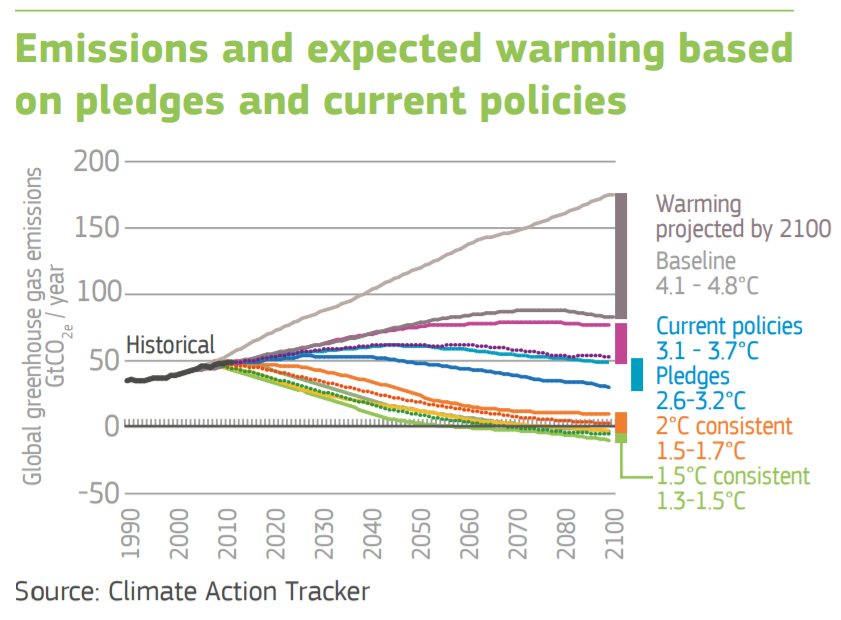
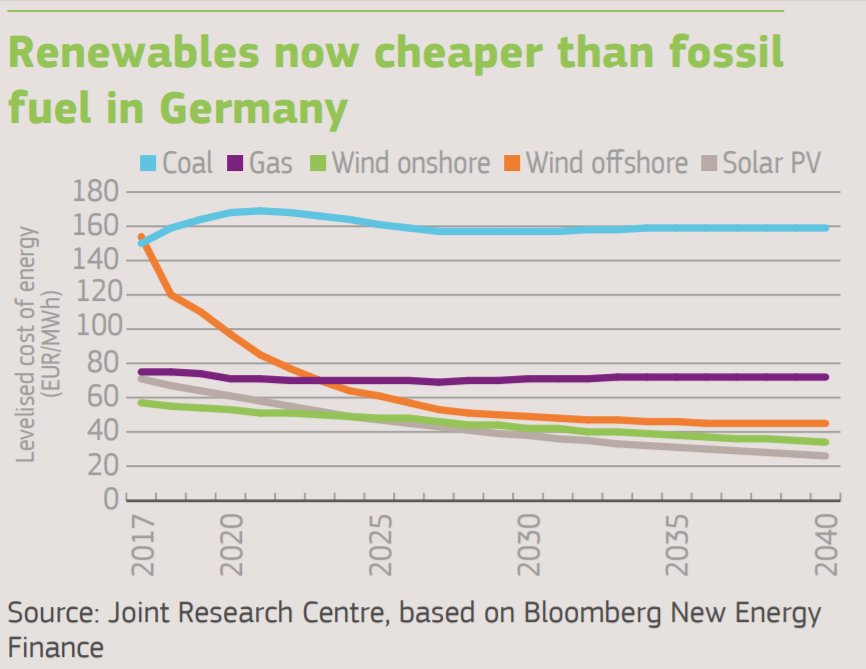
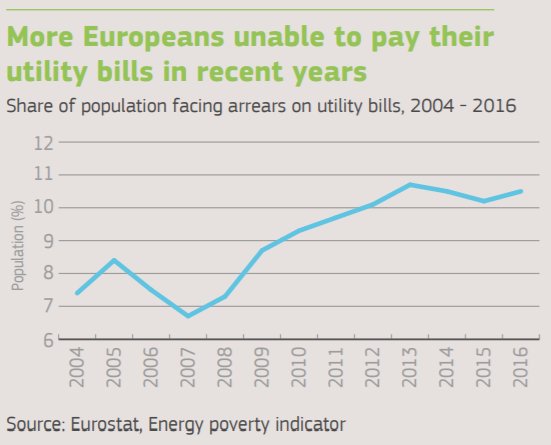
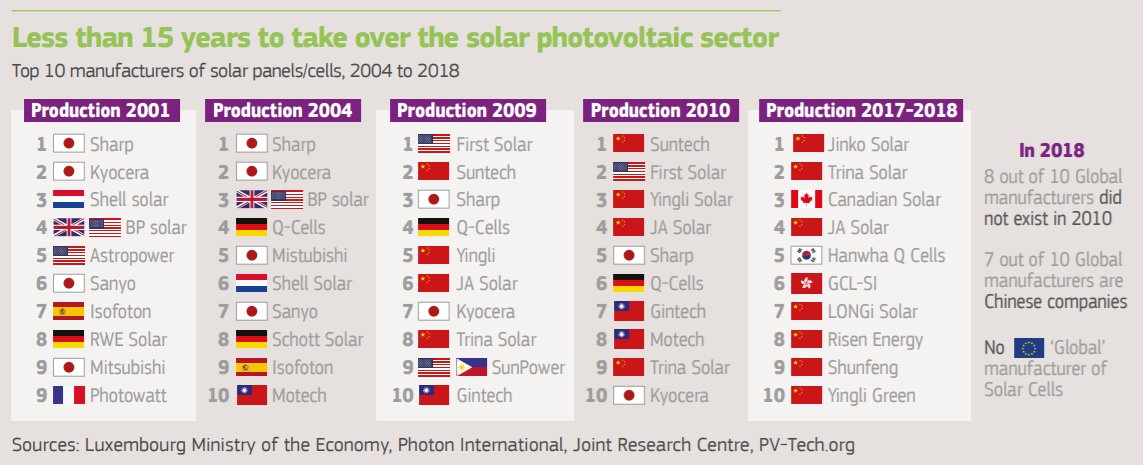
1/ The EPSC - the European Commission's @ECThinkTank - has launched a new report on key trends shaping climate & energy policy in the short- to medium-term (2025-2030). The publication is aimed at laying the groundwork for upcoming discussions on stronger implementation.
Renewables will soon make up 20% of final energy consumption in the EU, and fossil fuels have declined from 81% (1995) to 72.6% (2016). The EU's new renewables target is 32% by 2030.
frameworks primarily designed for a centrally-controlled system.
China will have massive growth in oil & gas demand and is the world's largest GHG emitter. Asia-Pacific accounts for nearly 50% of GHG emissions. But clean tech also sees massive investment.
With declining domestic production of oil, gas & coal, a shift to clean technology will help minimize the EU's dependence on fuel imports and diversify energy supply.