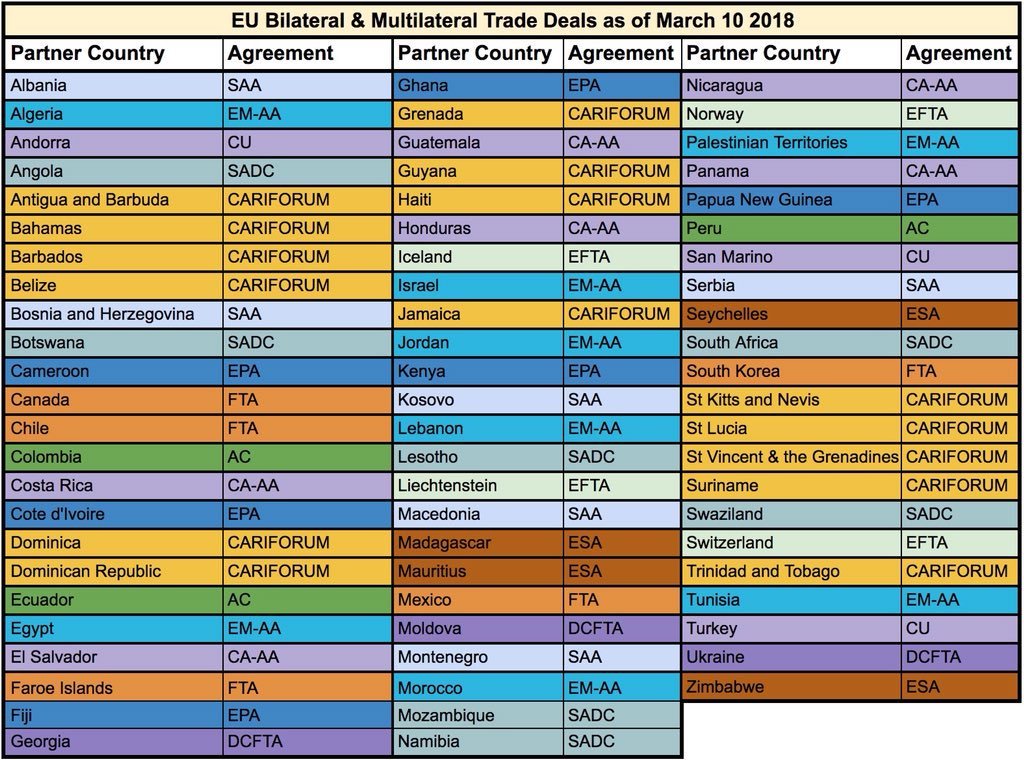
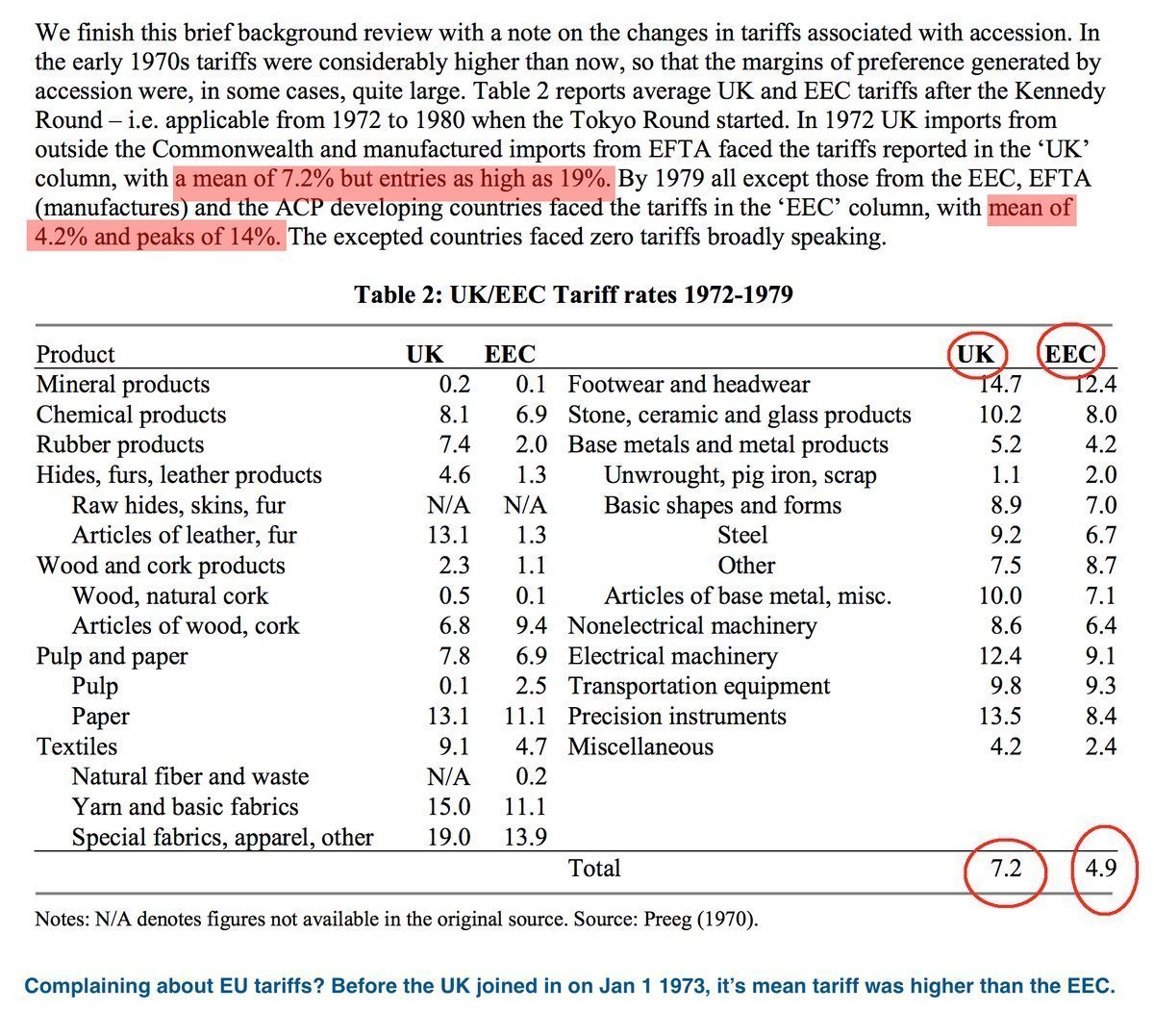
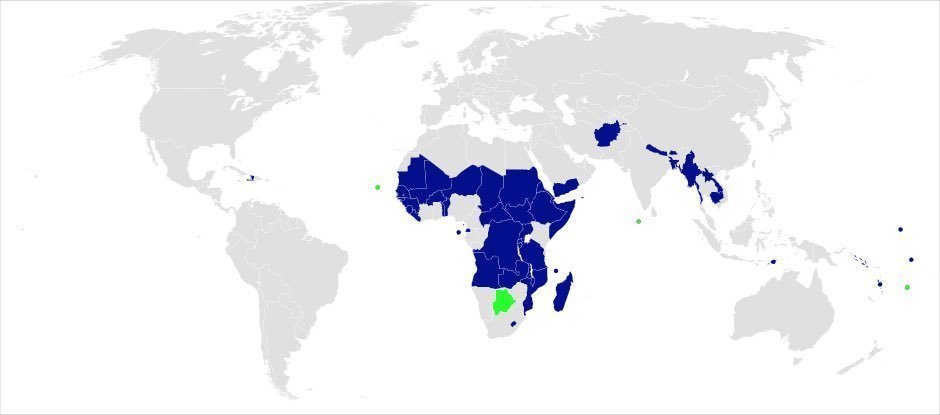
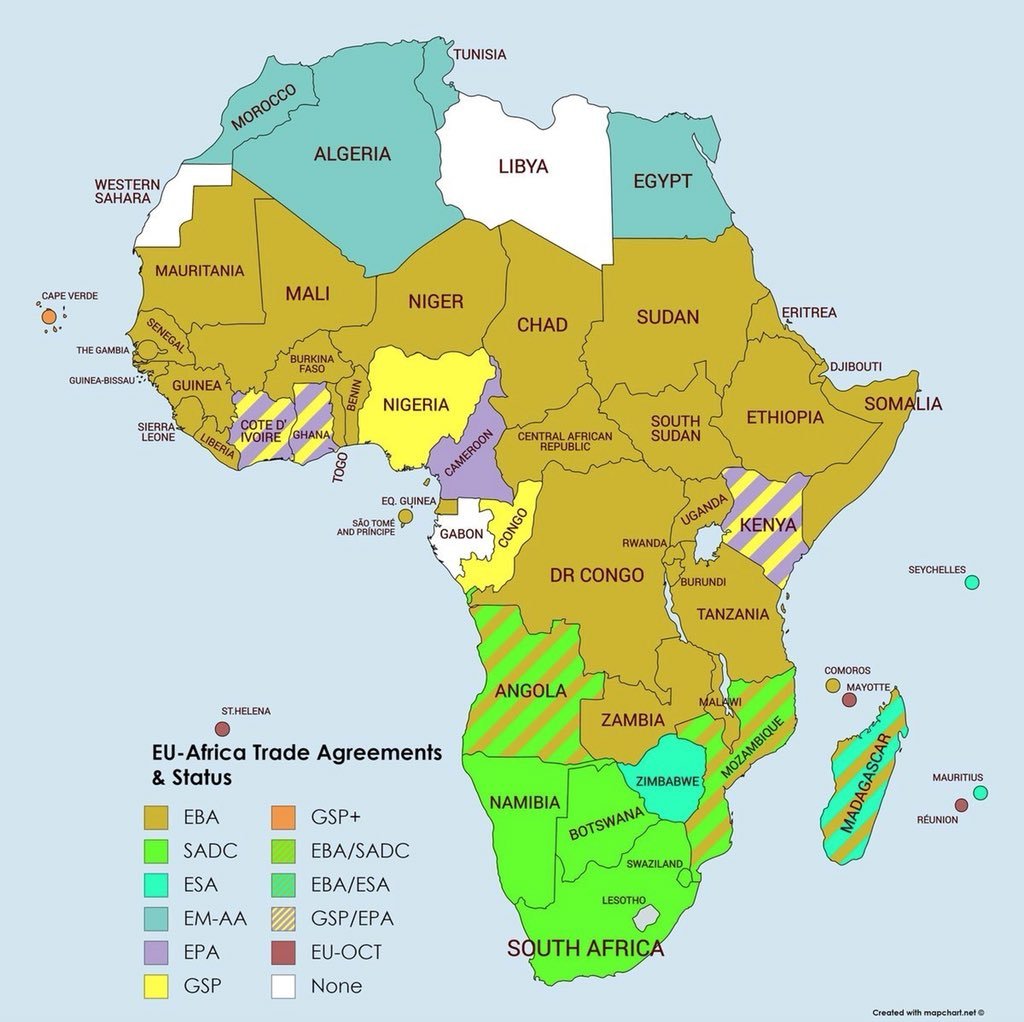
Most African countries are on zero tariffs for everything bar guns and ammunition. The few remaining are on General Scheme of Preferences (GSP), like Nigeria, or EU Association Agreement, and two cases of no reduction.



trade.ec.europa.eu/doclib/docs/20…
ec.europa.eu/romania/sites/…



aei.pitt.edu/34505/1/A674.p…


The Lomé Convention: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lom%C3%A9…
ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/1885…

ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/1885…

aei.pitt.edu/60103/1/BN_15.…


wto.org/english/docs_e… …



In 1964 the first UNTAD (United Nations Conference of Trade and Development) conference was held in Geneva and the issue adressed
trade.ec.europa.eu/doclib/docs/20… …
The United States implemented their own GSP scheme in 1976.
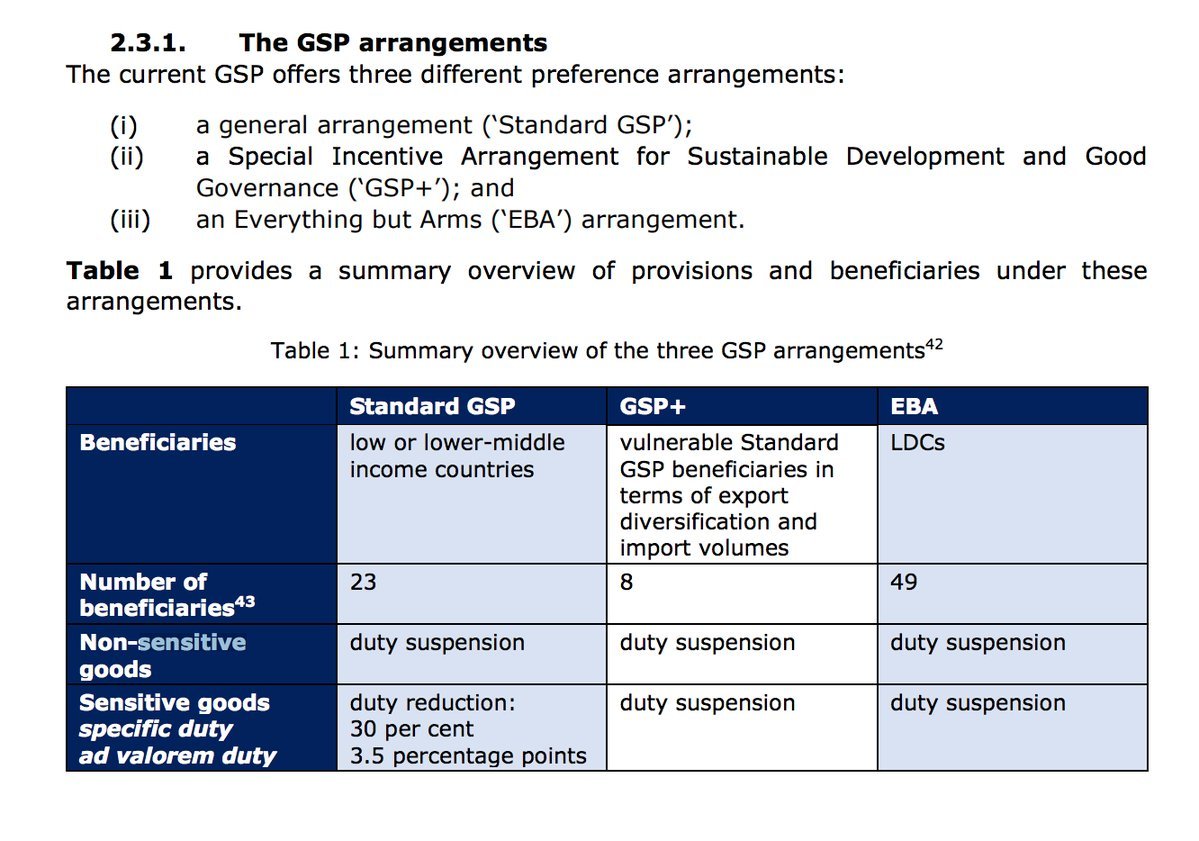
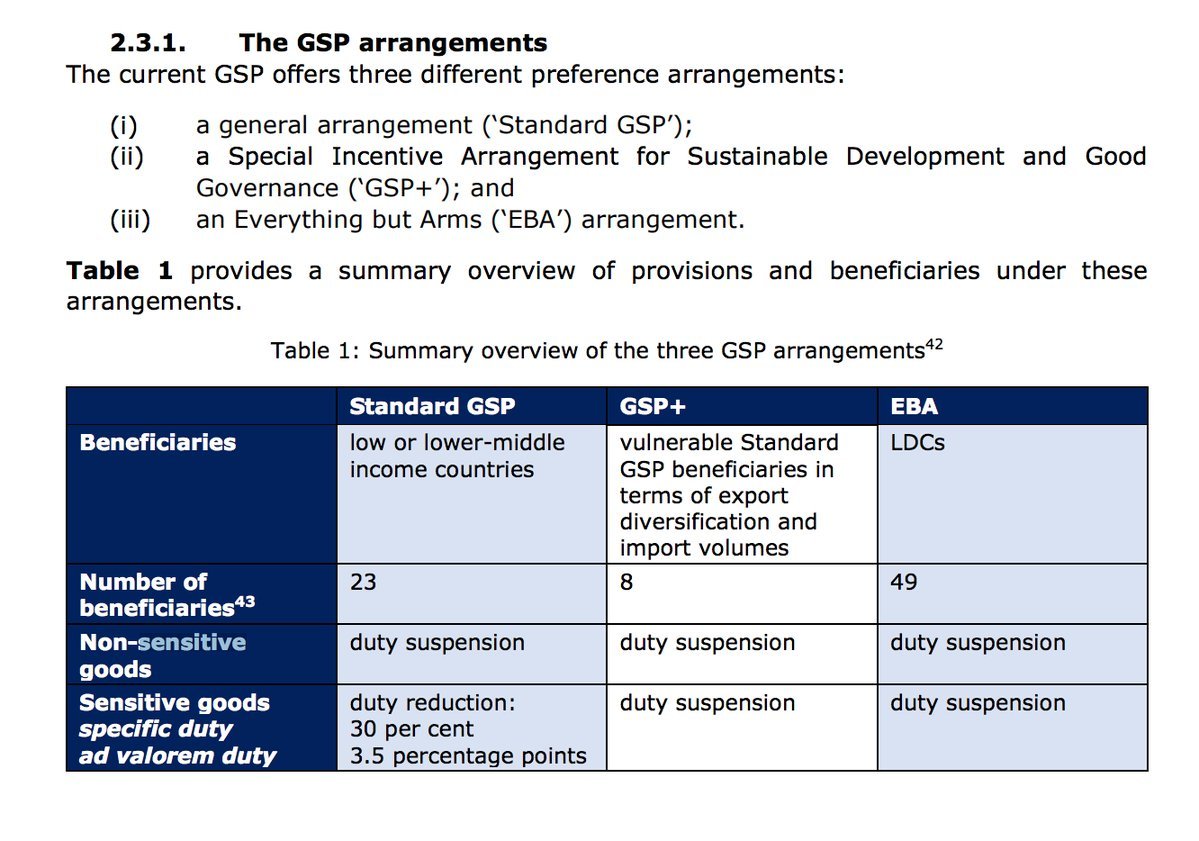
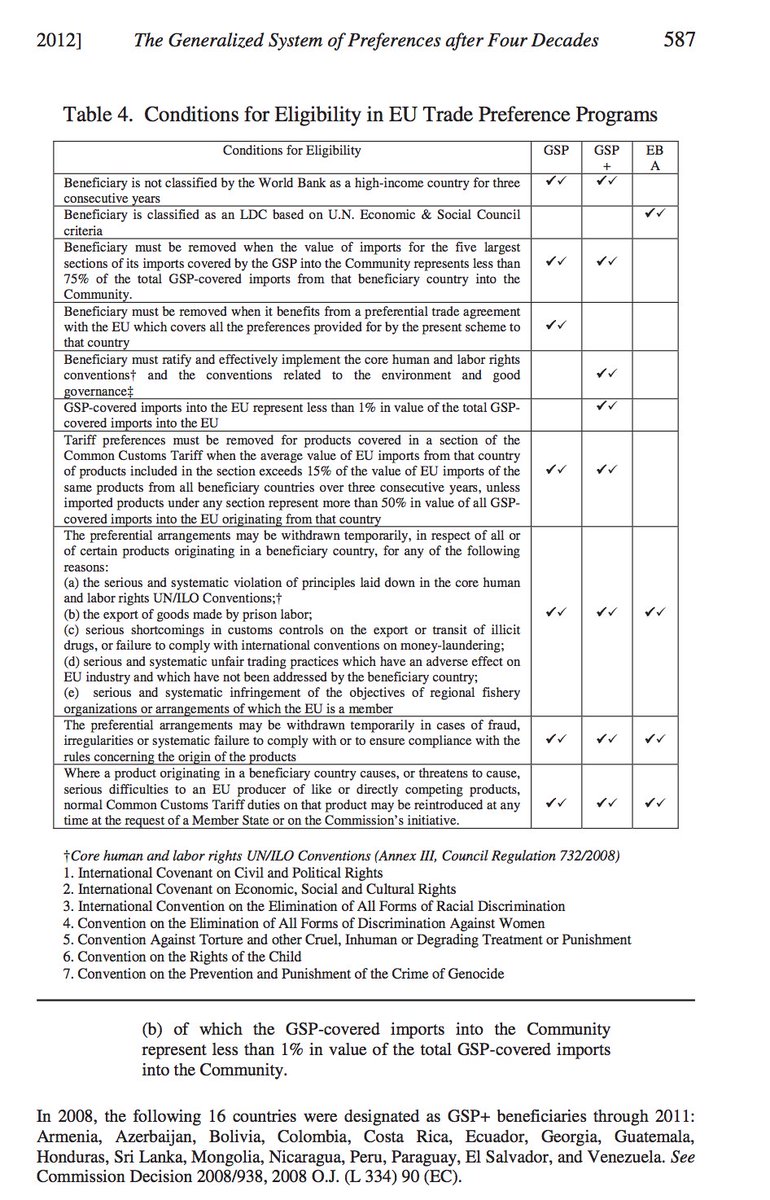
Each GSP scheme differs in the scope of tariff relief, but the EU's is the most comprehensive.
Roasted coffee tariff for Ghana which has an EPA and is GSP.
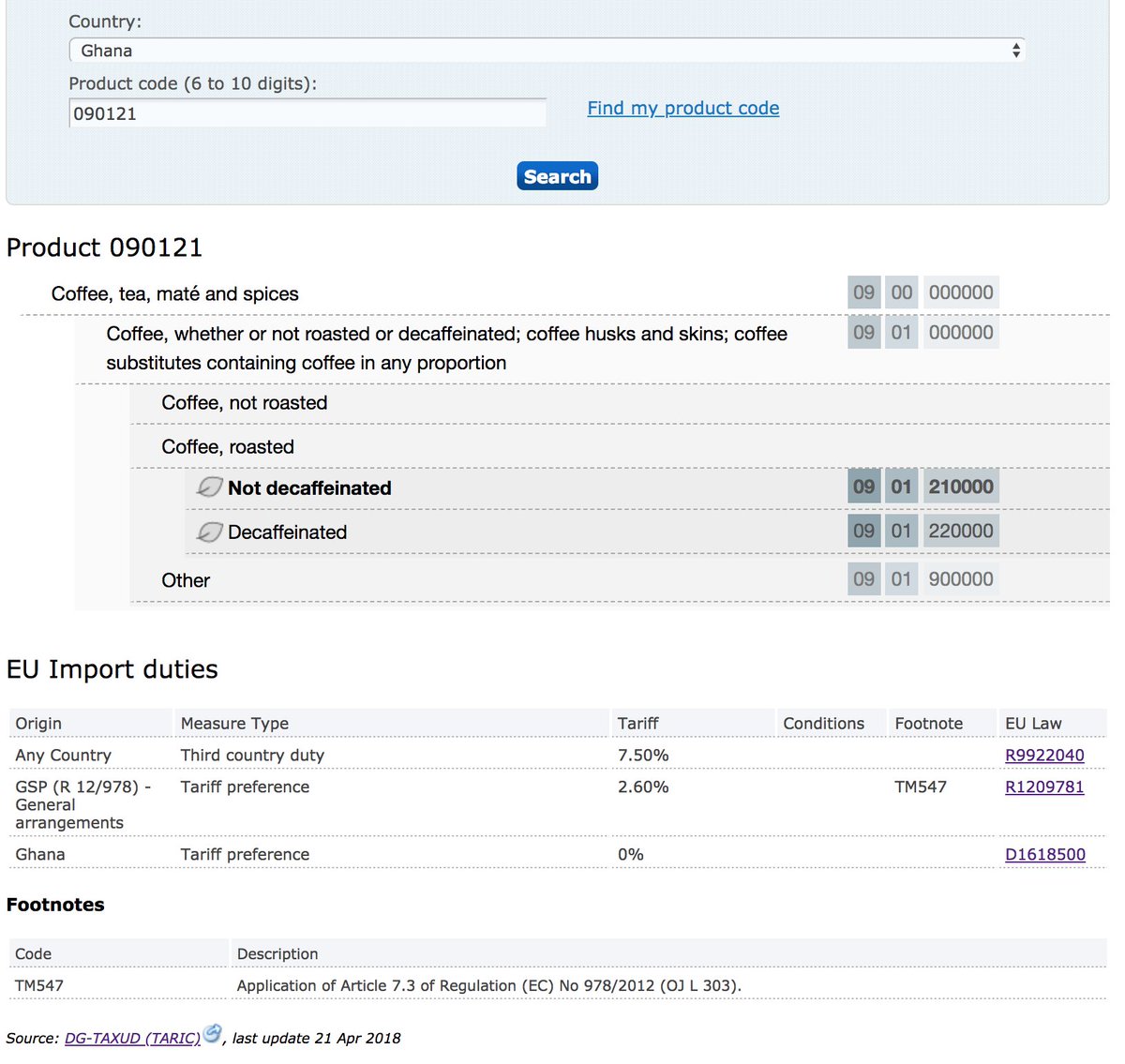
Without the EPA agreement it would classify as a GSP and be on a 2.6% tariff and if it dropped out of GSP income criteria, and had no EPA, it would be on the full tariff of 7.5%.

It thus included China, Brazil, India and Saudi Arabia among others.
digitalcommons.law.msu.edu/cgi/viewconten…
unctad.org/en/Publication…

In additions lower income nations have received tariff relief under GSP.
In contrast he GSP scheme was sanctioned under WTO rules, (initially via a waiver) and by 1979 by a new "enabling clause" in the GATT Treaty.
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enabling_…
ecampus.wto.org/admin/files/Co…

en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cotonou_A…

europarl.europa.eu/meetdocs/2009_… …

This continued until 2014 when the EU called time on the matter. tralac.org/news/article/5…

In the case of Kenya they delay until its too late and for two months in late 2014 drop back to standard GSP.
trade.ec.europa.eu/doclib/docs/20…

And as of now most have extensive tariff elimination through EBA and EPA.
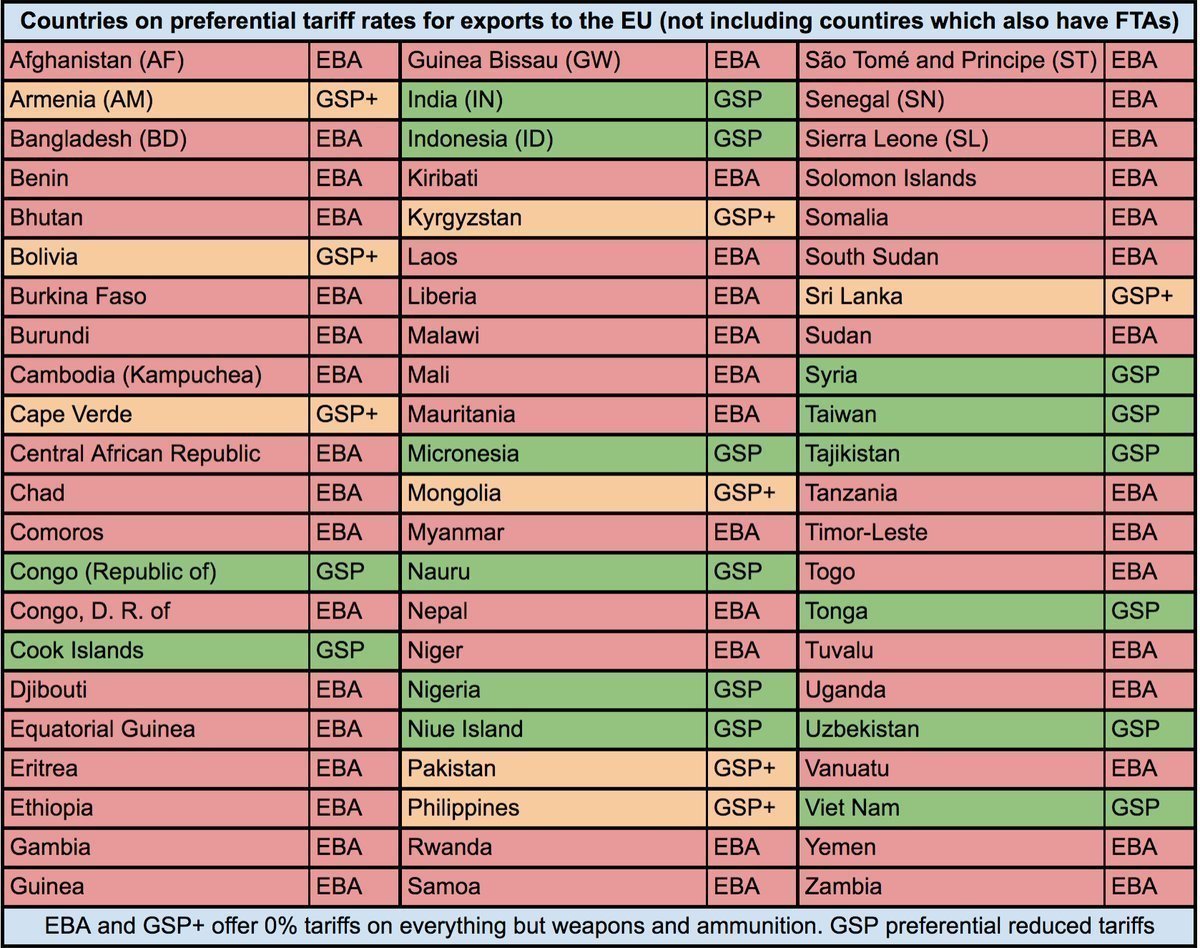
To verify these images, you can compare with this list of countries on this UK Government website. gov.uk/government/pub…