1/18
But easily mixed up with Lagrange and Legendre. Why all the French "L" mathematicians in 1700s? @AdamRodman

So when you connect 2 balloons, the smaller balloon empties into the bigger one. WTF?!!
6/18
A. Larger fecal load in the sigmoid colon --> greater intraluminal pressure
B. Sigmoid colon have smaller diameter --> higher intraluminal pressure
C. More penetrating vasa recta --> more diverticula
13/18
Once bladder is distended beyond 400-500 cc, how effective will the contractile muscles be in generating bladder pressure to excrete urine? Not so much (P=2T/R).
Reason why catheterization is indicated in these situations.
- Dilated cardiomyopathy is associated with poor myocardial circulation?
- Esophageal varices are at increased risk of bleeding at greater diameters?
- Small arteriolar muscles are effective in controlling pressure?
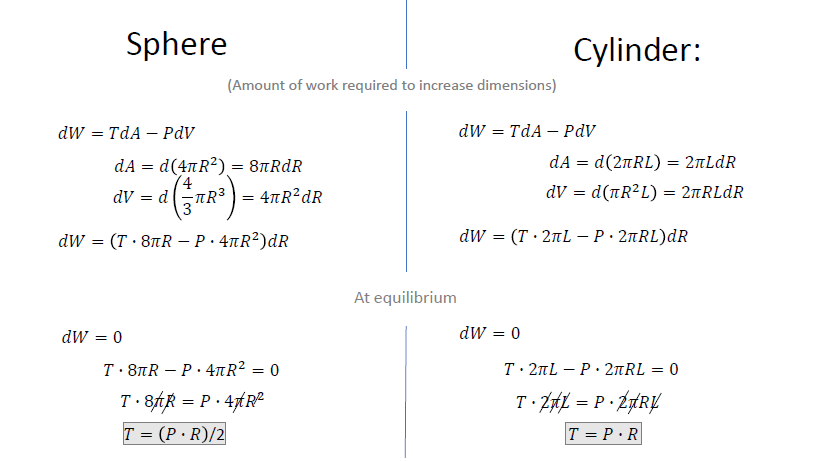
(1) System is at equilibrium,
(2) Wall is elastic,
(3) Pressure is constant at interval volume change, etc...
Which may not be all true in the complex body (e.g., wall can be viscoelastic, etc.)
17/18
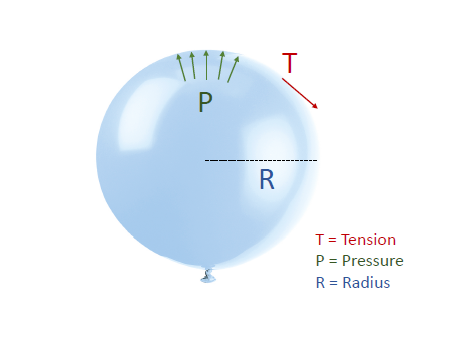
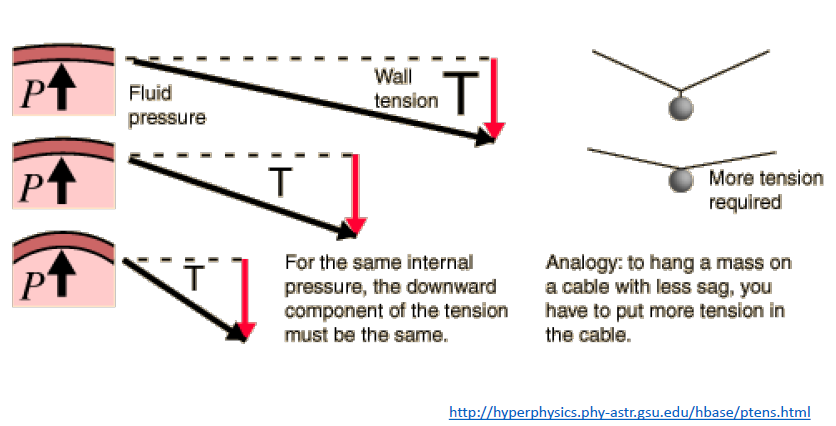
* Laplace describes relationship between wall tension, radius, and pressure
* For a given wall tension, smaller radius is associated with greater pressure
* This law has applications to multiple anatomical systems
* Be careful not to overgeneralize given assumptions