Thyroid as a #target of adjuvant #autoimmunity /#infammatory syndrome due to mRNA‐based SC2 vaccination.
#Vaccines contain #adjuvants which are not exempt from adverse efects and can #trigger the autoimmune/infammatory syndrome induced by adjuvants (#ASIA).
#Vaccines contain #adjuvants which are not exempt from adverse efects and can #trigger the autoimmune/infammatory syndrome induced by adjuvants (#ASIA).
Multiple endocrine organs have receptors for ACE2.
mRNA of ACE2, the SARS-CoV2 receptor, is expressed in the thyroid cells.
ACE2 receptor is abundantly expressed by the thyroid. Elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines could increase the expression ofACE2 on the thyroidgland.
mRNA of ACE2, the SARS-CoV2 receptor, is expressed in the thyroid cells.
ACE2 receptor is abundantly expressed by the thyroid. Elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines could increase the expression ofACE2 on the thyroidgland.
ASIA covers a wide range of diseases like macrophagic myofasciitis syndrome, post-vaccination phenomena, #GulfWar syndrome #GWS and Silicosis.
After mass vaccination with SARS-CoV2 vaccines, some cases of Graves’ disease have been reported. #Grave ‘s disease after #Pfizer.
After mass vaccination with SARS-CoV2 vaccines, some cases of Graves’ disease have been reported. #Grave ‘s disease after #Pfizer.
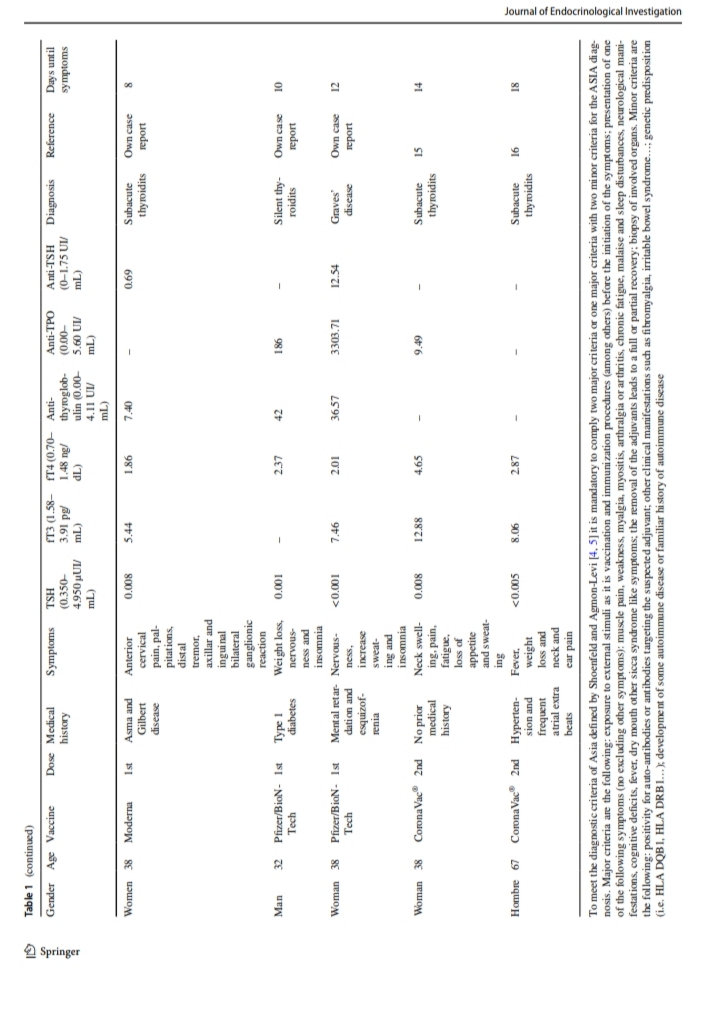
Case 1: A 38-year-old female, intense anterior cervical pain and mild distal tremor and palpitations. She had received a 1st dose of Moderna vaccine 8 days before the onset of the symptoms. On physical examination, the right thyroid lobe was increased in size
and painful on superficial palpation.
Case 2: A 32-year-old male with type 1 diabetes was evaluated because of palpitations and insomnia. He had been vaccinated with a 1st dose of Pfzer vaccine 10 days prior to the onset of these symptoms.
Case 2: A 32-year-old male with type 1 diabetes was evaluated because of palpitations and insomnia. He had been vaccinated with a 1st dose of Pfzer vaccine 10 days prior to the onset of these symptoms.
Case 3: A 38-year-old woman without prior history of thyroid disease but with history of schizophrenia was evaluated because of behavioural disturbance with nervousness, insomnia and sweating. She had received a 1st dose of the Pfzer vaccine 12 days before
Silent thyroiditis is considered a variant of chronic autoimmune thyroiditis, or #Hashimoto ’s Disease, forming part of the spectrum of autoimmune pathology with thyroid involvement.
“To our knowledge, only a case with silent thyroiditis has been described in the scientific
“To our knowledge, only a case with silent thyroiditis has been described in the scientific
literature in the context of SARS-CoV2 infection.”
Subacute or De Quervain’s has been associated with various viral infections such as adenovirus, Coxsackievirus and, among others, SARS-CoV2. Subacute thyroiditis is not an autoimmune disorder per se, but one possible explanation
Subacute or De Quervain’s has been associated with various viral infections such as adenovirus, Coxsackievirus and, among others, SARS-CoV2. Subacute thyroiditis is not an autoimmune disorder per se, but one possible explanation
could be that viral infection or virus-induced tissue damage might cause activation of the antigen-HLA B35 complex, leading to immune-mediated destruction of the thyroid follicular cell.
LNP is an adjuvant too. The RNA molecules would already exert immunostimulatory effects
LNP is an adjuvant too. The RNA molecules would already exert immunostimulatory effects
and would also stimulate the pathogen recognition patterns of innate immunity. IMHO: Double adjuvants?
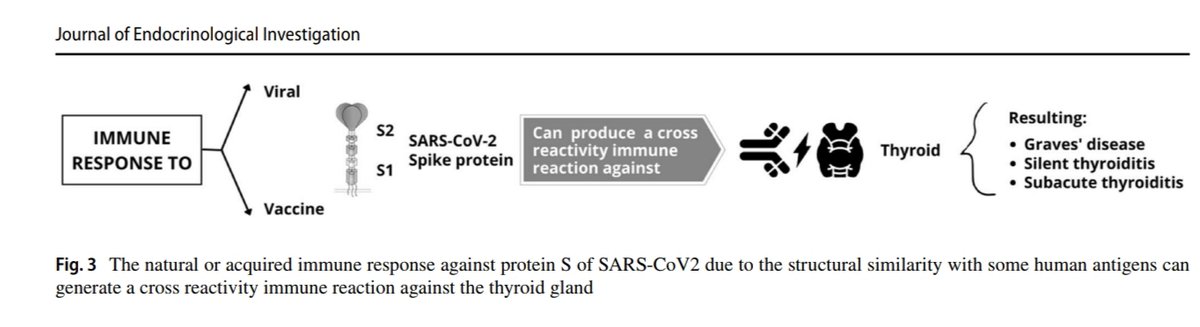
It is possible that proteins generated due to the vaccine cross-react with thyroid target proteins due to the molecular mimicry triggering autoimmunity together with an
It is possible that proteins generated due to the vaccine cross-react with thyroid target proteins due to the molecular mimicry triggering autoimmunity together with an
inflammatory reaction in genetically predisposed individuals. These phenomena could be enhanced by adjuvants in the context of post-vaccination ASIA.
Conclusion: The autoimmune/infammatory syndrome induced by adjuvants involving the thyroid could be an adverse effect of SARS-CoV2 vaccination and could be underdiagnosed.
end of thread
link.springer.com/article/10.100…
end of thread
link.springer.com/article/10.100…
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh