author: marieb (ninth edition)
- contain carbon.
-All organic compounds are covalently bonded molecules, and many are large.
-All other chemicals in the body
-These include water, salts, many acids and bases.
Example of Inorganic Compounds are:
• Water
Importance of water:
-high heat capacity
-high heat of vaporization
-polar solvent properties
-reactivity
-cushioning
A salt is an ionic compound containing cations other than H+ and anions other than the hydroxyl ion (OH-).
Acids and Bases
Acids- have a sour taste, can react with (dissolve) many metals, and "burn" a hole in your rug.
Bases- have a bitter taste, feel slippery
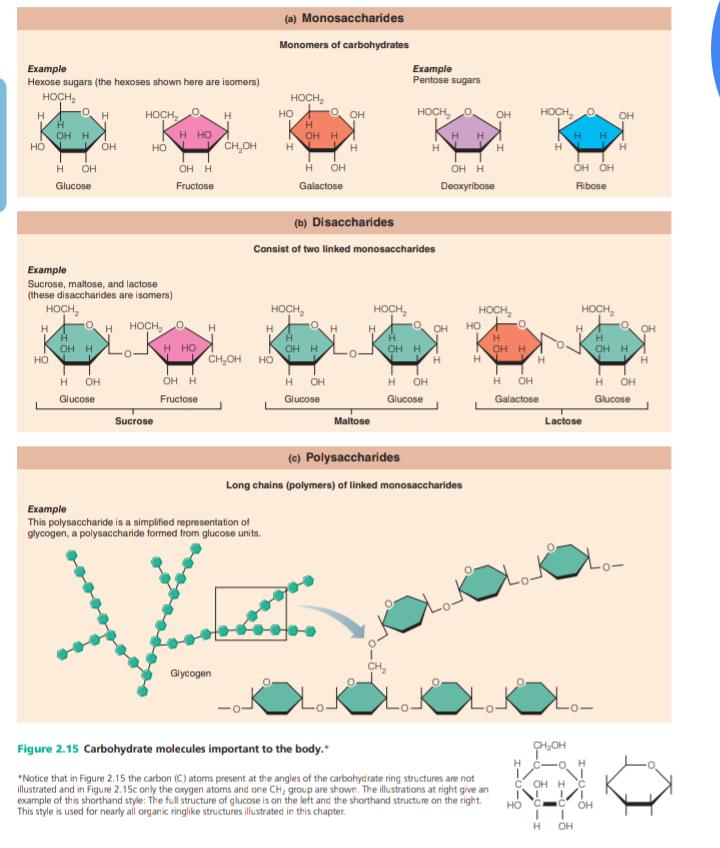
-A group of molecules that includes sugars and tarches, represent 1-2% of cell mass.
-It contanins carbon, hydrogen, oxygen.
-It can classified according to size and solubility as a monosaccharide (one sugar), disaccharide (two sugars) or polysaccharide (many sugar)
-simple sugars
-single-chain /single-ring structures containing from three to seven carbon atoms.
Disaccharide
-double sugar
-formed when two monosaccharides are joined by dehydration synthesis.
Polysaccharides
-polymers of simple sugars linked together.
- are insoluble in water but dissolve readily in other lipids and in organic solvents such as alcohol and ether.
-all lipids contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen but the proportion of oxygen in lipids is much lower.
-composes 10-30% of cell mass and is the basic structural material of the body.
-proteins which include enzymes (biological catalyst), hemoglobin of the blood etc.
-all proteins contain carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen, and many contain sulfur as well.
Amino acid structures
a. Generalized structure of all amino acids.
b. Glycine- simplest amino acids
c. Aspartic acid- has an acid group (---COOH) in the R group.
d. Lysine-( a basic amino acid) has an amine group. (--NH2) in the R group.
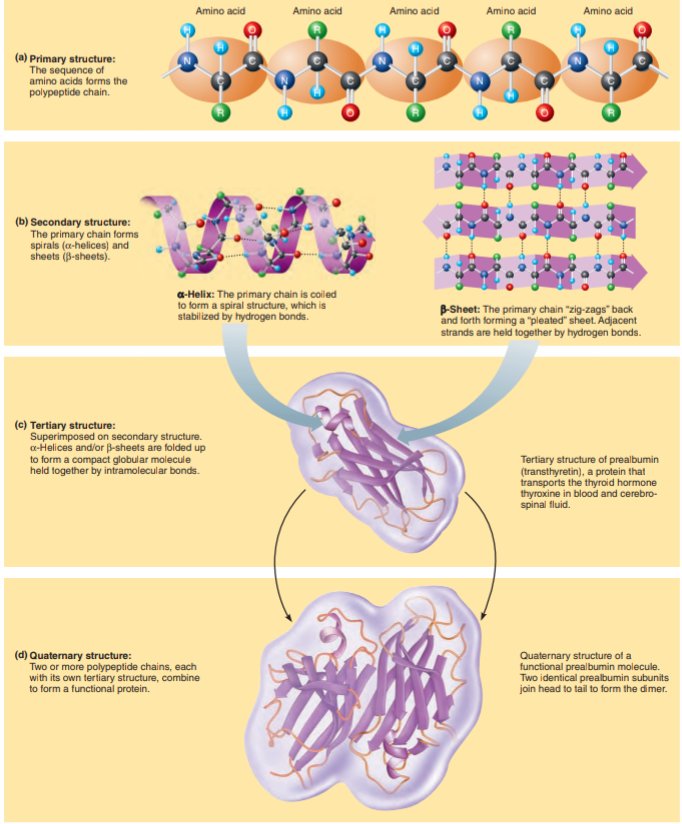
a. Primary structure- the sequence of amino acids forms the polypeptide chain.
b. Secondary syructure- The primary chain forms spirals and sheets.
.
Enzymes are globular proteins that act as a biological catalysts.
Three basic steps appear to be involved in enzyme action.
1. Substrate(s) bind to the enzyme's active site, temporarily forming an enzyme-substrate complex.
3. The enzyme releases the product(s) of the reaction.
Nucleic acids-composed of caebon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen and phosphorous, are the largest molecules in the body.
The nucleic acids include two major classes of molecules:
1. deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
2. ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Five major varieties of nitrogen-containing bases can contribute to nucleotide structure:
2. guanine
3. cytosine
4. thymine
5. uracil
DNA
Major cellular site: Nucleus
Major functions: Is the genetic material; directs protein synthesis; replicates itself before cell division.
Sugar: Deoxyribose
Bases: denine, guanine, cytosine, thymine.
Structure:Double strand coiled into a double helix
Major cellular site: Cytoplasm (cell area outside the nucleus)
Major functions: carries out the genetic instructions for protein synthesis
Sugar: Ribose
Bases: Adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil.
Structure: Single strand, straight or folded.
-ATP is the primary energy-transferring molecule in cells and it provides a form of energy that is immediately usable by all body cells.
-ATP can be compared to a tightly coiled spring ready to uncoil with tremendous energy when the catch is released