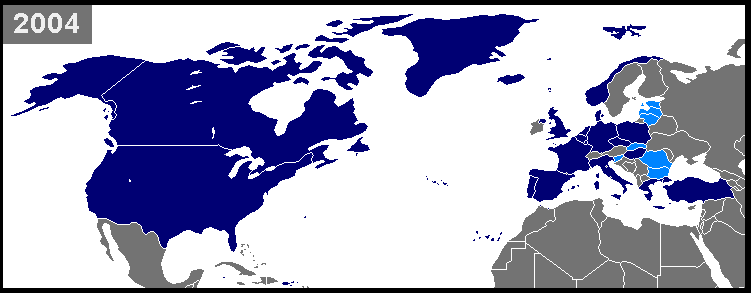
The seventh and final installment is "On Russia's Doorstep: Bringing in the Baltics"

“I’m against NATO enlargement. When NATO approaches the borders of the Russian Federation, you can say that there will be two military blocs, and this will be a restoration of what we already had.”
Indeed, the Lithuanian President was so bold as to directly "apply" for NATO membership via a letter (which had never been done).
(Thx @NATO#Archives for 👇)

By the mid-1990s, due to the Balkan Wars, @NATO was focusing on deploying Peacekeeping operations.



As a 1999 editorial in the Norwegian paper @Aftenposten remarked,
"BALTBAT almost functions as a preparatory school for NATO membership"
“Quite bluntly, the Russians need to get over the neuralgia on this
subject [of Baltic membership]"