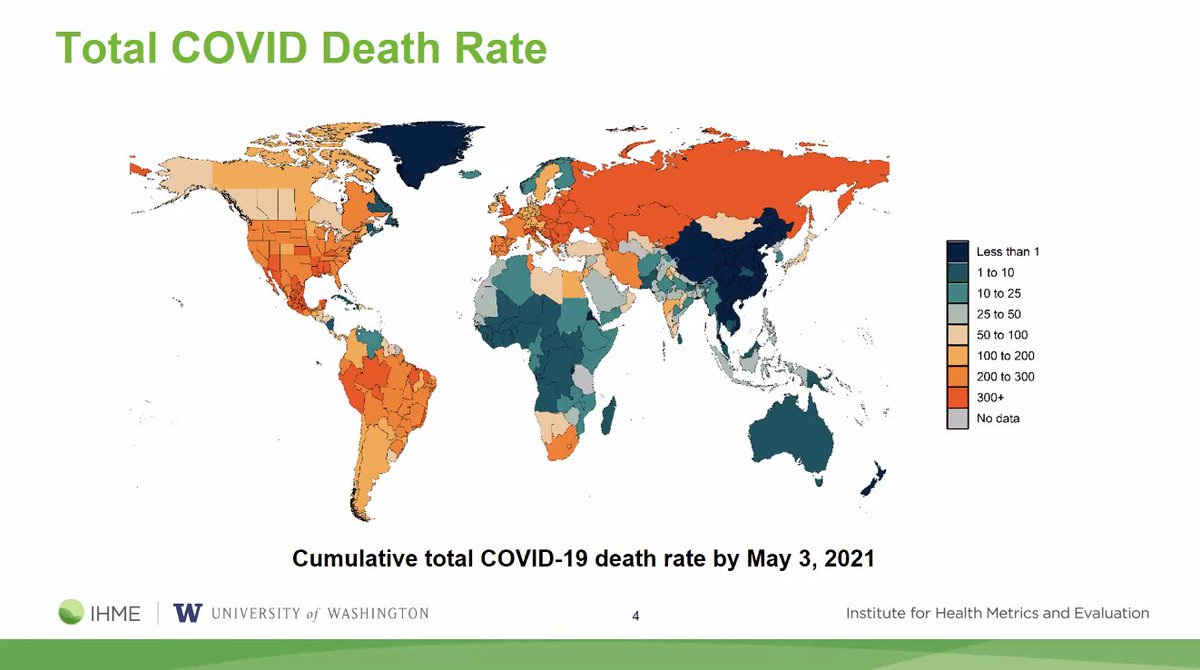
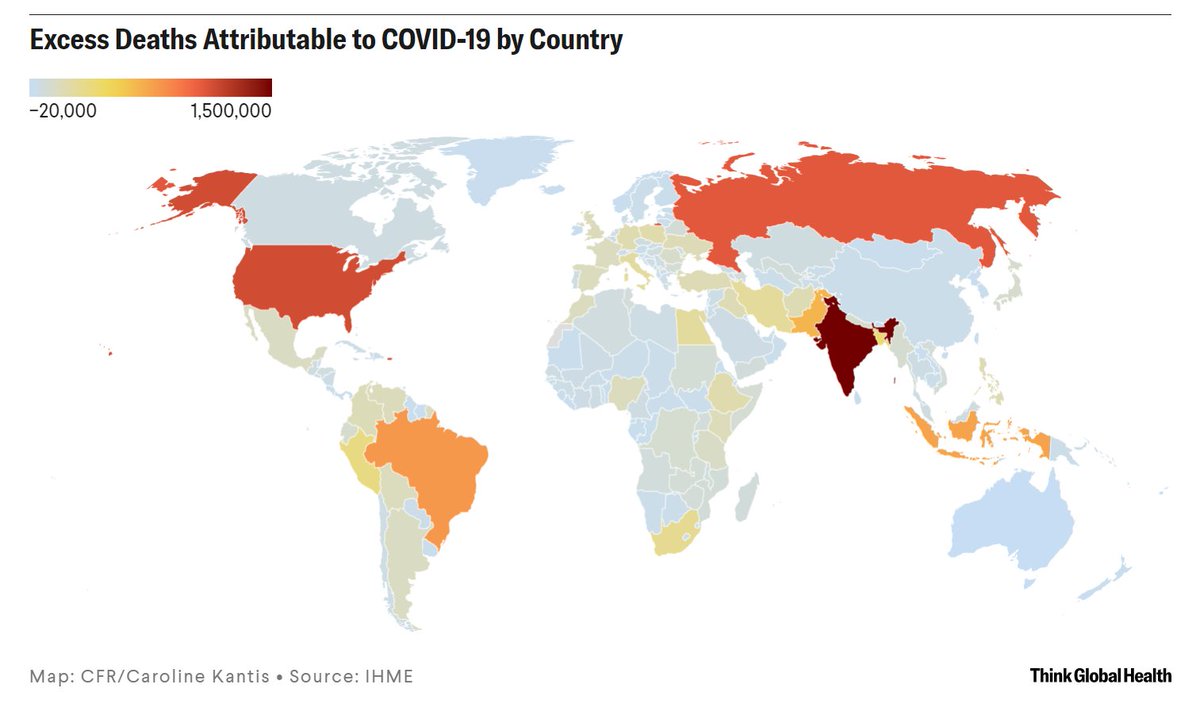
This morning, we're releasing a major change in our COVID-19 model (➡️covid19.healthdata.org). We're now incorporating excess mortality to approximate the total COVID-19 death rate worldwide.
Our understanding of the magnitude of COVID-19 to date has been much worse than what we have been thinking. 🗓️ We are also extending our COVID-19 projections out to September 1, 2021 (they previously went out to August 1, 2021).
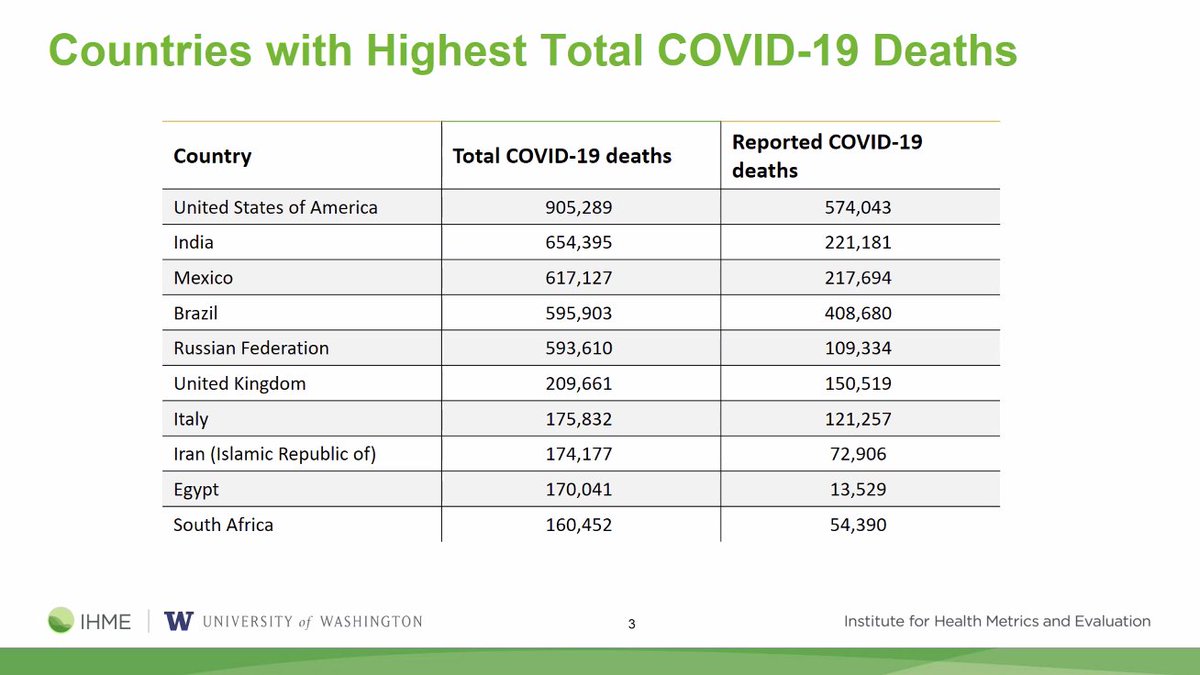
With this total COVID-19 mortality adjustment, these are the countries that we estimate currently have the highest total COVID-19 deaths .vs. reported COVID-19 deaths: 
What kind of statistical methods are we using to calculate total COVID-19 mortality? Dr. Murray explains:
Reported COVID-19 mortality is strongly related to how much testing a country has done. So total COVID-19 mortality includes predicted ratios, and we've used these kinds of statistical methods in our annual #GBDstudy.
Key takeaways on our new modeling approach outlined below. 📺 To watch the full video of Dr. Murray discussing total COVID-19 mortality, visit: bit.ly/IHME-Episodes 

Our press release on this major update to our modeling methods ⬇️ healthdata.org/news-release/c…
Detailed description of our new excess mortality methods ⬇️ healthdata.org/special-analys…
COVID-19 is a larger cause of a death in the United States than the 1918 influenza pandemic, says IHME Director Dr. Christopher Murray. The total population size of the US was much smaller back then, so it's not the same rate. ➡️covid19.healthdata.org
In addition to incorporating total COVID-19 mortality, we've also extended our projections out to September 1 (they previously went out to August 1). Dr. Murray shares key model insights 📈🌍🌏🌎⤵️
COVID-19 model📊covid19.healthdata.org
Full video 📺 bit.ly/IHME-Episodes
COVID-19 model📊covid19.healthdata.org
Full video 📺 bit.ly/IHME-Episodes
COVID-19 is the #1 cause of death in the world this week. We are observing about 30,000 deaths per day and estimate that 21% of people globally have been infected as of May 3. healthdata.org/sites/default/… 

We are expecting 9.4 million cumulative deaths from COVID-19 by September 1, 2021 at the global level, according to our model. That’s an extra nearly 2.5 million deaths from now until September 1.
COVID-19 model 📊 covid19.healthdata.org
Full video 📺 bit.ly/IHME-Episodes
COVID-19 model 📊 covid19.healthdata.org
Full video 📺 bit.ly/IHME-Episodes
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh