🤔, can B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) & high-sensitive troponin I (hsTnI) improve the diagnosis of #cardiomyopathy & prognostication of major adverse #cardiac events (MACE) in people with #musculardystrophy?
academic.oup.com/ehjqcco/ehjqcc…
academic.oup.com/ehjqcco/ehjqcc…
Heart disease is recognized as the leading cause of morbidity & mortality in patients with muscular dystrophy
This study prospectively followed 117 people (median age, 42 (interquartile range [IQR], 26-50) years; 49 [41.9%] women) with limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, type 1 myotonic dystrophy, or facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy.
BNP & hsTnI were markers of cardiomyopathy (area under the curve [AUC], 0.64; P=0.017; & AUC, 0.69; P=0.001, respectively).
Participant risk stratification for MACE was based on cutoff values of BNP & hsTnI defined a priori as 30.5000 pg/mL & 7.6050 ng/L, respectively.
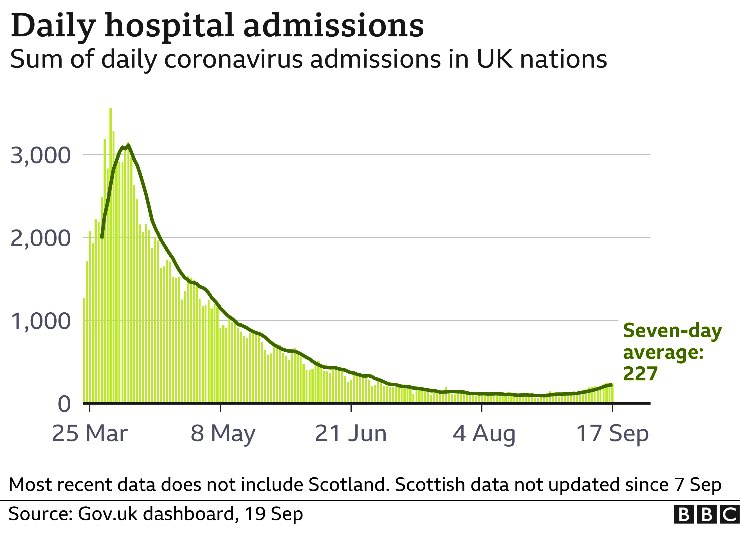
Over a median follow-up period of 2.09 (IQR, 1.17-2.81) years there were 36 confirmed MACE.
Participants with BNP & hsTnI levels above the respective cutoff values had a 3.70-fold (P=0.001) and 3.24-fold (P=0.002) greater risk of MACE, respectively, compared with patients with biomarker levels below.
Participants with biomarker levels above both cutoff values had a 4.08-fold (P=0.001) greater risk of MACE. Notably, inflammatory biomarkers did not show clinical utility for heart disease in this group.
The authors conclude that their study demonstrates the diagnostic & prognostic value of BNP & hsTnI as part of a comprehensive cardiac assessment to augment the management & treatment of heart disease in people with #musculardystrophy.
Evaluating the Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Biomarkers for Heart Disease and Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Patients With Muscular Dystrophy #EHJQCCO @ESC_Journals academic.oup.com/ehjqcco/ehjqcc…
@MDAorg @MD_Canada @MDUK_News @MD_Trailblazers @DuchenneUK @MDA_Advocacy @ParentProjectMD @Cardiomyopathy @Cardio1425
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh