Which #OECD countries have lowered #electricity #emissions? How did they do it, at what pace, at what price?
My 4th round of 4-country profiles: #Austria #Finland, #Italy & #USA
For comparison, I now also include price & emissions average (AVG) from full 24-country sample!
🧵
My 4th round of 4-country profiles: #Austria #Finland, #Italy & #USA
For comparison, I now also include price & emissions average (AVG) from full 24-country sample!
🧵
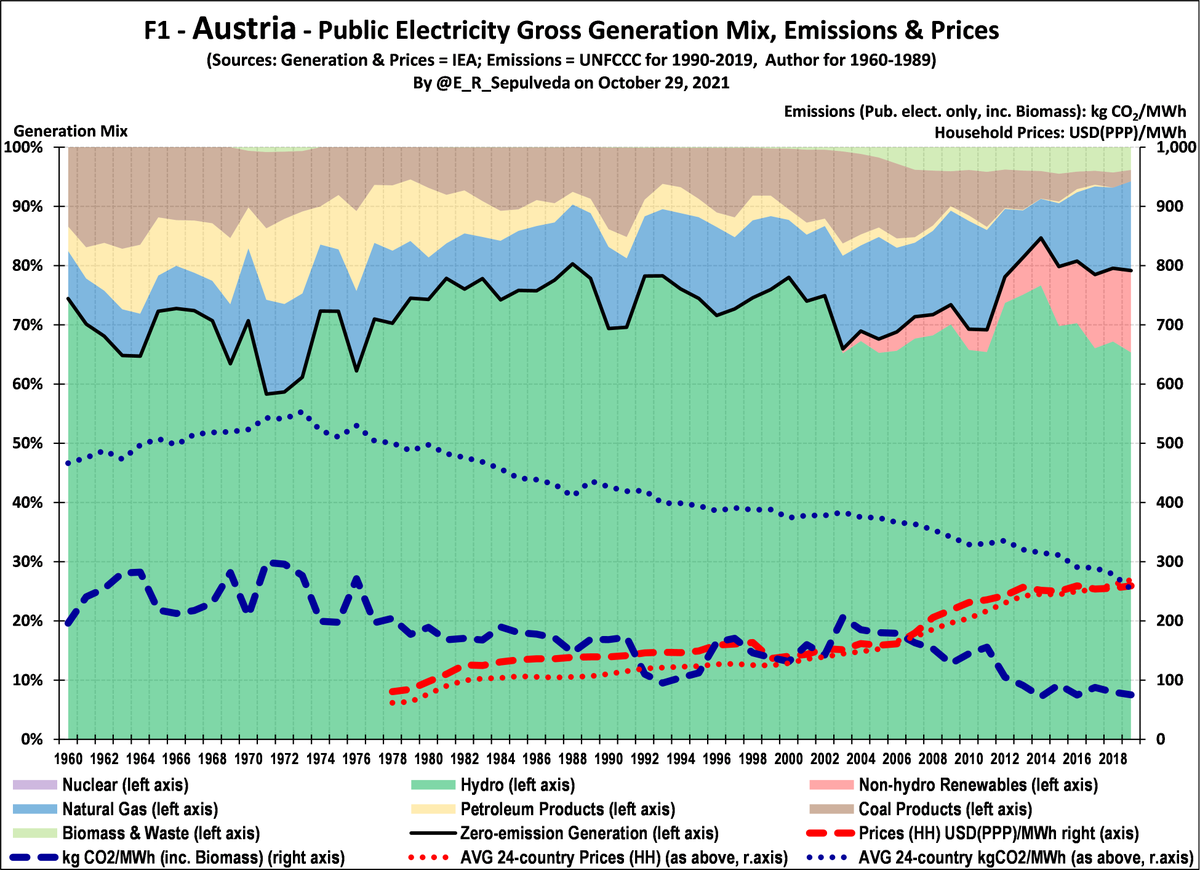
First off, Austria, with ample hydro resources (70%), resulting in whole-period low emissions, well below 24-country AVG
Remaining oil & coal now replaced with non-hydro renewables & gas, further lowering emissions
Prices have tracked AVG prices, with increase last 15 years
Remaining oil & coal now replaced with non-hydro renewables & gas, further lowering emissions
Prices have tracked AVG prices, with increase last 15 years
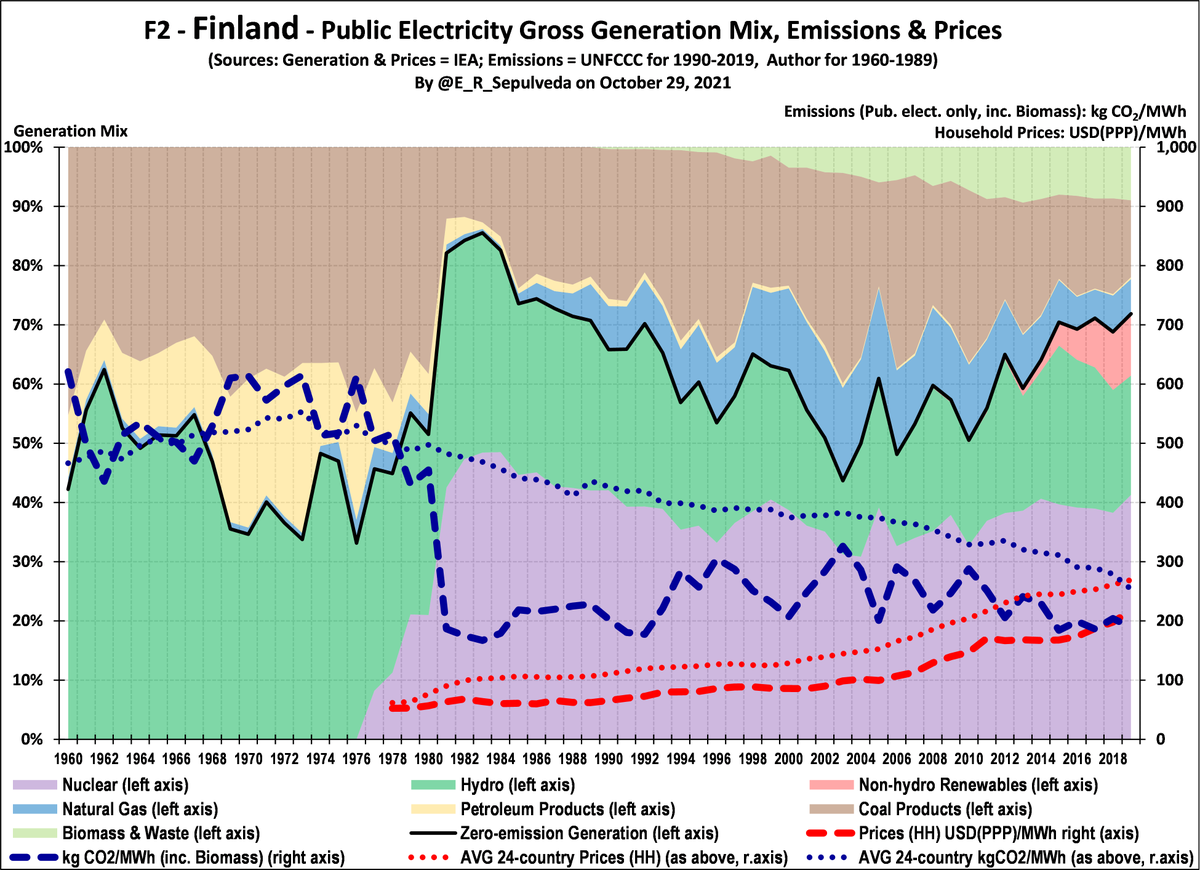
Finland reduced emissions intensity by 70% in 8 years due to nuclear rollout of late-1970s. Went from AVG to low emissions, maintaining below-AVG prices.
Emissions have stayed below AVG with stable nuclear & hydro stable, supplemented by non-hydro renewables recently.
Emissions have stayed below AVG with stable nuclear & hydro stable, supplemented by non-hydro renewables recently.
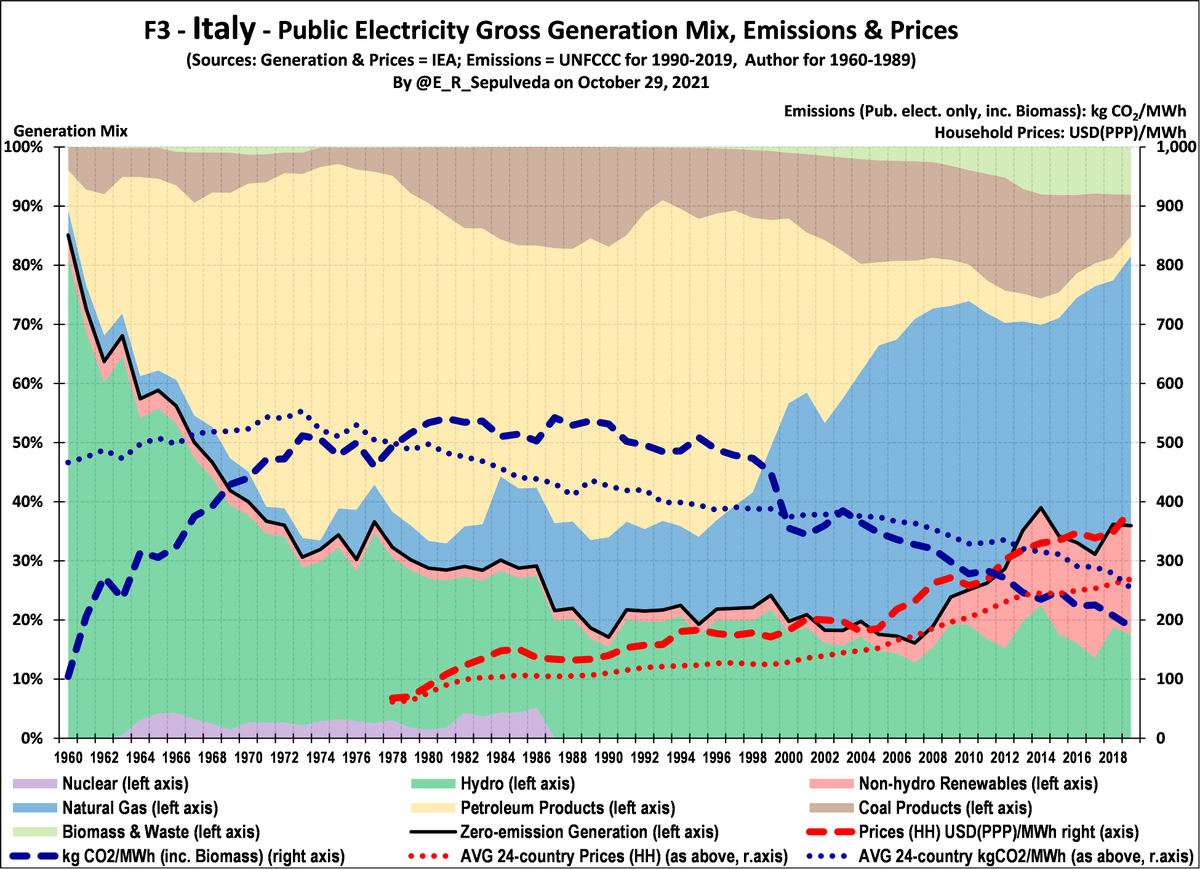
Italy is interesting for two reasons: no other country increased emissions as much from 1960 to 1990, because all new demand was met by FF; & only sample country to shut down nuclear (post-Chernobyl).
Prices have spiked last decade as non-hydro renewables & gas displace oil.
Prices have spiked last decade as non-hydro renewables & gas displace oil.
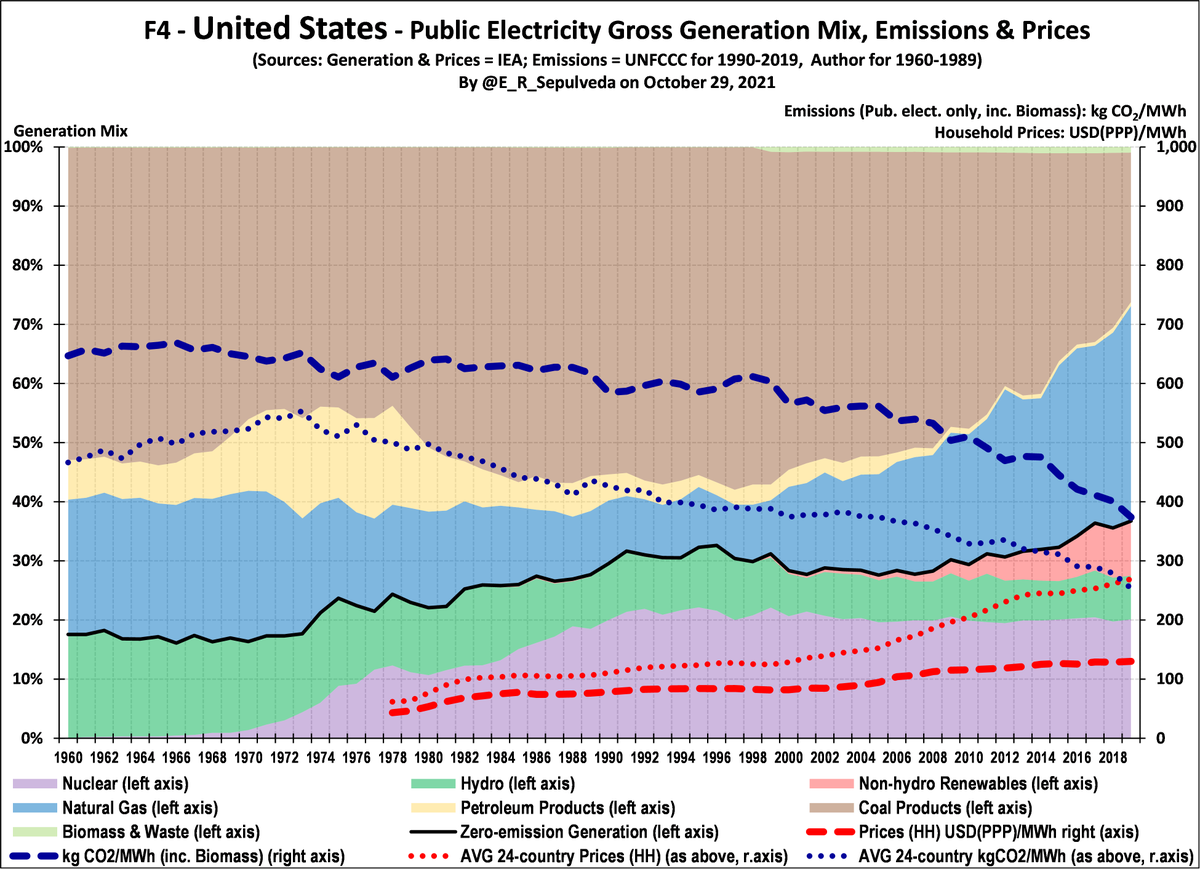
Lastly, USA has had higher emissions & lower prices than AVG over entire period.
Emissions first decreased moderately as nuclear displaced some gas & oil. From 1998, based on stable nuclear & hydro, gas & non-hydro renewables displaced some coal.
Prices rel. stable over period
Emissions first decreased moderately as nuclear displaced some gas & oil. From 1998, based on stable nuclear & hydro, gas & non-hydro renewables displaced some coal.
Prices rel. stable over period
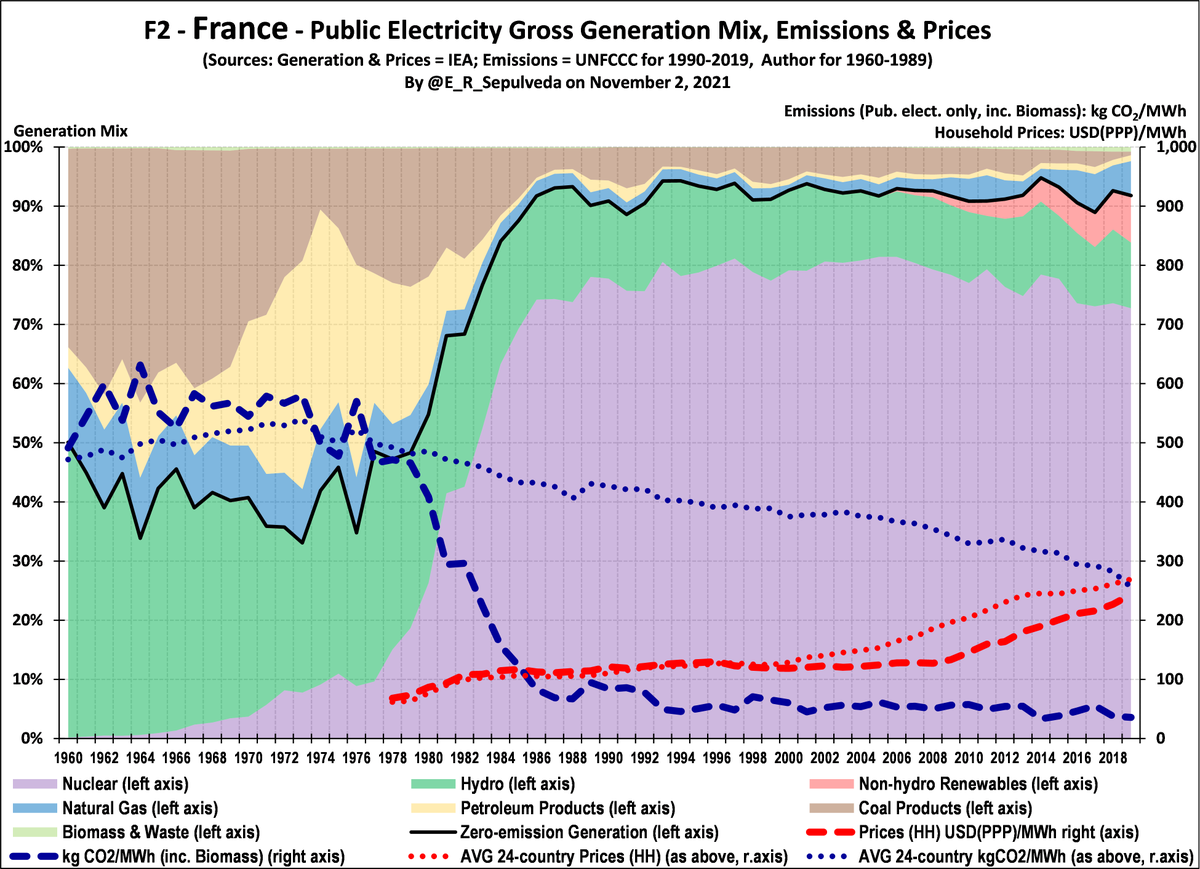
Eight #OECD countries remaining in the series, including #Belgium, #Denmark, #France, #Germany, #Greece, #Netherlands, #NZ, #Slovakia
Stay tuned.
Stay tuned.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh