
#Stagflation
Definition of #stagflation
❎Stagflation is a period of rising inflation but falling output and rising unemployment.
❎Stagflation is often a period of falling real incomes as wages struggle to keep up with rising prices.
1
Definition of #stagflation
❎Stagflation is a period of rising inflation but falling output and rising unemployment.
❎Stagflation is often a period of falling real incomes as wages struggle to keep up with rising prices.
1
❎Stagflation is often caused by a rise in the price of commodities, such as oil. it occurred in the 1970s following the tripling in the price of oil.
❎A degree of stagflation occurred in 2008, following the rise in the price of oil and the start of the global recession.
2
❎A degree of stagflation occurred in 2008, following the rise in the price of oil and the start of the global recession.
2
❎Stagflation is difficult for policy makers. For example, the Central Bank can increase interest rates to reduce inflation or cut interest rates to reduce unemployment. But, they can’t tackle both inflation and unemployment at the same time.
Diagram stagflation
Diagram stagflation

Higher oil prices increase costs of firms causing SRAS to shift to the left.
AD/AS diagram showing stagflation (higher price level P1 to P2 and lower real GDP Y1 to Y2)
⌛️ Causes of Stagflation :
4
AD/AS diagram showing stagflation (higher price level P1 to P2 and lower real GDP Y1 to Y2)
⌛️ Causes of Stagflation :
4
🆘Oil price rise
Stagflation is often caused by supply side shock. Example, rising commodity prices, such as oil prices, will cause rise in business costs (transport more expensive) & short run aggregate supply will shift to the left. This causes higher inflation & lower GDP
5
Stagflation is often caused by supply side shock. Example, rising commodity prices, such as oil prices, will cause rise in business costs (transport more expensive) & short run aggregate supply will shift to the left. This causes higher inflation & lower GDP
5
🆘Powerful trade unions.
If trade unions have strong bargaining power – they may be able to bargain for higher wages, even in periods of lower economic growth. Higher wages are a significant cause of inflation.
6
If trade unions have strong bargaining power – they may be able to bargain for higher wages, even in periods of lower economic growth. Higher wages are a significant cause of inflation.
6
🆘Falling productivity.
If an economy experiences falling productivity – workers becoming more inefficient; costs will rise and output fall.
7
If an economy experiences falling productivity – workers becoming more inefficient; costs will rise and output fall.
7
🆘Rise in structural unemployment.
If there is a decline in traditional industries, we may get more structural unemployment and lower output. Thus we can get higher unemployment – even if inflation is also increasing.
8
If there is a decline in traditional industries, we may get more structural unemployment and lower output. Thus we can get higher unemployment – even if inflation is also increasing.
8
🆘Supply shocks.
If there is disruption to supply chains, there prices will start rising. The supply shock will also cause decrease in unemployment. For example, in 2021, UK supply shocks caused moderate degree of stagflation.
9
If there is disruption to supply chains, there prices will start rising. The supply shock will also cause decrease in unemployment. For example, in 2021, UK supply shocks caused moderate degree of stagflation.
9
❎Moderate stagflation
if there is a rise in inflation & fall in the growth rate
ie. the economy is growing at slow rate. This is less damaging than higher inflation & negative growth. But, it still represents deterioration in the trade-off between unemployment and inflation
10
if there is a rise in inflation & fall in the growth rate
ie. the economy is growing at slow rate. This is less damaging than higher inflation & negative growth. But, it still represents deterioration in the trade-off between unemployment and inflation
10
Stagflation and Phillips Curve
The traditional Phillips curve suggests there is a trade-off between inflation and unemployment. A period of stagflation will shift the Phillips curve to the right, giving a worse trade-off.
The traditional Phillips curve suggests there is a trade-off between inflation and unemployment. A period of stagflation will shift the Phillips curve to the right, giving a worse trade-off.

Phillips curve shifting to the right, indicating stagflation (higher inflation and higher unemployment.
12
12
Stagflation in the 1970s
In 1974, we have an inflation spike of 25%, at the same time, we see negative GDP growth. This was caused by the oil price boom and also end of the Barber Boom.
In 1974, we have an inflation spike of 25%, at the same time, we see negative GDP growth. This was caused by the oil price boom and also end of the Barber Boom.

This shows how in the 1970s, the US economy faced a worse trade off- there was higher inflation and higher unemployment. The Phillips Curve was shifting to the right. 

Stagflation in 2010/11
In 2011, the UK experienced a rise in #inflation to 5%, at the same time, the economy remained in depression with negative growth / very low growth.
In 2011, the UK experienced a rise in #inflation to 5%, at the same time, the economy remained in depression with negative growth / very low growth.
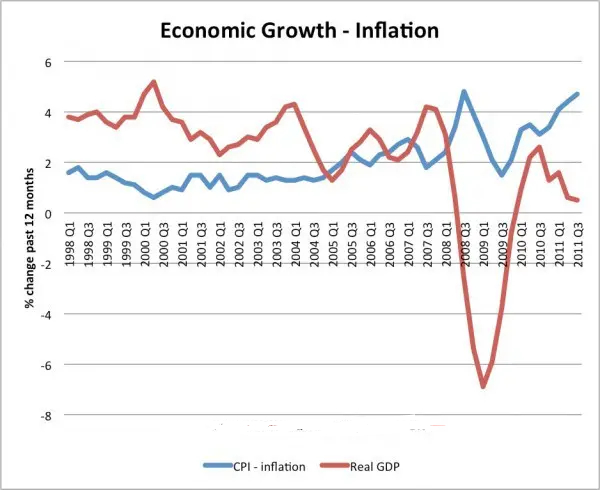
This period of stagflation was caused by:
⛔️Higher oil prices
⛔️Higher food prices
⛔️Impact of devaluation on the value of the Currency increasing import prices.
⛔️Impact of higher taxes, which increased inflation but reduced living standards.
16
⛔️Higher oil prices
⛔️Higher food prices
⛔️Impact of devaluation on the value of the Currency increasing import prices.
⛔️Impact of higher taxes, which increased inflation but reduced living standards.
16
Solutions to stagflation
There are no easy solutions to stagflation.
✅Monetary policy can generally try to reduce inflation (higher interest rates) or increase economic growth (cut interest rates). Monetary policy cannot solve both inflation and recession at the same time.
17
There are no easy solutions to stagflation.
✅Monetary policy can generally try to reduce inflation (higher interest rates) or increase economic growth (cut interest rates). Monetary policy cannot solve both inflation and recession at the same time.
17
✅One solution to make the economy less vulnerable to stagflation is to reduce the economies dependency on oil. Rising oil prices are the major cause of stagflation
✅The only solution is supplyside policies to increase productivity, it enables higher growt without inflation
18
✅The only solution is supplyside policies to increase productivity, it enables higher growt without inflation
18
✅In 2010/11, the Central Bank decided to keep interest rates low (at 0.5%) because they felt low growth was a bigger problem than some temporary cost-push inflation.
19
19
♀️ Misery index
The misery index is a measure of unemployment + inflation
Stagflation leads to rise in both unemployment & inflation so high misery index indicates period of stagflation.This shows in 2012, the UK experiencd misery index of 14% due to high unemployment & inflation
The misery index is a measure of unemployment + inflation
Stagflation leads to rise in both unemployment & inflation so high misery index indicates period of stagflation.This shows in 2012, the UK experiencd misery index of 14% due to high unemployment & inflation

Stagflation of the 1970s
In the 1970s, the US experienced a sharp rise in inflation due to the pressure of rising oil prices
The inflation also led to rising unemployment as the post-war economic boom stalled.

In the 1970s, the US experienced a sharp rise in inflation due to the pressure of rising oil prices
The inflation also led to rising unemployment as the post-war economic boom stalled.


2022 A return to Stagflation
we are seeing rise in global inflation due to supply side shocks, rising oil prices and supply chains adjusting to Covid shocks. However, with high inflation, we are also seeing rapid growth (eg. UK grew 7.1% in 2021) as it recovered from Covid slump
we are seeing rise in global inflation due to supply side shocks, rising oil prices and supply chains adjusting to Covid shocks. However, with high inflation, we are also seeing rapid growth (eg. UK grew 7.1% in 2021) as it recovered from Covid slump
However, the economic growth figures are slightly misleading. Most consumers don’t feel there is growth of 7.1% because real wages have been squeezed by rising prices. Therefore, it may feel like stagflation to many consumers even it economic stats don’t show classic stagflation
Final words
it was first occurred during the 1970s when developed economies faced rapid inflation and high unemployment
The prevailing economic theory at the time could not easily explain how it could occur
how long it will be this time only god knows
let’s hope for the best
it was first occurred during the 1970s when developed economies faced rapid inflation and high unemployment
The prevailing economic theory at the time could not easily explain how it could occur
how long it will be this time only god knows
let’s hope for the best
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh




