link.springer.com/article/10.100…
jamanetwork.com/journals/jamap…
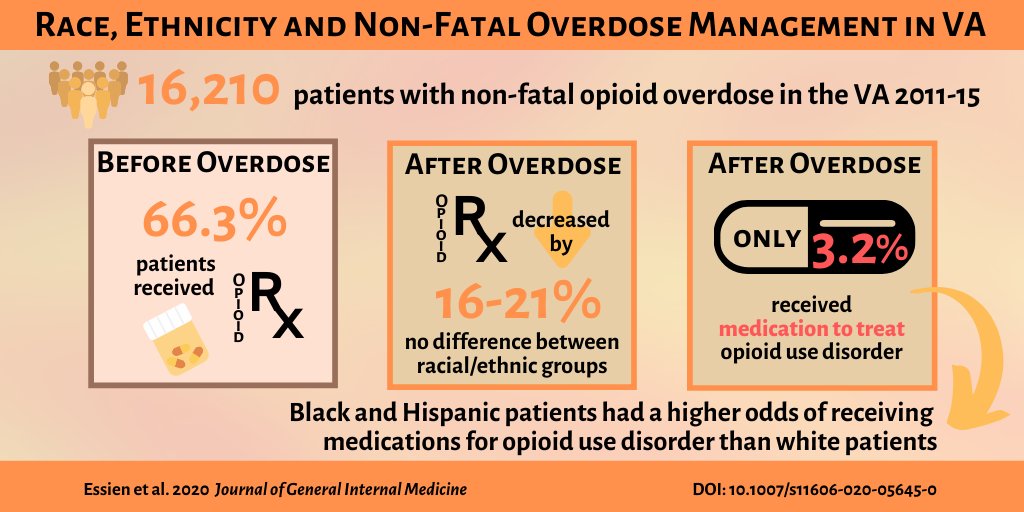
1) opioid prescribing before and after a non-fatal opioid overdose and,
2) receipt of MOUD (i.e., buprenorphine, methadone, and naltrexone) following opioid overdose. 3/n
1) frequency of receiving opioids was reduced by 18.3, 16.4, and 20.6 % in whites, blacks, and Hispanics (not statistically significant).
2) few received MOUDs (2.9% white, 4.6% black, and 5.5% Hispanic). Black and Hispanic patients had higher odds of receipt. 4/n
Special thanks to @walidgellad, whose leadership in this space is making a difference in how we care for Veterans with opioid use disorder. 6/6