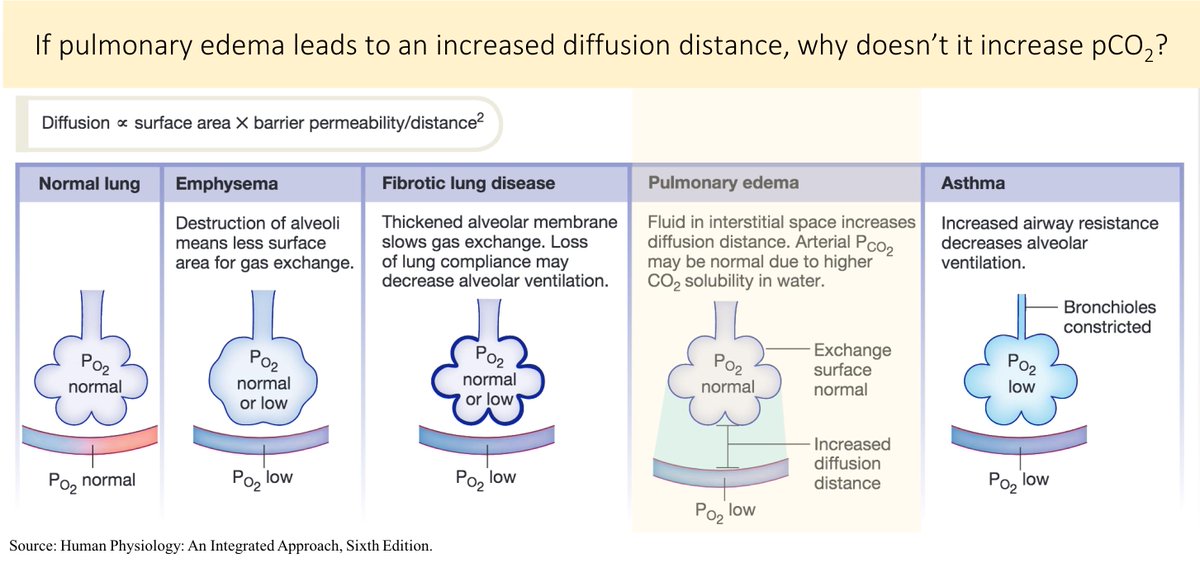
What explains this difference (i.e., why don't pneumonia or pulmonary edema lead to an increase in pCO₂ if they DO lead to a decrease in pO₂)
[Hg = hemoglobin]
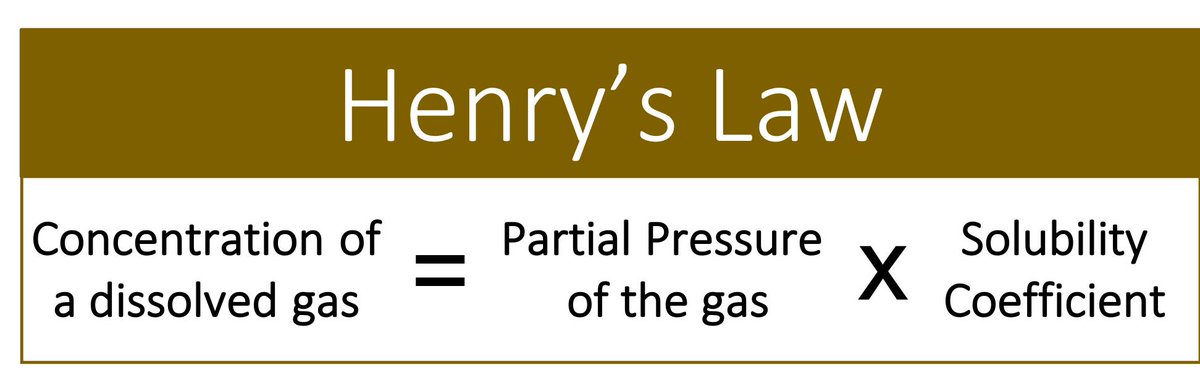
To understand the answer (CO₂ is more soluble than O₂), we must first revisit Henry’s Law (see picture and video).
