Pulmonary #embolism (lung blood clot) was >10 times more common after #SARSCoV2 infection (COVID19; ~15x over background rate), vs after getting #Pfizer's or #AstraZeneca's vaccine (~1.2x> background)
Similar greater risks with COVID-19 for #DVT & #VTE
🧵
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…
Similar greater risks with COVID-19 for #DVT & #VTE
🧵
medrxiv.org/content/10.110…

2) First of all – as the authors note – in those #vaccinated against COVID-19, "thrombosis, thrombocytopenia, and thrombosis with thrombocytopenia were very rare events."
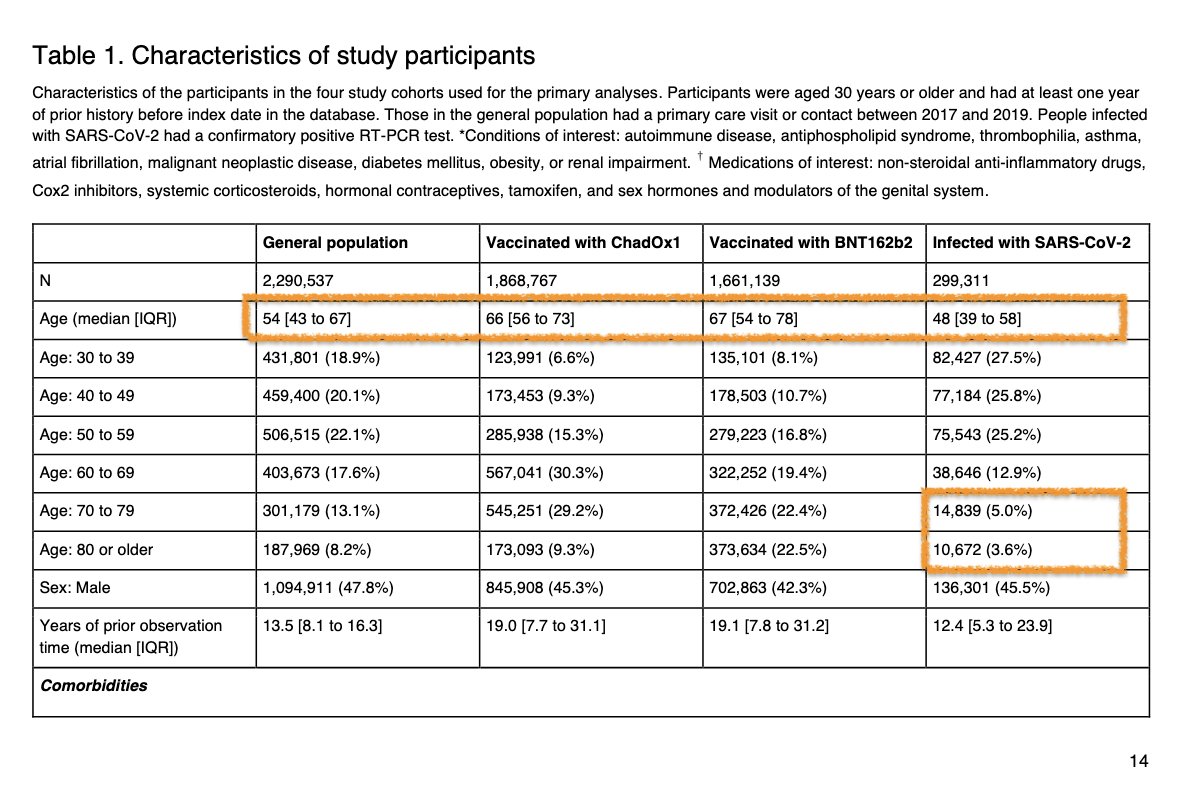
3) Data from 1.9 Million (M) recipients of AstraZeneca, ~1.7 M of Pfizer, and ~300k COVID-19 cases (few old) – compared with ~2.3 M in the general population.
These cohorts were used to calculate the observed incidence vs. background (SIR) or observed vs. expected # of cases.
These cohorts were used to calculate the observed incidence vs. background (SIR) or observed vs. expected # of cases.

4) The risk of thrombocytopenia was slightly elevated with the AZ vaccine (SIR 1.25), but not Pfizer's vaccine – immune thrombocytopenia as common in COVID-19.
The risk of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) was not higher following vaccination, but was higher in COVID-19 (SIR 2.56)
The risk of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) was not higher following vaccination, but was higher in COVID-19 (SIR 2.56)

5) The risk of Venous thromboembolism (VTE) was not elevated in vaccinated individuals.
The risk of #VTE was instead markedly (~8-fold) higher in #COVID19 cases
Note that this is all from a #preprint (not peer-reviewed)
The risk of #VTE was instead markedly (~8-fold) higher in #COVID19 cases
Note that this is all from a #preprint (not peer-reviewed)

6) Given a data period early in the UK's vaccination campaign, the data was skewed toward older people – possible underestimate of AstraZeneca's rare thrombocytopenia cases.
However, #Delta's greater severity may further favor AZ (shifted risk-benefit): amp.ft.com/content/6e6d64…
However, #Delta's greater severity may further favor AZ (shifted risk-benefit): amp.ft.com/content/6e6d64…
7) Herein, vaccine recipients (i.e. those prioritized early) were older, had more co-morbidities & greater medication use – this may have increased the risk estimates for the vaccines.
Note also that the SARS-CoV-2 / COVID-19 group herein is quite young, also vs. general group
Note also that the SARS-CoV-2 / COVID-19 group herein is quite young, also vs. general group
8) Similar data for cerebral (CVT) & portal (PVT) vein thrombosis following COVID-19 (vs. influenza and COVID-19 mRNA #vaccination) have been reported earlier (heading 2 below, based on this preprint by Taquet et al osf.io/a9jdq/):
drcedernaes.com/2021/07/vaccin…
drcedernaes.com/2021/07/vaccin…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh










