Our new paper:
Pre-sleep Protein Ingestion Increases Mitochondrial Protein Synthesis Rates During Overnight Recovery from Endurance Exercise: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Open access link:
link.springer.com/article/10.100…
A thread 🧵👇
#protein #casein #whey
Pre-sleep Protein Ingestion Increases Mitochondrial Protein Synthesis Rates During Overnight Recovery from Endurance Exercise: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Open access link:
link.springer.com/article/10.100…
A thread 🧵👇
#protein #casein #whey

We have previously shown that pre-sleep protein ingestion improves overnight myofibrillar protein synthesis.
In addition, we have shown that long-term pre-sleep protein supplementation improves muscle mass and strength gains.
2/
In addition, we have shown that long-term pre-sleep protein supplementation improves muscle mass and strength gains.
2/

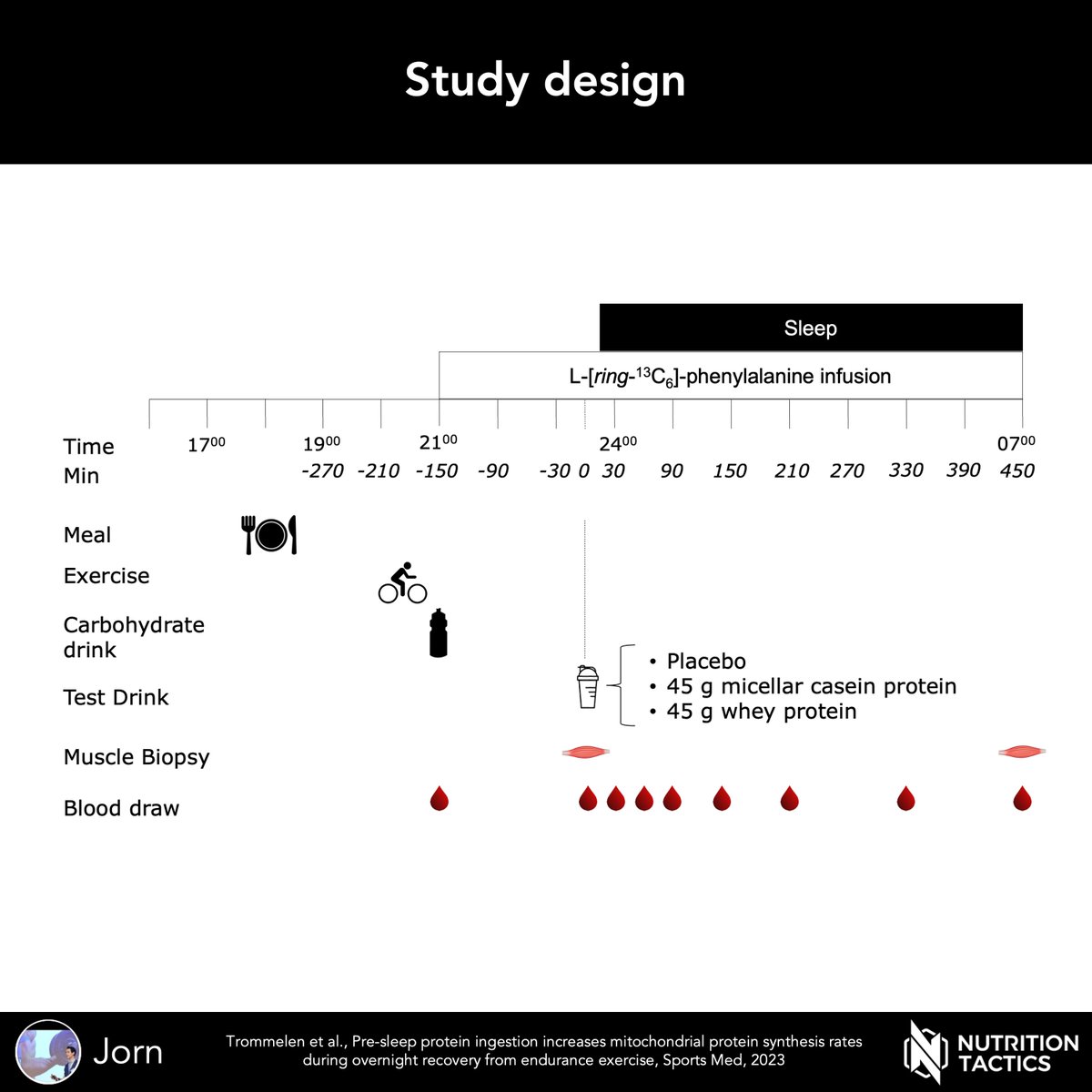
Our new study had several study novelties:
- endurance exercise was performed
- mitochondrial protein synthesis was assessed
- whey and casein protein were compared
3/
- endurance exercise was performed
- mitochondrial protein synthesis was assessed
- whey and casein protein were compared
3/
The ingestion of the slowly digesting casein protein resulted in AA response that was still elevated upon waking the next morning.
However, the rapidly digesting whey protein also increased AA availability during most of the night. Likely because of the large 45 g dose.
4/
However, the rapidly digesting whey protein also increased AA availability during most of the night. Likely because of the large 45 g dose.
4/

In line with our earlier work, protein ingestion stimulated overnight myofibrillar protein synthesis rates.
There was no significant difference between casein and whey.
5/
There was no significant difference between casein and whey.
5/

Protein ingestion stimulated overnight mitochondrial protein synthesis rates.
Again, there was no significant difference between casein and whey.
It's important to point out here….
6/
Again, there was no significant difference between casein and whey.
It's important to point out here….
6/

…that this is the first study to show that postexercise mitochondrial protein synthesis can be stimulated by protein ingestion (day or night)!
So how can we possibly explain this discrepancy?
In short: timing of the protein and the measurement period.
7/
So how can we possibly explain this discrepancy?
In short: timing of the protein and the measurement period.
7/
Conclusions:
- pre-sleep protein is also a good strategy for endurance athletes
- protein ingestion can stimulate mitochondrial protein synthesis rates
- no difference between whey and casein protein
8/
- pre-sleep protein is also a good strategy for endurance athletes
- protein ingestion can stimulate mitochondrial protein synthesis rates
- no difference between whey and casein protein
8/
I’ll happily answer any questions!
9/9
And please help share the thread/link to paper:
9/9
And please help share the thread/link to paper:
https://twitter.com/JornTrommelen/status/1630911941068701696?s=20
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh





