The key point: the higher the solubility coefficient (aka Henry's Law constant), the more soluble the gas.
khanacademy.org/science/health…
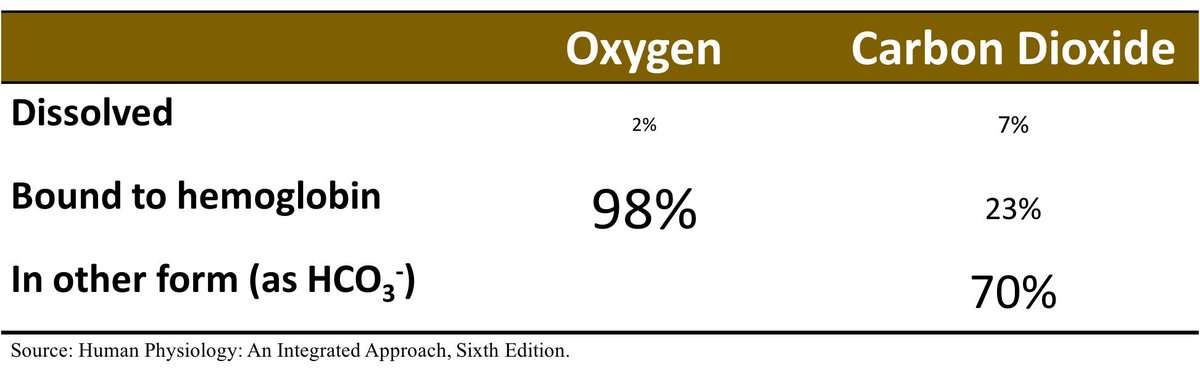
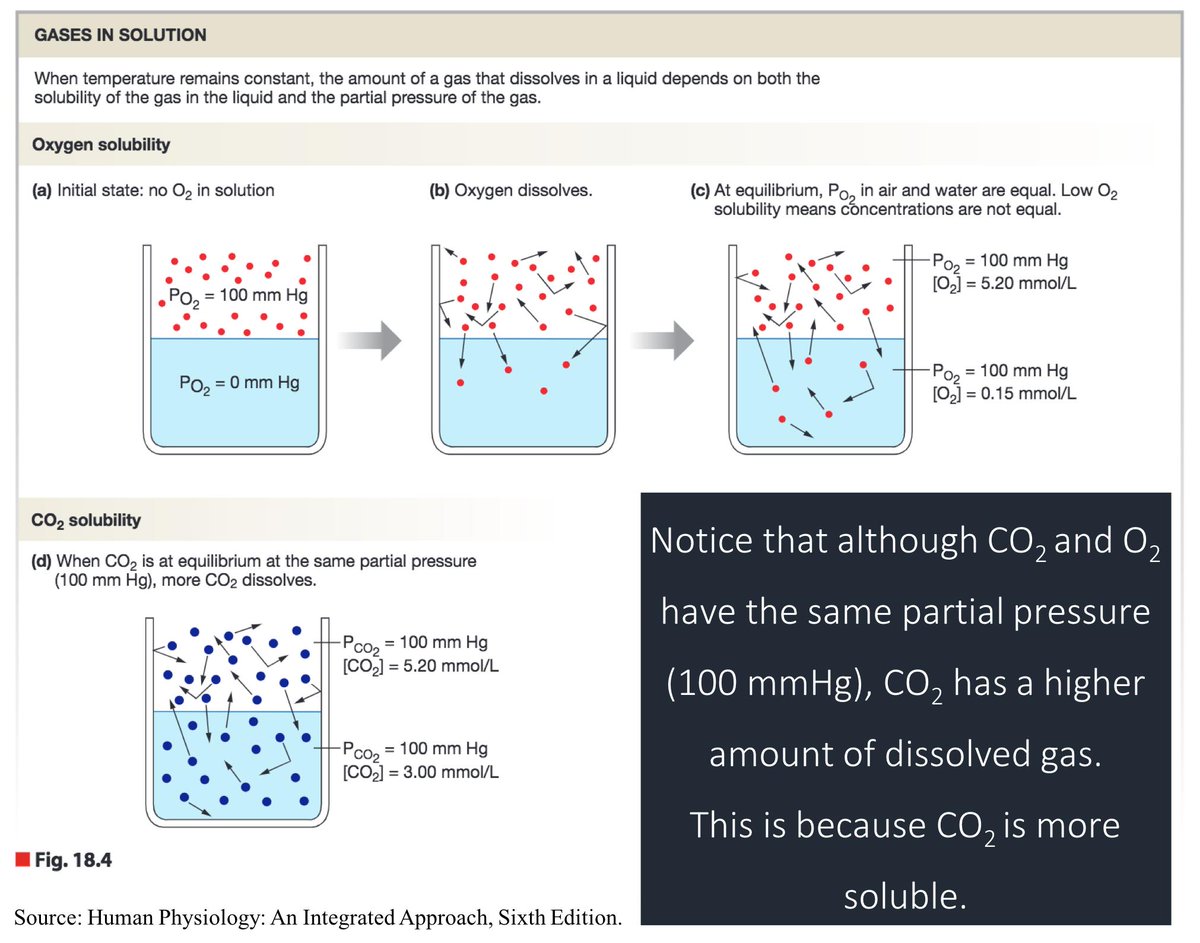
And here are the solubility coefficients for CO₂ and O₂:
CO₂ = 0.57
O₂ = 0.024
As you can see, CO₂ is 24 times more soluble, in water, than O₂.
elsevier.com/books/guyton-a…
The rate of DIFFUSION of a gas is dependent on both solubility and molecular weight. CO₂ is heavier than O₂, narrowing the difference a bit.
With O₂ used as reference, the diffusion coefficient of CO₂ is 20.3.
➜ the rate of diffusion of CO₂ in H₂O is 20x that of O₂.
What this means is that even when O₂ diffusion is severely limited (as with pneumonia, pulmonary edema, or interstitial lung disease), CO₂ diffusion continues unabated.
The lungs continue to expire CO₂ leaving pCO₂ unchanged.
Once HCO₃⁻ is returned to the lungs, it must be converted back to CO₂
Here's the thing: the reaction of CO₂ with H₂O requires minutes for equilibrium. If gas exchange had to wait for this reaction, it would be too slow and CO₂ could not easily be eliminated.
How does the body manage the fact that the reaction that converts HCO₃⁻ back to CO₂ is very slow?
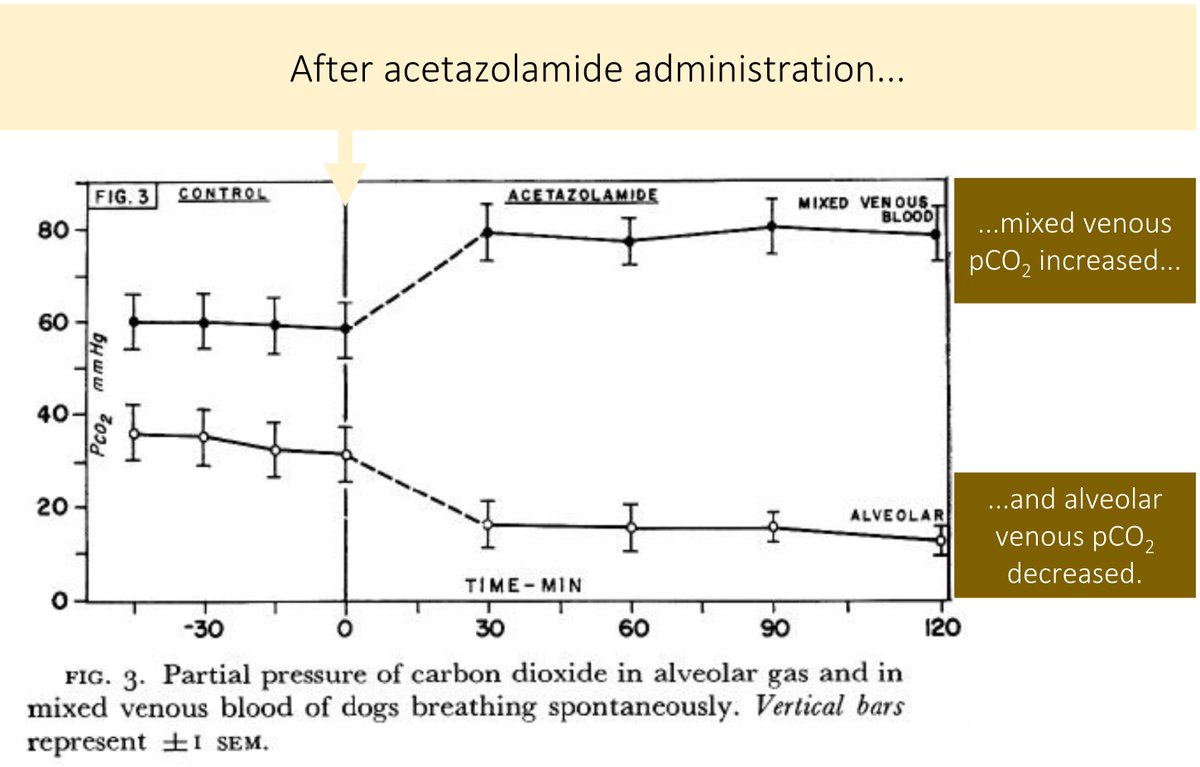
In fact, if enough acetazolamide is administration, the pCO₂ may rise.
This was seen in a study published in 1961 when acetazolamide was administered to anesthetized dogs.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/13630836
Another mechanism that may contribute to the rarity of diffusion-mediated hypercapnia: hypoxemia-mediated stimulation of ventilation, leading to CO₂ washout.
Before summarizing, let's look again at a version of the original question.
What explains why pneumonia and pulmonary edema don't lead to an increase in pCO₂ if they DO lead to a decrease in pO₂)
[Hg = hemoglobin]
⭐️Why doesn't pneumonia (or other issues with gas diffusion) lead to increased pCO₂?⭐️
➜ CO₂ is 24x more soluble than O₂ and has 20x greater diffusion capacity
➜ this means that even when fluid affects O₂ diffusion, CO₂ remains unaffected