Our new work:
No upper limit to the anabolic response to protein ingestion?
Challenges current views on:
1⃣Dose-response relationship
2⃣"Excessive" protein getting oxidized
3⃣Protein distribution
4⃣MUCH more!
Paper:
1/10 🧵 cell.com/cell-reports-m…

No upper limit to the anabolic response to protein ingestion?
Challenges current views on:
1⃣Dose-response relationship
2⃣"Excessive" protein getting oxidized
3⃣Protein distribution
4⃣MUCH more!
Paper:
1/10 🧵 cell.com/cell-reports-m…

It is generally accepted that a single bolus of 20 g protein results in a near-max stimulation of muscle protein synthesis in healthy young adults.
Excessive protein is thought to be oxidized.
This is the basis for the recommendation to distribute daily protein intake.
2/10
Excessive protein is thought to be oxidized.
This is the basis for the recommendation to distribute daily protein intake.
2/10

I was skeptical:
1⃣Meal frequency does not appear to strongly impact muscle mass in chronic studies
2⃣Some animals consume infrequent but GIGANTIC meals (e.g. snakes)
3⃣MPS studies typically seem too short to allow large amounts of protein to be fully digested
3/10
1⃣Meal frequency does not appear to strongly impact muscle mass in chronic studies
2⃣Some animals consume infrequent but GIGANTIC meals (e.g. snakes)
3⃣MPS studies typically seem too short to allow large amounts of protein to be fully digested
3/10

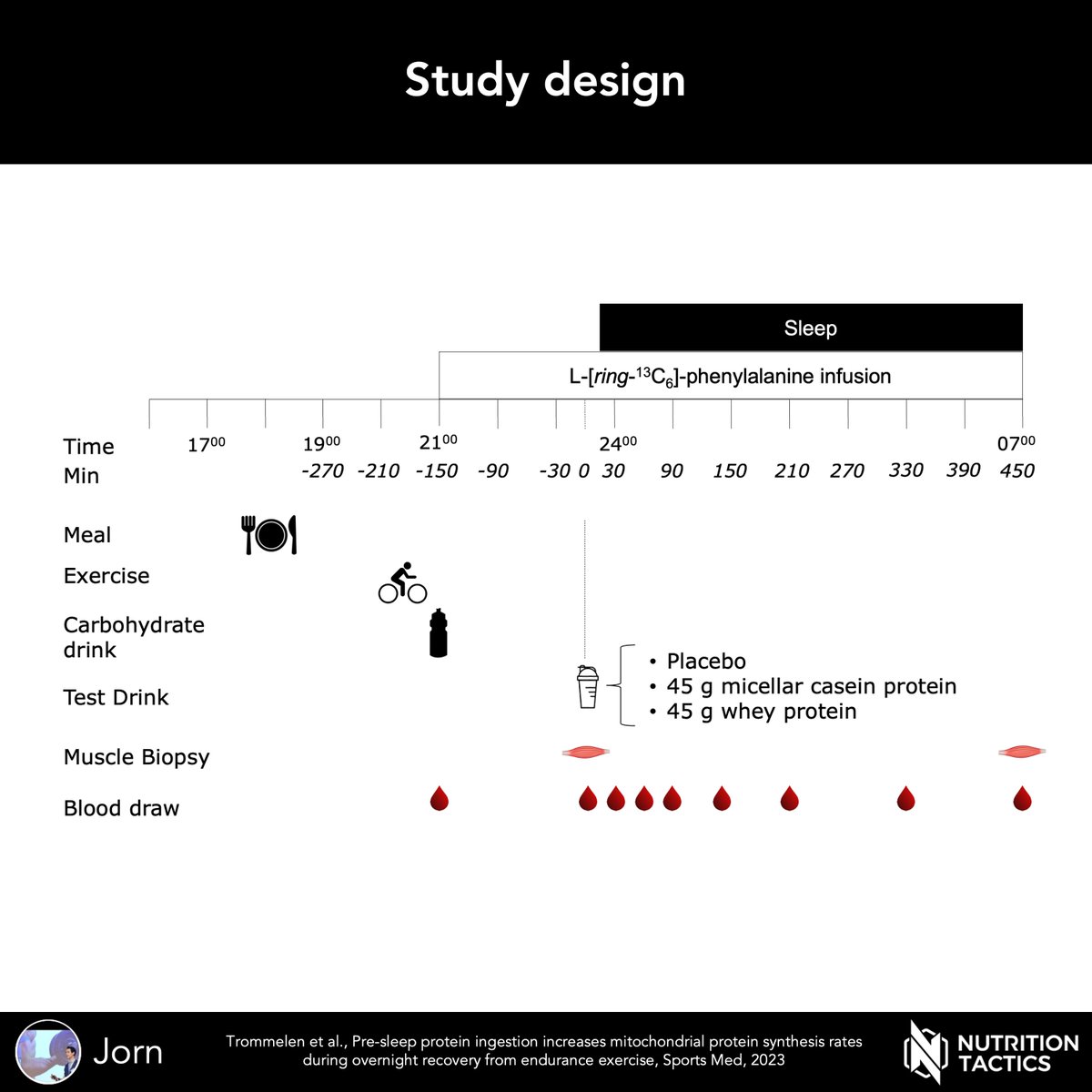
Therefore, we performed a study comparing:
- 0PRO
- 25PRO
- 100PRO
Milk protein (intrinsically labeled for gold standard methodology)
Postexercise in young adults
Prolonged 12-h assessment period with muscle biopsies every 4 h to determine MPS timeline
4/10
- 0PRO
- 25PRO
- 100PRO
Milk protein (intrinsically labeled for gold standard methodology)
Postexercise in young adults
Prolonged 12-h assessment period with muscle biopsies every 4 h to determine MPS timeline
4/10

Whereas plasma amino acid concentrations did not differ anymore from placebo after ~5 h in 25PRO....
...they were still substantially higher in 100PRO at the end of the 12-h postprandial period.
This suggests that 100PRO was still digesting (confirmed with tracers)
5/10
...they were still substantially higher in 100PRO at the end of the 12-h postprandial period.
This suggests that 100PRO was still digesting (confirmed with tracers)
5/10

Whole-body protein metabolism
100PRO had by far the highest protein synthetic response and the most positive net balance
Protein intake stimulated an increase in AA oxidation, but that increase seems negligible compared to the increase in protein synthesis.
6/10
100PRO had by far the highest protein synthetic response and the most positive net balance
Protein intake stimulated an increase in AA oxidation, but that increase seems negligible compared to the increase in protein synthesis.
6/10

Myofibrillar protein synthesis
100PRO was ~30% higher vs 25PRO over the 12-h
~20% in the first 4 h
~40% in the last 8 h
Thus, a large amount of protein has an added benefit in the early phase, but the main benefit is a more prolonged response vs a moderate amount
7/10
100PRO was ~30% higher vs 25PRO over the 12-h
~20% in the first 4 h
~40% in the last 8 h
Thus, a large amount of protein has an added benefit in the early phase, but the main benefit is a more prolonged response vs a moderate amount
7/10

Some implications
1⃣Dose-response
Protein in excess of 20 g gets effectively used and is not "wasted"
(at least in healthy young adults following resistance exercise)
2⃣Protein distribution
- evidence was already questionable
- now mechanistic supports also falls away
8/10
1⃣Dose-response
Protein in excess of 20 g gets effectively used and is not "wasted"
(at least in healthy young adults following resistance exercise)
2⃣Protein distribution
- evidence was already questionable
- now mechanistic supports also falls away
8/10
3⃣Time-restricted feeding
How long are you actually fasted?
If protein intake is high during the feeding period, you may still not be fasted for >12 h later....
In addition, our data suggests that prolonged anabolism does not negatively impact muscle autophagy markers.
9/x
How long are you actually fasted?
If protein intake is high during the feeding period, you may still not be fasted for >12 h later....
In addition, our data suggests that prolonged anabolism does not negatively impact muscle autophagy markers.
9/x
The paper has infinite more data and discussion.
Would love to hear your thoughts on my best work yet:
@mackinprof
@DrMyohead
@donlayman
@LeighBreen
@gareth_wallis
@Gonzalez_JT
@donlayman
@BenjaminTWall
@Nicholas_Burd
@BioLayne
@OllyWitard
Would love to hear your thoughts on my best work yet:
@mackinprof
@DrMyohead
@donlayman
@LeighBreen
@gareth_wallis
@Gonzalez_JT
@donlayman
@BenjaminTWall
@Nicholas_Burd
@BioLayne
@OllyWitard
https://x.com/JornTrommelen/status/1737186614747500647?s=20
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh