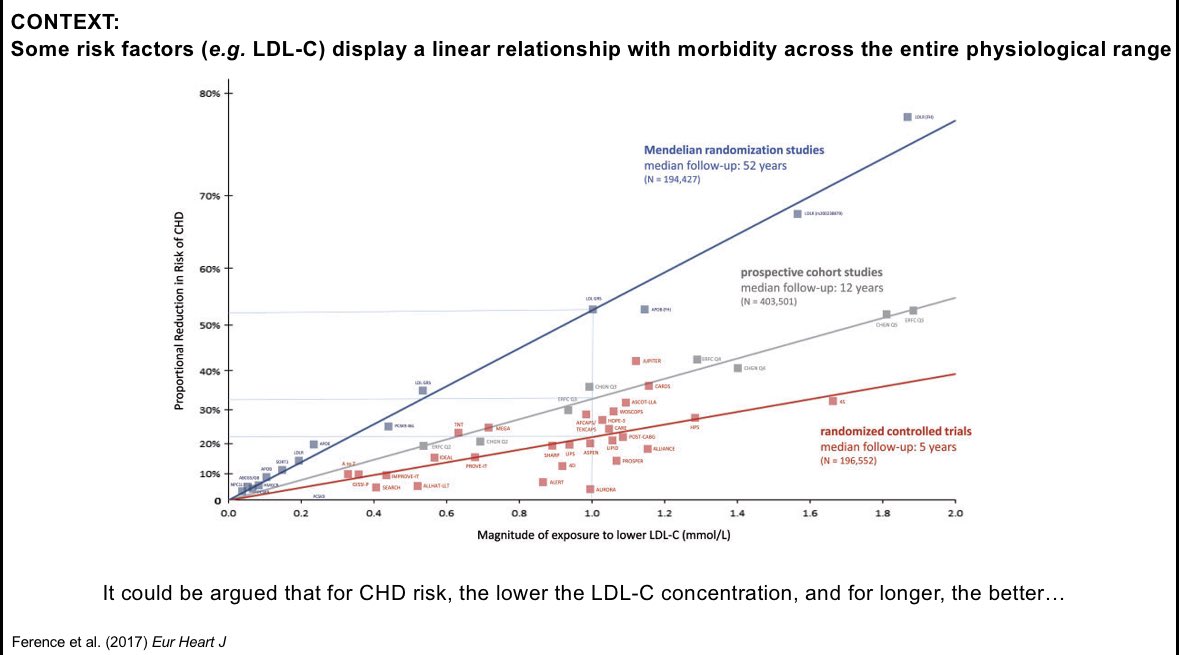
Restricting total carbs has a much bigger effect than just restricting sugars in the first 24 hours
Check out our latest study (led by @AaronHengist) on carb and sugar restriction 🧵 (1/11)
doi.org/10.1007/s00394…
#lchf #lowcarb #carbs #highfat #keto #ketogenic #diet #health
Check out our latest study (led by @AaronHengist) on carb and sugar restriction 🧵 (1/11)
doi.org/10.1007/s00394…
#lchf #lowcarb #carbs #highfat #keto #ketogenic #diet #health

The main aim was to see if restricting sugars or total carbs alters physical activity levels
This is because previous studies suggested fasting can lower physical activity & this can happen quickly
We wanted to know if this was due to carbs or energy
What did we find?
2/11
This is because previous studies suggested fasting can lower physical activity & this can happen quickly
We wanted to know if this was due to carbs or energy
What did we find?
2/11
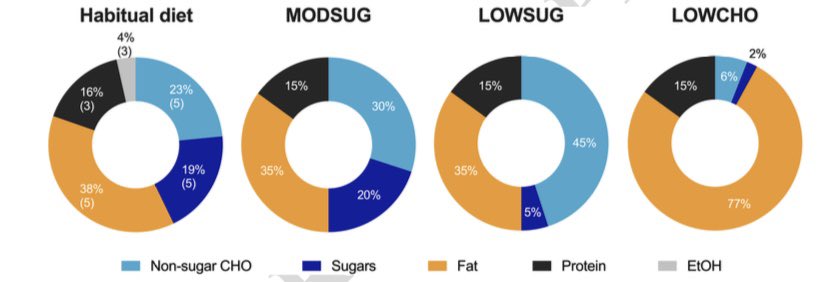
25 people (15 female) ate 3 diets for 24 hours with a variety of metabolic and energy balance measures
3/11


3/11


Fuel use changed rapidly
Low-carb increase fat oxidation 🔥 and decreased carb oxidation within hours
Restricting just sugars made little difference 🍬
4/11
Low-carb increase fat oxidation 🔥 and decreased carb oxidation within hours
Restricting just sugars made little difference 🍬
4/11

Similarly, blood sugar and insulin responses didnt differ much with sugar restriction but were much lower with total carb restriction.
This might be surprising but makes sense with the knowledge that table sugar has a lower glycemic index than many non-sugar carbs 🍬🍚
5/11
This might be surprising but makes sense with the knowledge that table sugar has a lower glycemic index than many non-sugar carbs 🍬🍚
5/11

One of the only differences with sugar restriction was blood lactate concentrations
Probably because fructose is converted into lactate by the liver and thereby provides fuel for the brain and muscle 🧠 💪🏻
6/11
Probably because fructose is converted into lactate by the liver and thereby provides fuel for the brain and muscle 🧠 💪🏻
6/11

Levels of fat in the blood were higher after the low-carb, high-fat breakfast, and were lower the following morning when fasted
This likely reflects increased fat oxidation 🔥
7/11
This likely reflects increased fat oxidation 🔥
7/11

Ketosis was rapidly induced by the low-carb diet, especially in women
Remarkably, women also showed increased LDL-cholesterol within 24 h of low-carb 🍳🥓
8/11
Remarkably, women also showed increased LDL-cholesterol within 24 h of low-carb 🍳🥓
8/11

Despite these large changes in metabolism, differences in physical activity and energy intake were pretty much absent
9/11

9/11


Summary
Restricting total carbs affects metabolism rapidly and more drastically than just restricting sugars
Some effects were larger in women than men
Energy balance (short-term) was unaffected
Stay tuned for the 12-week data!
10/11
Restricting total carbs affects metabolism rapidly and more drastically than just restricting sugars
Some effects were larger in women than men
Energy balance (short-term) was unaffected
Stay tuned for the 12-week data!
10/11
Thanks to @rankprize @UniofBath & Cosun Nutrition Center for funding, and participants for their efforts!
11/11
11/11
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh