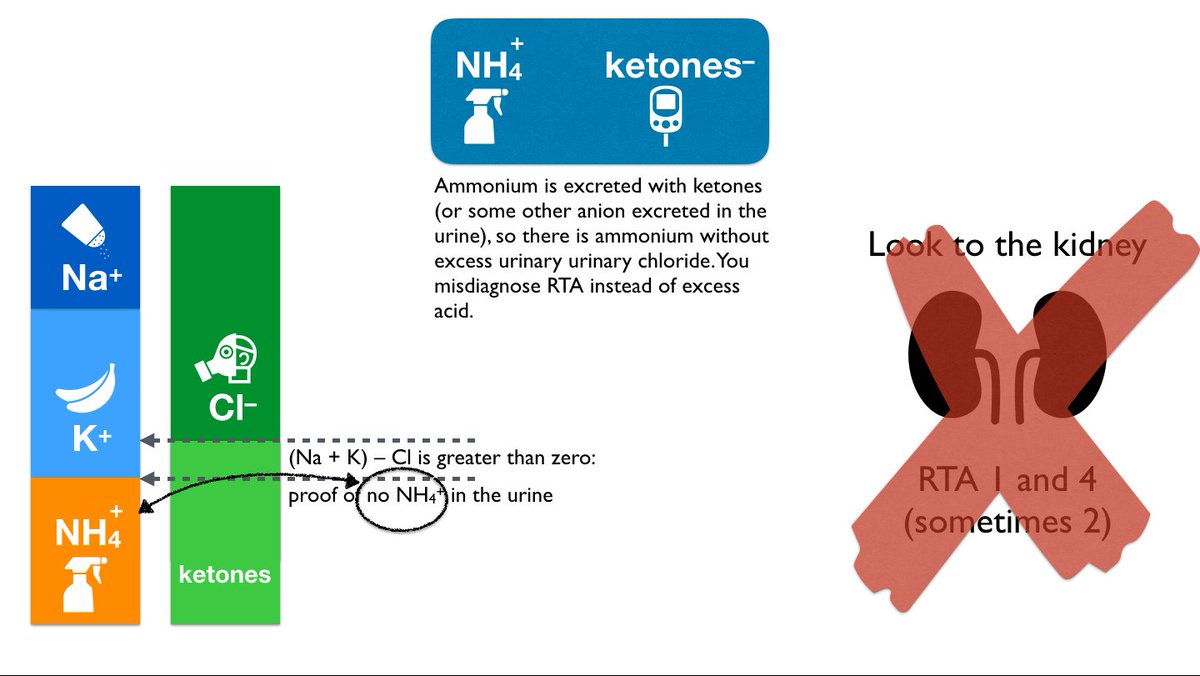
In metabolic acidosis the kidneys try to excrete excess acid as ammonium NH4+. This is essential because even at a pH of 4.4, the hydrogen concentration is
50 mmol of H+/ 0.04 mmol/L = 1,250 liters of urine
The easiest way to do this would be to directly measure urine NH4+ but...
1. Correct the serum glucose so it is below 200
2. Recheck U/A
3. If the patient still has glucosuria realize that the patient has proximal tubule dysfunction and that the metabolic acidosis is proximal RTA (type 2)