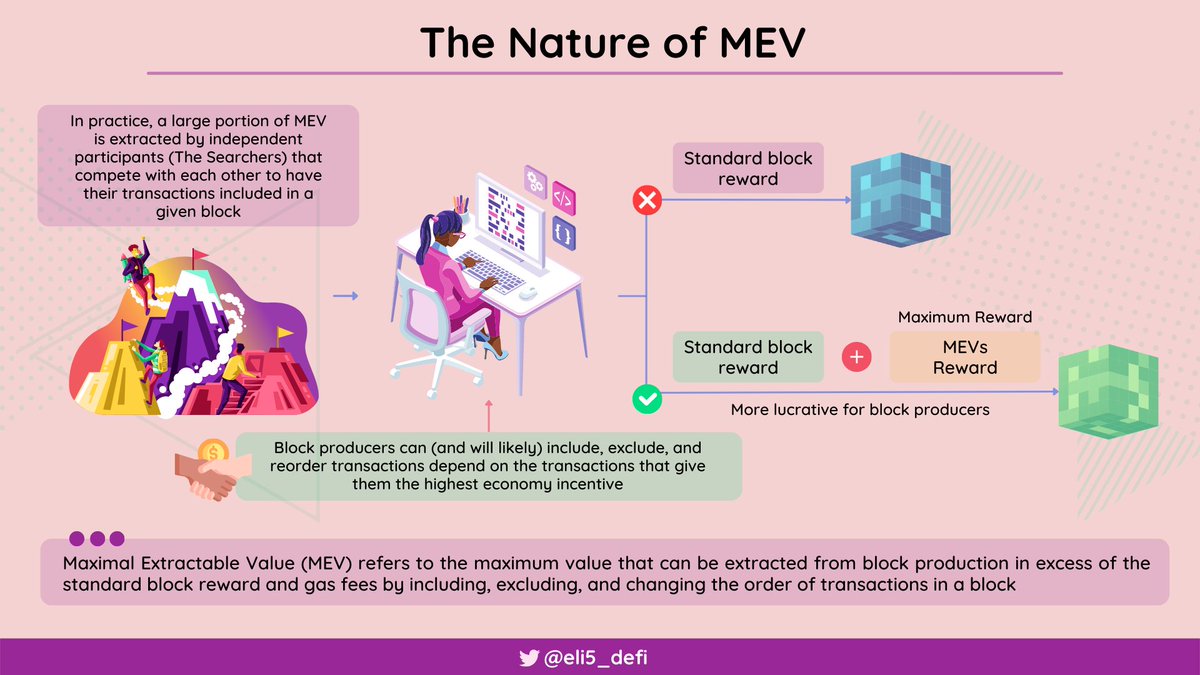
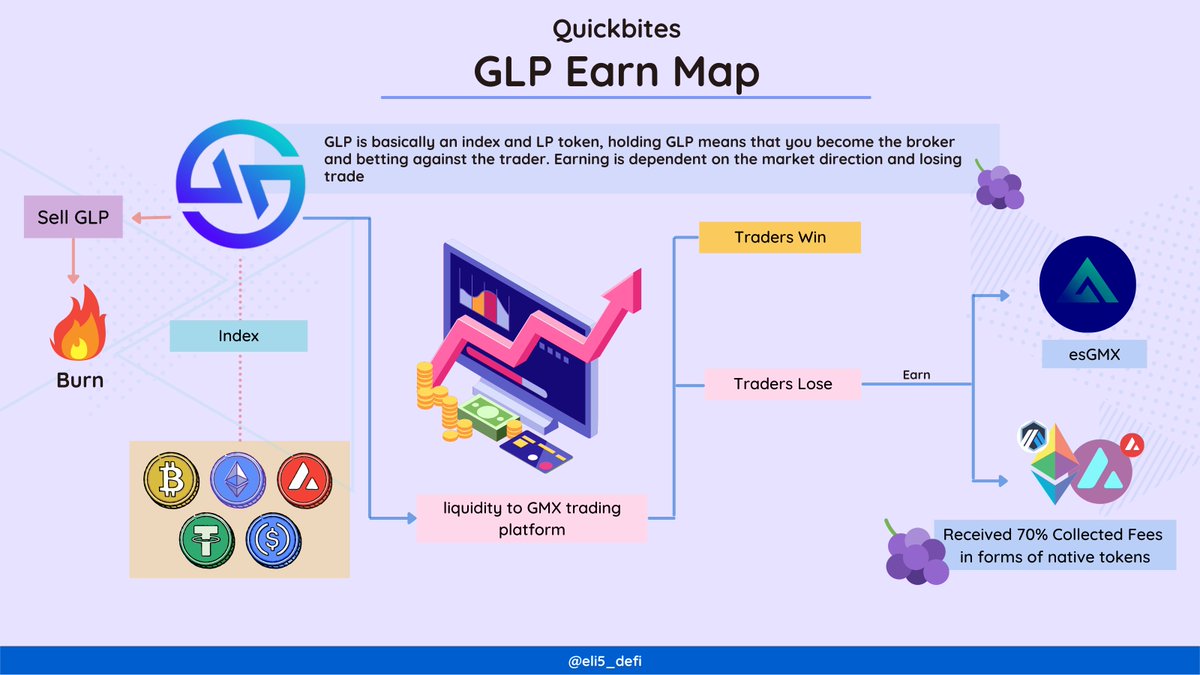
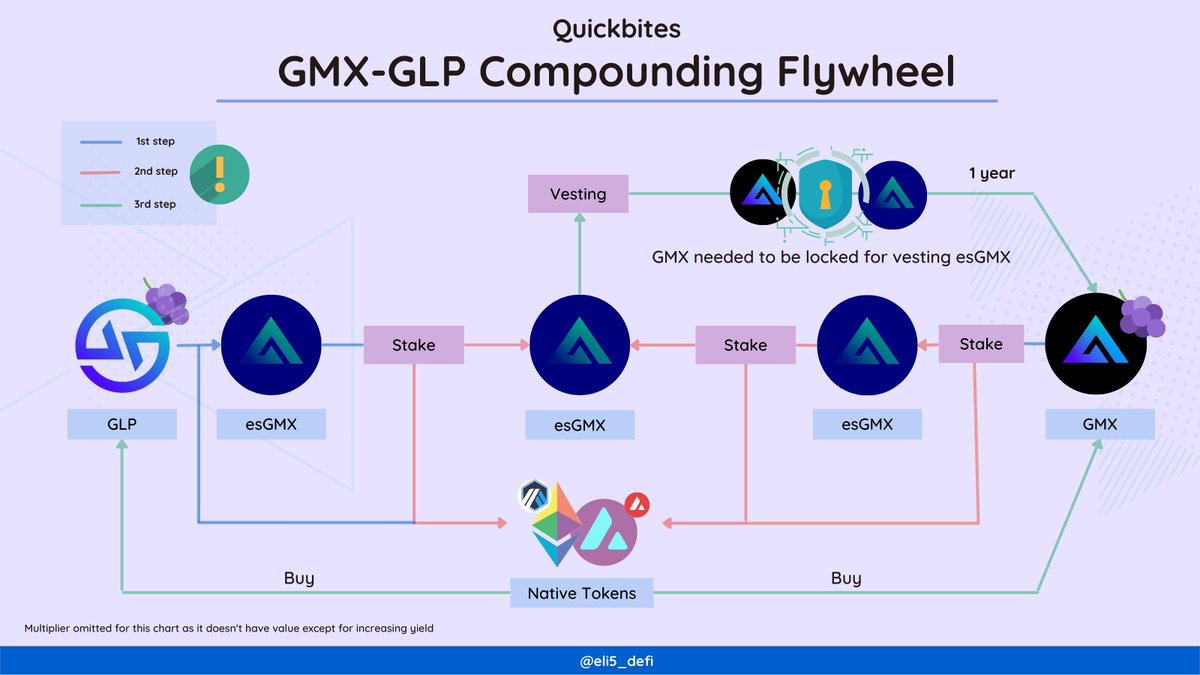
1/ #GM! What is modularity? how can it solve the data availability? How does it unlock the potential of scalable networks?
Find out in our #visualguide: The Age of #Modular #Blockchain Part 1.
#Cryptocurrency #Ethereum #DeFi #Rollups #Arbitrum #Optimism #ZK $ETH $OP $ARBI
Find out in our #visualguide: The Age of #Modular #Blockchain Part 1.
#Cryptocurrency #Ethereum #DeFi #Rollups #Arbitrum #Optimism #ZK $ETH $OP $ARBI

2/ Blockchain networks by design faces the 'Blockchain #Trilemma'. Decentralized networks can only provide two of three aspects at any given time with respect to decentralization, security, and scalability. 

3/ To achieve scalability, decentralized network must solve the data availability problem. Data availability refers to the idea that all transaction-related data is available to nodes on the blockchain network, but this process is resources incentive and causes network bottleneck 

4/ Besides the data availability problem, less problematic issues such as data retrieval also arises. However, compared to data availability, data retrieval is easier to solve as it does not affect the primary transaction process in the nodes. 

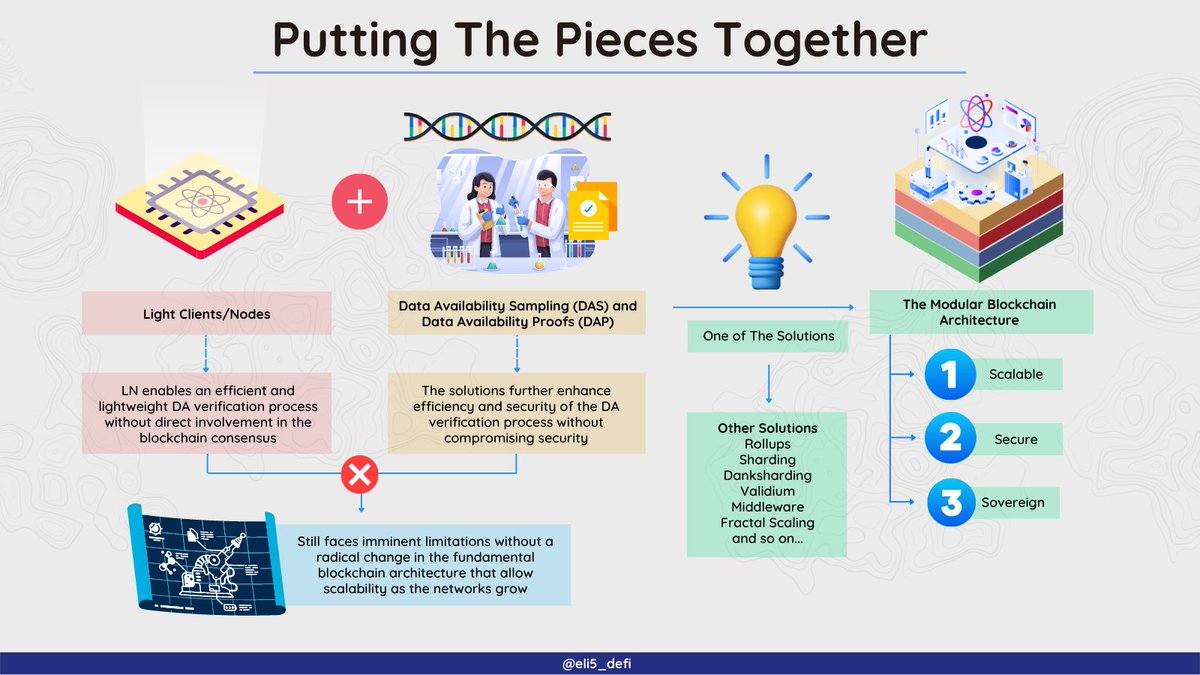
5/ Many innovations have been developed to overcome the DA limitations. Mainly divided into on-chain solutions and off-chain solutions. They don't need to work singularly and can complement each other. 

6/ Data availability sampling (#DAS) and data availability proofs (#DAP) is the on-chain solution for data availability problem. The implementation of both methods become the foundation for #sharding and the modular #blockchain architecture. 

7/ A light node/ client (LN) is a cost-effective node, which only downloads the block headers, the minimum data needed to transact. Running light nodes have a lower barrier of entry due to its minimal bandwidth and storage threshold. 

8/ LN, DAS and DAP are still facing imminent limitations from current #monolithic blockchain architectures. This brings a novel solution to the table: #Modular Blockchains that ideally should be infinitely scalable, self-sovereign whilst maintaining security. 
9/ Modular blockchain architectures decouple the distinct function in the network to handle particular duties and outsource other objectives to one or more separate layer. There are 4 main layers:
- Execution
- Settlement
- Consensus
- Data Availability
- Execution
- Settlement
- Consensus
- Data Availability

10/ Modular blockchain layer are stackable and can be combined according to the functionalities needed. This approach will significantly reduce the burden in the base/ settlement layer and enables the base layer to overcome the congested network. 

11/ Modular blockchains also enable scalability by separating data availability into different layers. The looming of the DA problem as the network grows will be averted and the network will be able to grow as intended. 

12/ Modular architectures have their own disadvantages, several concerns pointed out related to its development and design:
- Security Risk
- Development Complexity
- Monetary incentive and policy
- Security Risk
- Development Complexity
- Monetary incentive and policy

13/ Modular blockchain is one of the scalability solutions proposed, there are others solutions but the endgame is to have all the solutions to complement, propagate new ideas and trail new path for innovation. The ultimate winner should be the user. 

14/ References
@jneu_net, @KyrianLabs, @likebeckett, @VitalikButerin, @ParityTech, @Maven11Capital, @Delphi_Digital, @MessariCrypto
@jneu_net, @KyrianLabs, @likebeckett, @VitalikButerin, @ParityTech, @Maven11Capital, @Delphi_Digital, @MessariCrypto

15/ Rollups as mentioned in the #visualguide is one of the modular solution in Ethereum by separating execution layer from settlement. To understand more about #ZK rollups and #Optimistic rollups, please check below:
https://twitter.com/eli5_defi/status/1533504611273031680?s=20&t=iE65r5hQv6L9eDqb_tJD4Q
16/ We also mentioning #Sharding or #TheSurge in our previous as a part of #Ethereum future plan to splitting database horizontally.
$ETH
$ETH
https://twitter.com/eli5_defi/status/1551217791050530818?s=20&t=r6E_tKPn7K03l3tTbT0NVQ
17/ Amazing writing about modular scalability and other solutions from @knowerofmarkets also recommended to check:
theknower.substack.com/p/scaling-modu…
theknower.substack.com/p/scaling-modu…
18/ Great podcast from @Delphi_Digital, @cannngurel and @jadler0 on Modular Blockchain 101:
members.delphidigital.io/media/celestia…
members.delphidigital.io/media/celestia…
19/ Our next second part will be covering modular blockchain project in development or using modular architecture as its backbone:
@CelestiaOrg
@fuellabs_
@0xPolygonAvail
@0xPolygon
@eigenlayer
@StarkWareLtd
@zksync
@SkaleNetwork
@OasisProtocol
@cosmos
@CelestiaOrg
@fuellabs_
@0xPolygonAvail
@0xPolygon
@eigenlayer
@StarkWareLtd
@zksync
@SkaleNetwork
@OasisProtocol
@cosmos

20/ Tagged account below that developing/ involving in modular project for visibility:
@zmanian
@ekrahm
@sandeepnailwal
@buchmanster
@beller
@GDanezis
@jadler0
@nickwh8te
@musalbas
@anuragarjun
@sourcex44
@_khanhamzah
@Maven11Capital
@Mudit__Gupta
@zmanian
@ekrahm
@sandeepnailwal
@buchmanster
@beller
@GDanezis
@jadler0
@nickwh8te
@musalbas
@anuragarjun
@sourcex44
@_khanhamzah
@Maven11Capital
@Mudit__Gupta
21/ Tagged account below for their amazing and educational content in CT:
@blocmatesdotcom
@apolynya
@SalomonCrypto
@shivsakhuja
@mimiLFG
@ManoppoMarco
@Dynamo_Patrick
@rektdiomedes
@knowerofmarkets
@MeetWawa
@CryptoDragonite
@BarryFried1
@The_ReadingApe
@VirtualKenji
@blocmatesdotcom
@apolynya
@SalomonCrypto
@shivsakhuja
@mimiLFG
@ManoppoMarco
@Dynamo_Patrick
@rektdiomedes
@knowerofmarkets
@MeetWawa
@CryptoDragonite
@BarryFried1
@The_ReadingApe
@VirtualKenji
@blocmatesdotcom @apolynya @SalomonCrypto @shivsakhuja @mimiLFG @ManoppoMarco @Dynamo_Patrick @rektdiomedes @knowerofmarkets @MeetWawa @CryptoDragonite @BarryFried1 @The_ReadingApe @VirtualKenji 22/ If you love our thread please like and retweet, thank you and see you in the next #visualguide!
https://twitter.com/eli5_defi/status/1589239959994920961?s=20&t=aF44Lj4AyaFKIkXinZRGzg
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh