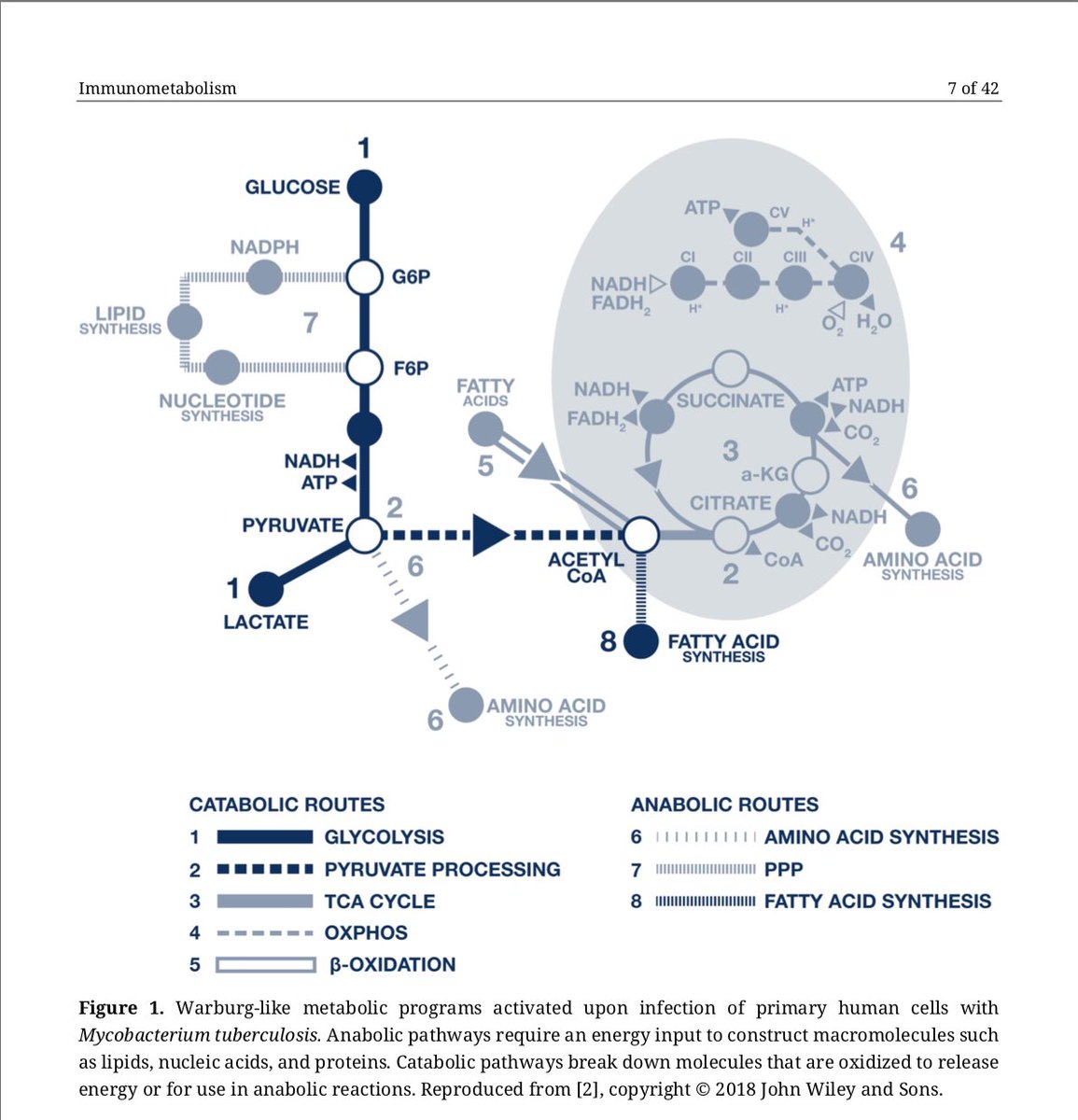
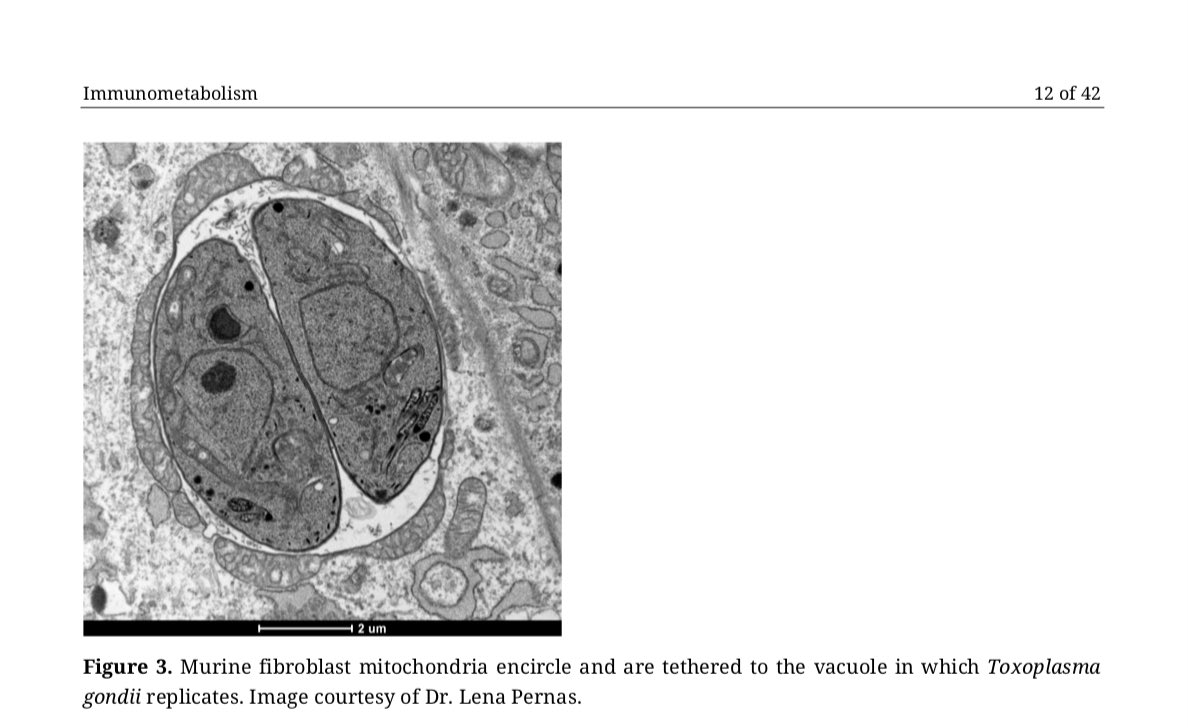
If you’re considering studying blockage of GPCRs in #LongCovid or related conditions, please start w/ the understanding that humans are not sterile...and that common human organisms/pathogens express proteins/metabolites that block/dysregulate GPCR signaling
https://twitter.com/berlincures/status/1401881318678581249
2/ Herpesvirus re-activation is common in #COVID-19, and may impact some LongCovid cases. The herpesviruses alone (EBV, CMV etc) create a wide range of proteins that block GPCR signaling: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P… Indeed, viral hijacking of GPCRs is a big topic in cancer research
3/ Beyond that, many commensal #bacteria derived from the human #microbiome appear capable of expressing metabolites that are GPCR mimics, that directly impact GPCR signaling. That means even changing microbiome dynamics could impact GPCR-related issues: ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
4/ Indeed, molecular mimicry (sequence homology) between #viral + bacterial GCPR protein/metabolite “mimics” and human CPCR proteins/ligands may account for the generation of “autoantibodies” connected to GPCR signaling issues
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh