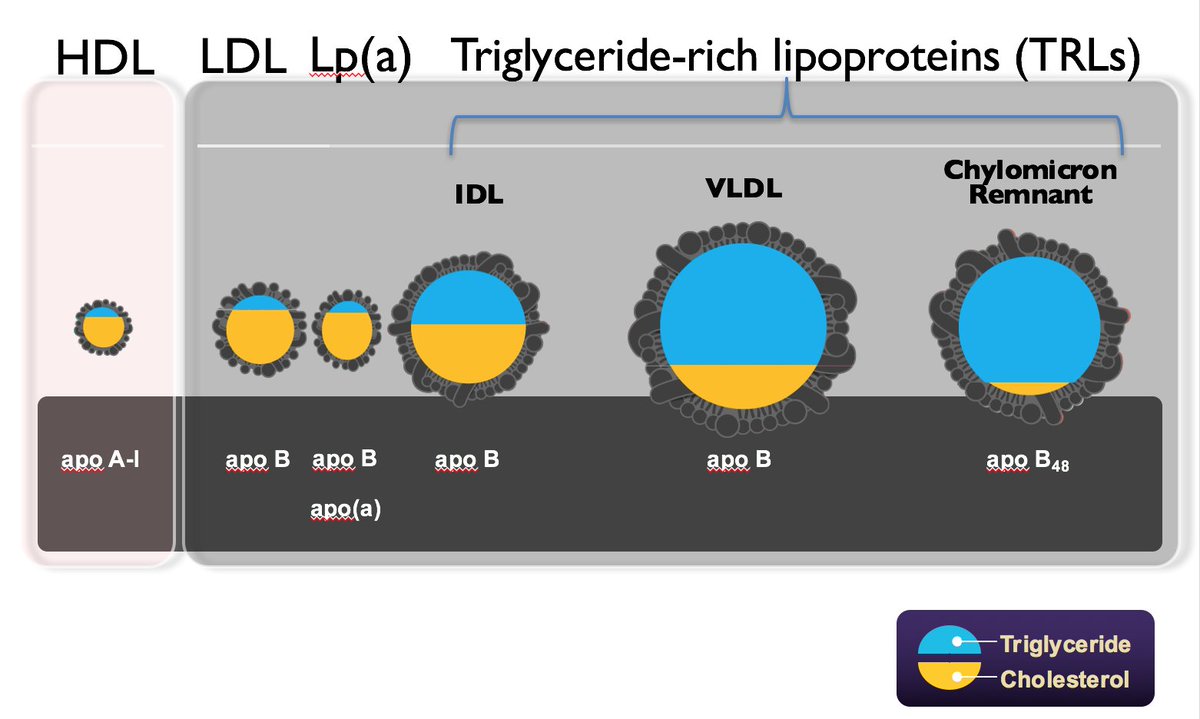
I am going to expand with some unpublished data on genome-wide polygenic scores for heart attack.
In ~2%, we can identify a monogenic mutation in LDLR, APOB, PCSK9.
What's going on in the remaining 4,900?

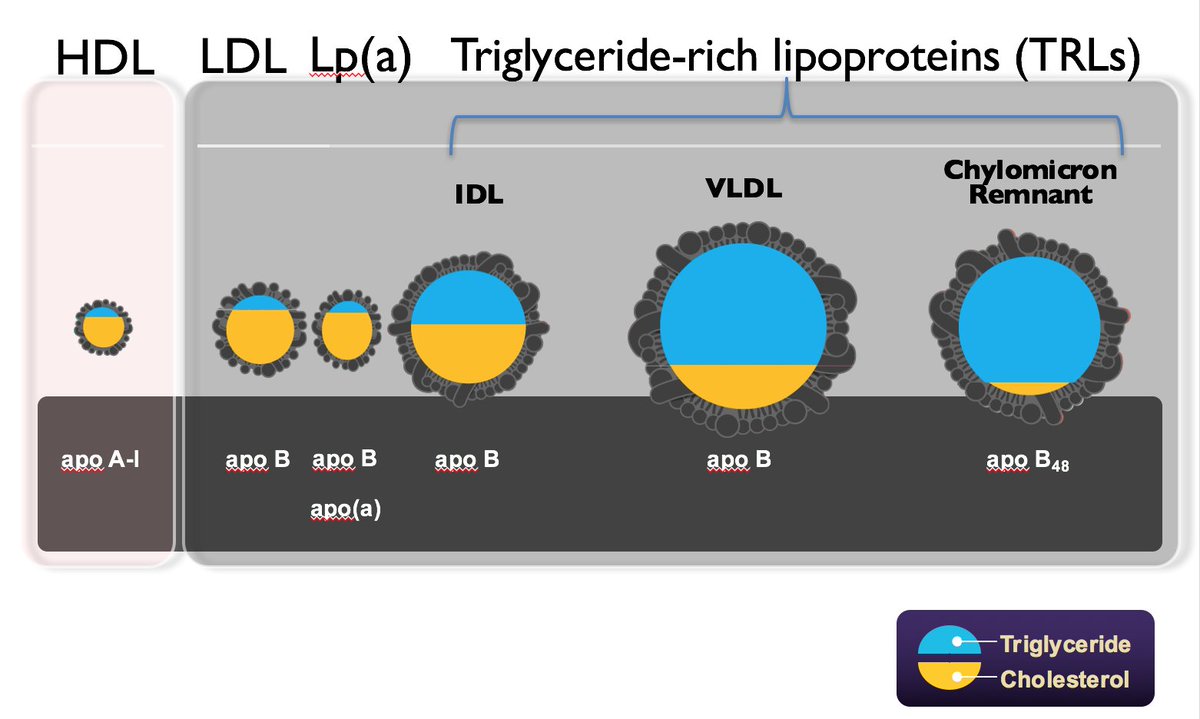
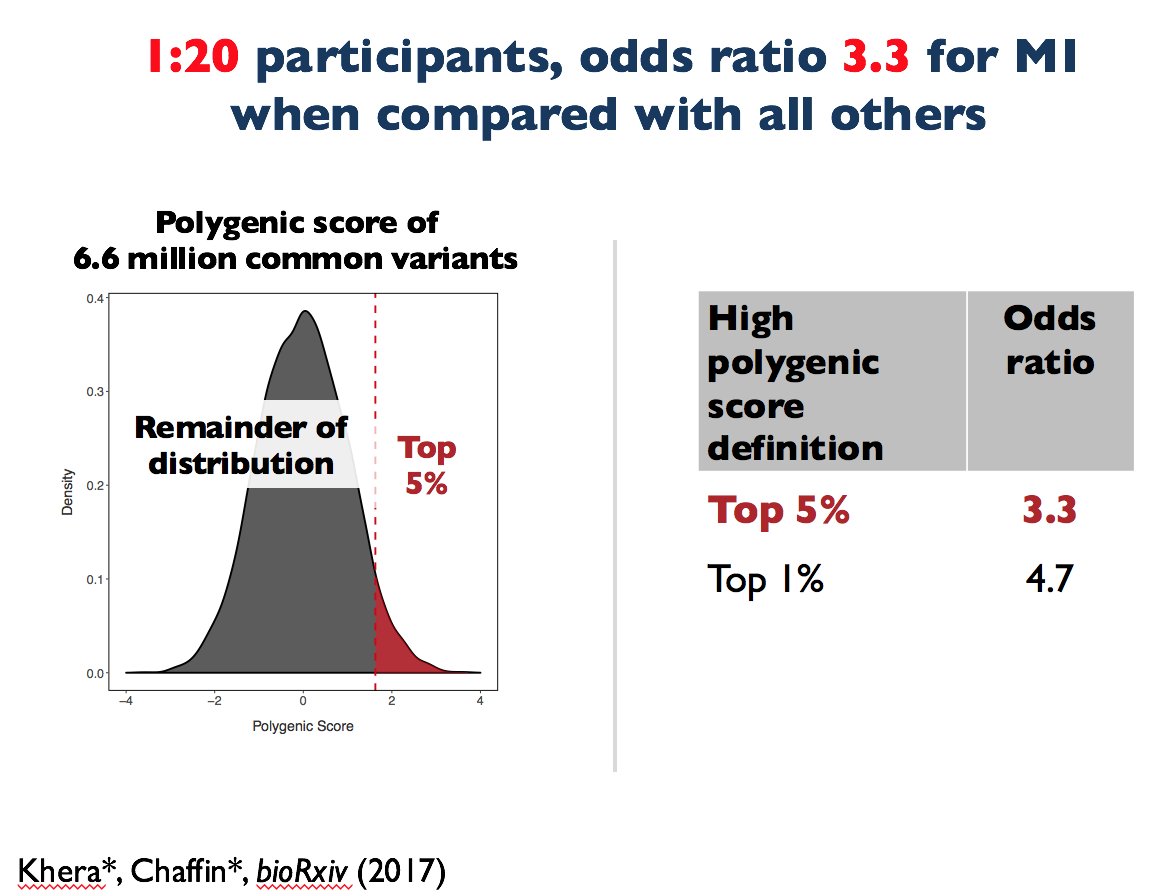
1. conforms to a Gaussian distribution
2. Those in the extreme of this distribution have levels of risk equivalent to monogenic mutation
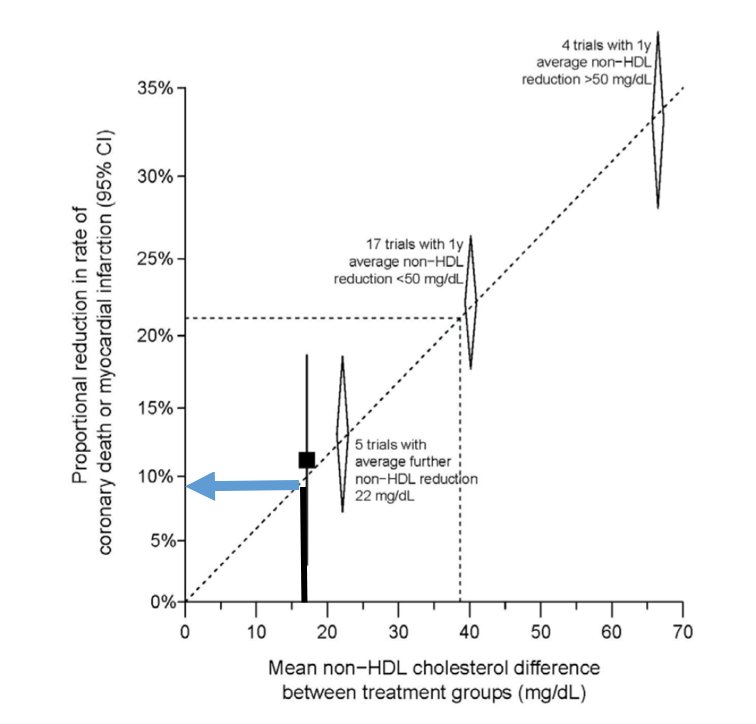
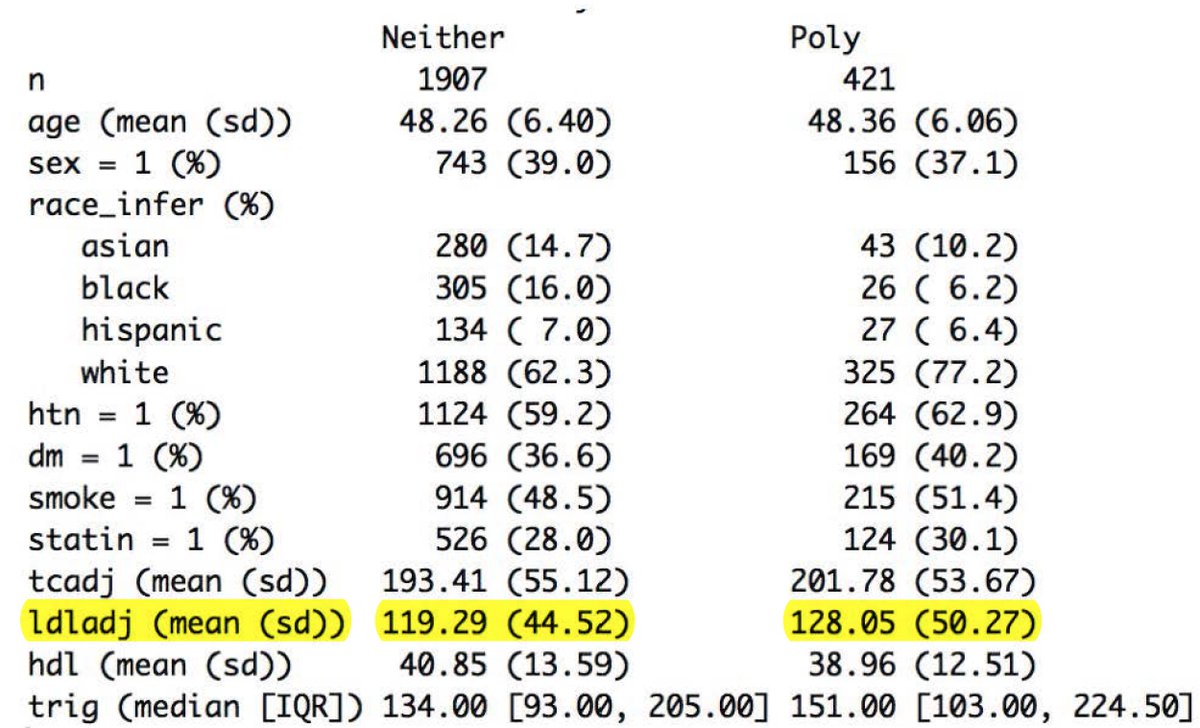
Look at the mean LDL in the high polygenic risk group versus all others: 128 mg/dl versus 119!
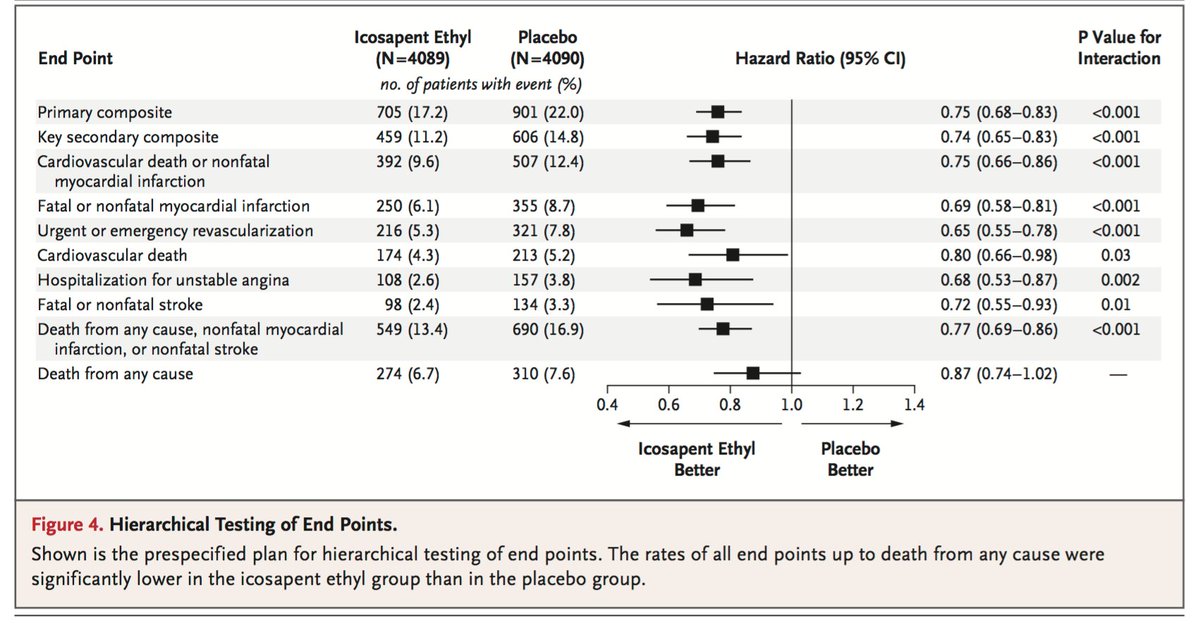
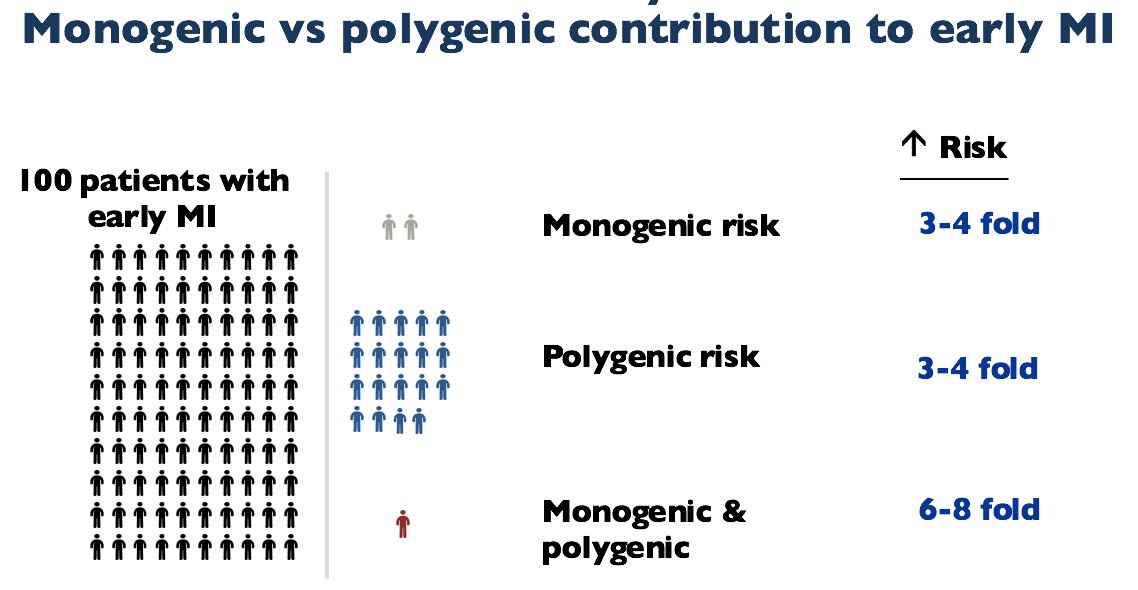
Below is a summary of the contribution of monogenic and polygenic models to early MI.
Note that those at polygenic risk are currently *UNAWARE* AND not being picked up by traditional risk factors.
Those with high scores are at much higher risk heart attack.
These patients not being picked up by usual risk factors.
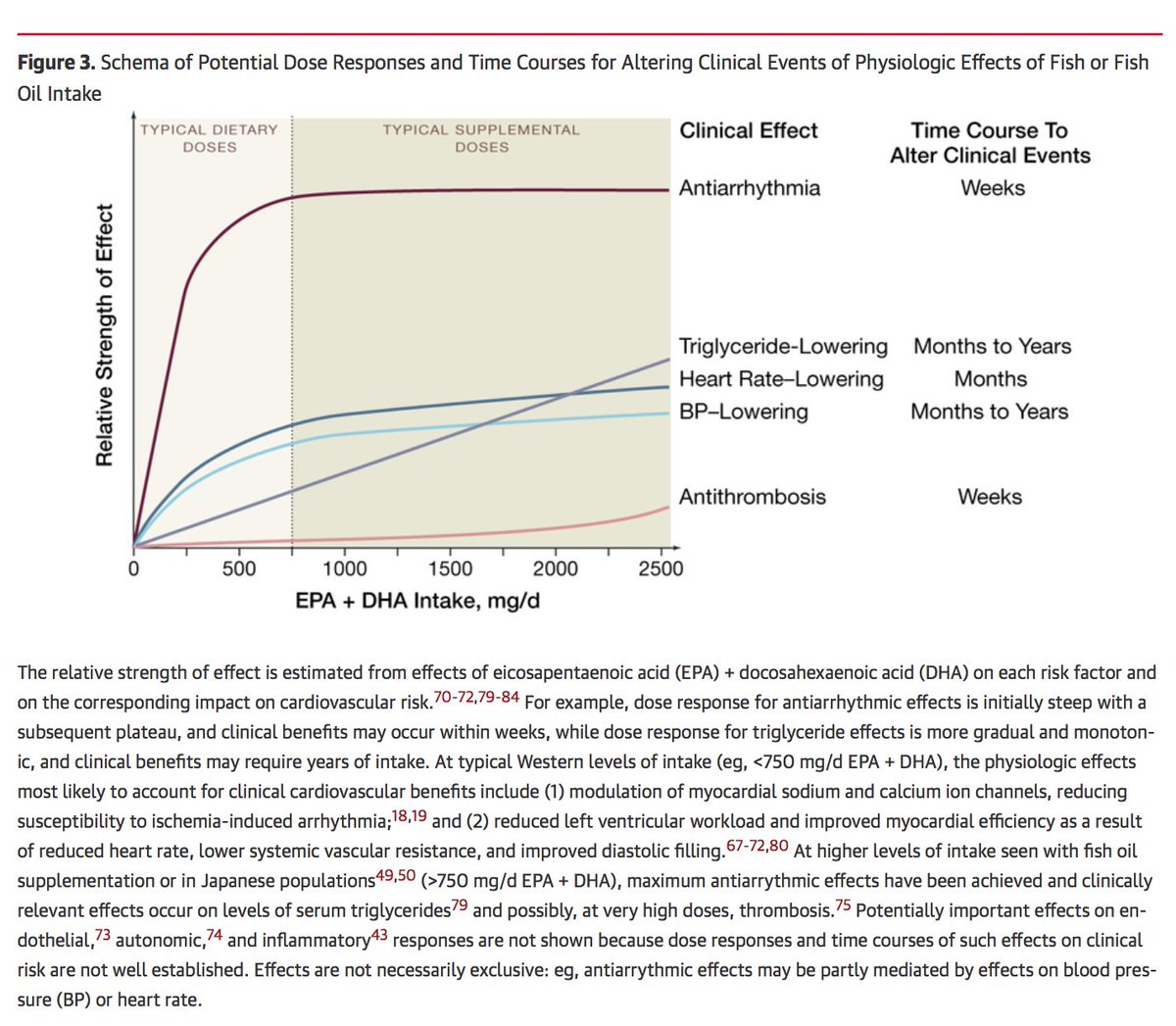
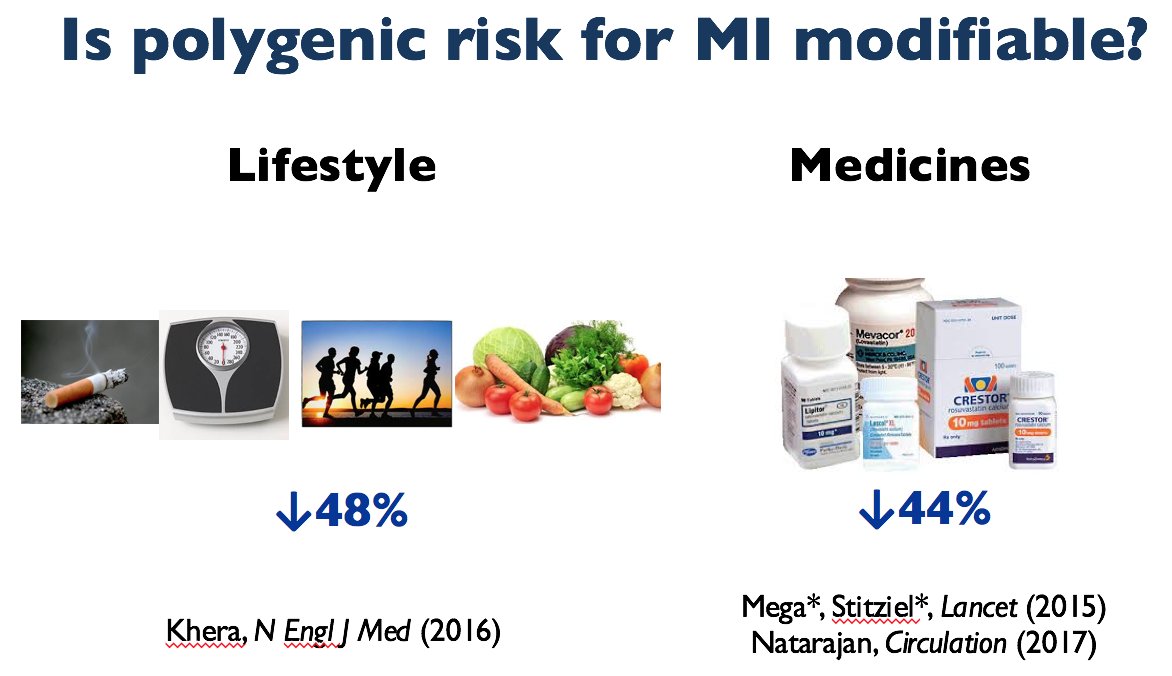
But, can one modify this high polygenic risk? Yes. By, lifestyle, statin
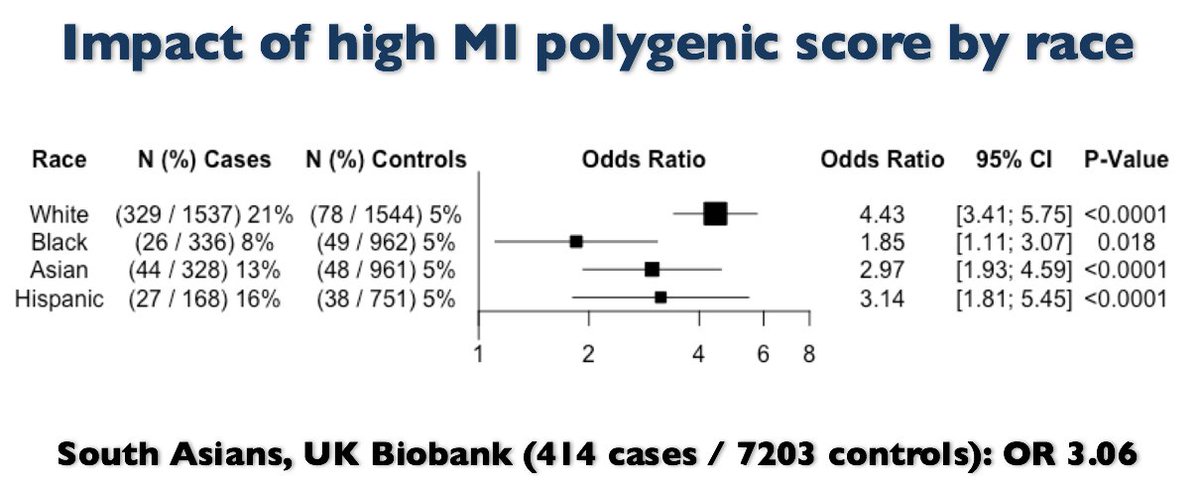
We took new genome-wide polygenic score derived/validated largely whites & asked if score predictive other ancestries.
Same score *WORKS* across range ancestries.
What are next steps needed in evidence base? Finis.
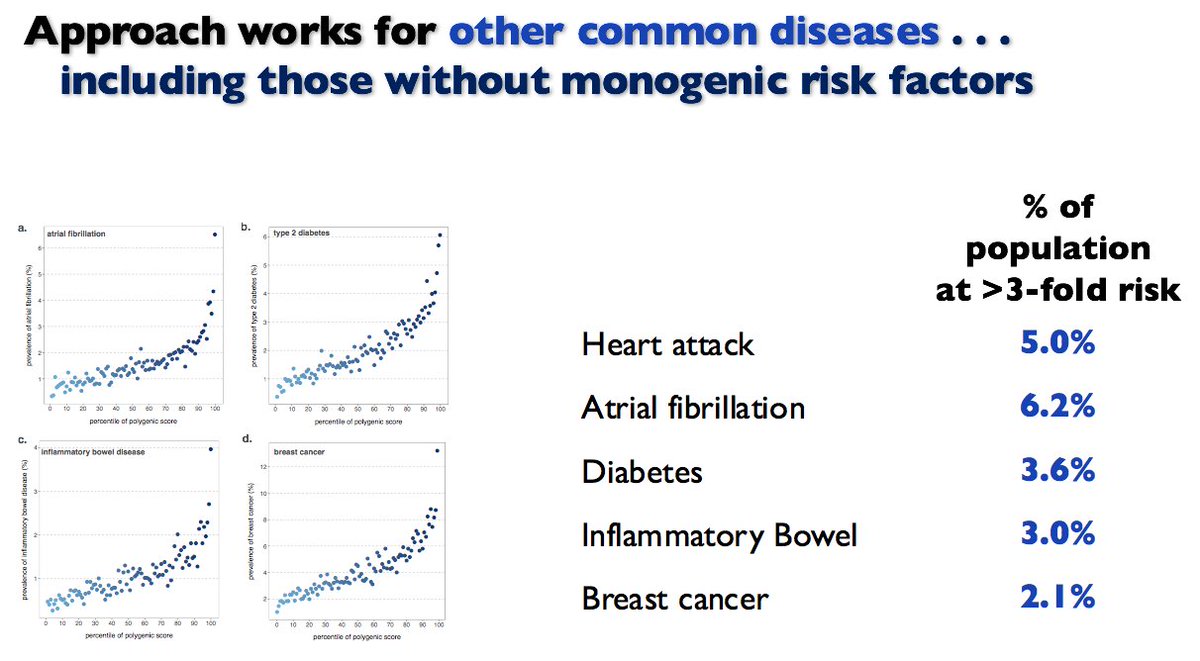
Despite incorporating 6.6M common variants, our genome-wide CAD polygenic score does *NOT* require whole genome sequencing.