transactions but after authentication, it must still be stored on the Beacon chain (main chain).
This could be the bottleneck in Ethereum's scaling solution.
This could be the bottleneck in Ethereum's scaling solution.
The expected transaction processing speed of Ethereum 2.0 will be over 10 seconds and subnet < 2s.
It shows that the horizontal scalability of the Avalanche subnet is significantly more efficient than sharding.
It shows that the horizontal scalability of the Avalanche subnet is significantly more efficient than sharding.
4) Security capabilities
• Sharding: In terms of security, Ethereum 2.0 has a complex model, especially between the stages of block proposer selection and random sampling of validators in epochs.
• Sharding: In terms of security, Ethereum 2.0 has a complex model, especially between the stages of block proposer selection and random sampling of validators in epochs.
• Subnet: Each subnet will have its own level of security.
Security is maintained by subnets having their own token that must be staked in conjunction with AVAX.
Security is maintained by subnets having their own token that must be staked in conjunction with AVAX.
So, in this respect, #Ethereum will have an advantage in ensuring the security of the network compared to subnet technology.
5) Decentralization
* Validator requirements:
• Avalanche: Stake 2000 AVAX ≈ $40K. CPU: 8 cores >= 2 GHz, RAM: 16 GB, Storage: 200 GB free space. OS: Ubuntu >= 18.04 or Mac OS X >= Catalina.
* Validator requirements:
• Avalanche: Stake 2000 AVAX ≈ $40K. CPU: 8 cores >= 2 GHz, RAM: 16 GB, Storage: 200 GB free space. OS: Ubuntu >= 18.04 or Mac OS X >= Catalina.
• Ethereum: Staked 32 ETH ≈ $54K. Using the software client Prysm CPU: 4 cores ≥ 2GHz, RAM: 16 GB, Storage: 100 GB free space.
👉 The requirements to become validators of the two networks are similar, and do not require too much of the asset value that needs to be staked as well as the hardware to operate.
But Ethereum is far superior thanks to its advantages in community and popularity, so the number of validators is much larger than Avalanche.
6) Closing thoughts
• Scalability is the top priority of a Blockchain network to be more applicable to life, replacing the traditional economy.
Both Subnets and Sharding are two solutions that promise to bring positive breakthroughs in this mass adoption.
• Scalability is the top priority of a Blockchain network to be more applicable to life, replacing the traditional economy.
Both Subnets and Sharding are two solutions that promise to bring positive breakthroughs in this mass adoption.
• Is there room for Avalanche and Ethereum 2.0 development to coexist?
👉 The popularity of new blockchains claiming to be ETH-killers stems from their fast transaction speeds and low transaction costs, while still utilizing Ethereum-like interfaces, wallets, and application development processes.
So, when Ethereum solves the above issue and attracts new users, whether those blockchains will still exist is an open question.
👉The answer is yes, besides providing scalability, subnets still offer other outstanding benefits for both developers and users:
👉The answer is yes, besides providing scalability, subnets still offer other outstanding benefits for both developers and users:
• Independent Token Economics: Subnets can have their own token economics with their own native tokens and fee markets.
• Subnet may require validators to meet a set of requirements.
• Support for Private Blockchains
• High TPS
• Subnet may require validators to meet a set of requirements.
• Support for Private Blockchains
• High TPS
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh









