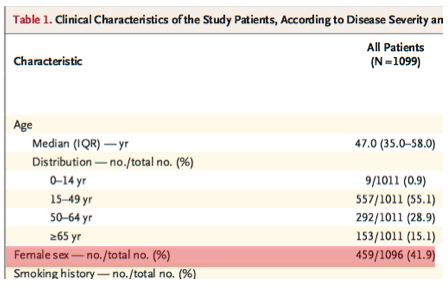
Do you want to learn the mechanisms of the drugs being tested for #COVID-19 (aka SARS-CoV-2)?
The WHO has launched the SOLIDARITY trial, rapidly testing 4 treatment regimens.
This is a quick primer.
sciencemag.org/news/2020/03/w…
#medtwitter #tweetorial
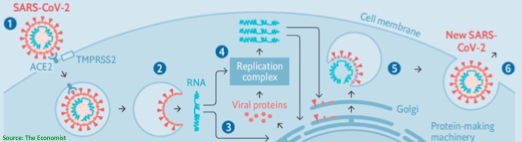
First, Remdesivir
🔹Adenosine nucleotide analogue that competes w/ ATP incorporation into viral RNA
🔹This inhibits viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and blocks replication (in vitro, at least)
See step 4 in the viral life cycle diagram below
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32020029
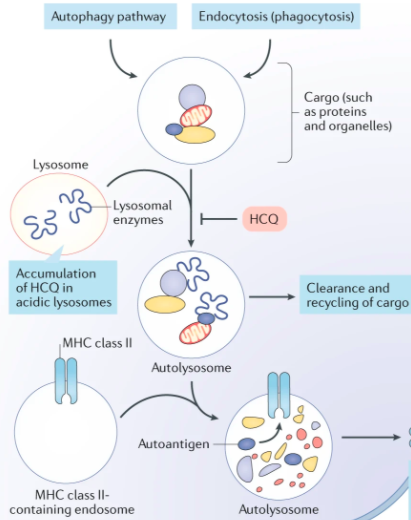
Next, hydroxychloroquine (HCQ)
🔹SARS-CoV-2 infects airway by endocytosis (tweet #2, step 1 in fig.)
🔹HCQ = weak base
🔹It accumulates in and inhibits lysosomes by ⬆️ pH, which blocks endocytosis
🔹HCQ also ⬇️ inflammatory cytokines (? significance)
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32034323
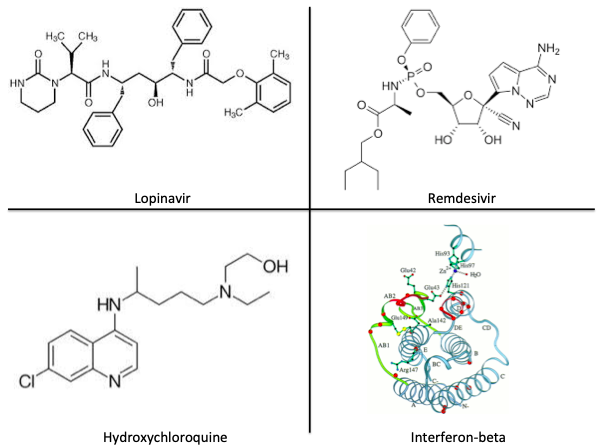
Third, lopinavir/ritonavir
🔹Lopinavir 🚫viral proteases, blocking formation of viral proteins (step 3 in diagram below) and interrupting replication
🔹Ritonavir is a Cytochrome-P3A inhibitor, preventing metabolism of lopinavir and ⬆️ serum levels
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14985565
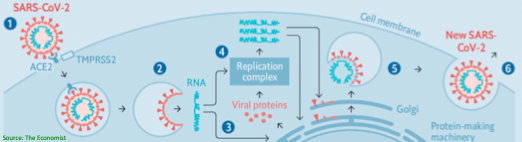
Finally, interferon-beta (IFN-b, combined w/ lopinavir/ritonavir)
🔹IFN-b reduces in vitro replication of other coronaviruses
🔹Exact mechanism of anti-viral activity is unknown
🔹Also likely augments systemic immune response (? significance)
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15288617
An important reminder:
In vitro effects don't = clinical efficacy.
There have been many unsuccessful trials of anti-viral meds (ex. in Ebola, Chikungunya, Dengue)
That's why trials like SOLIDARITY are needed, to identify what works and what doesn't.
nature.com/articles/d4158…