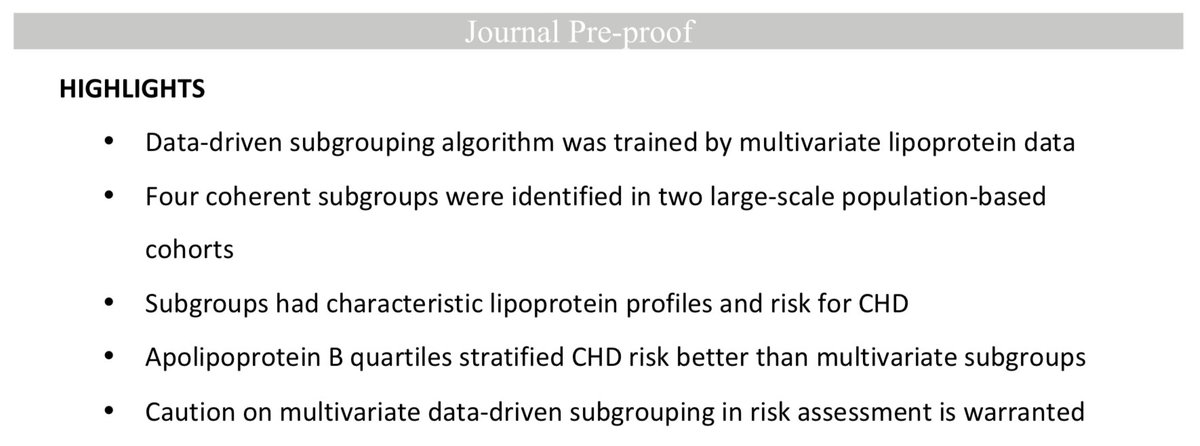
Phosphorylation of the overlooked #tyrosine 310 regulates the structure, #aggregation, and #microtubule- and #lipid-binding properties of #Tau
biorxiv.org/content/10.110…
Short #thread!
#AcademicTwitter #biochemistry #threadstory
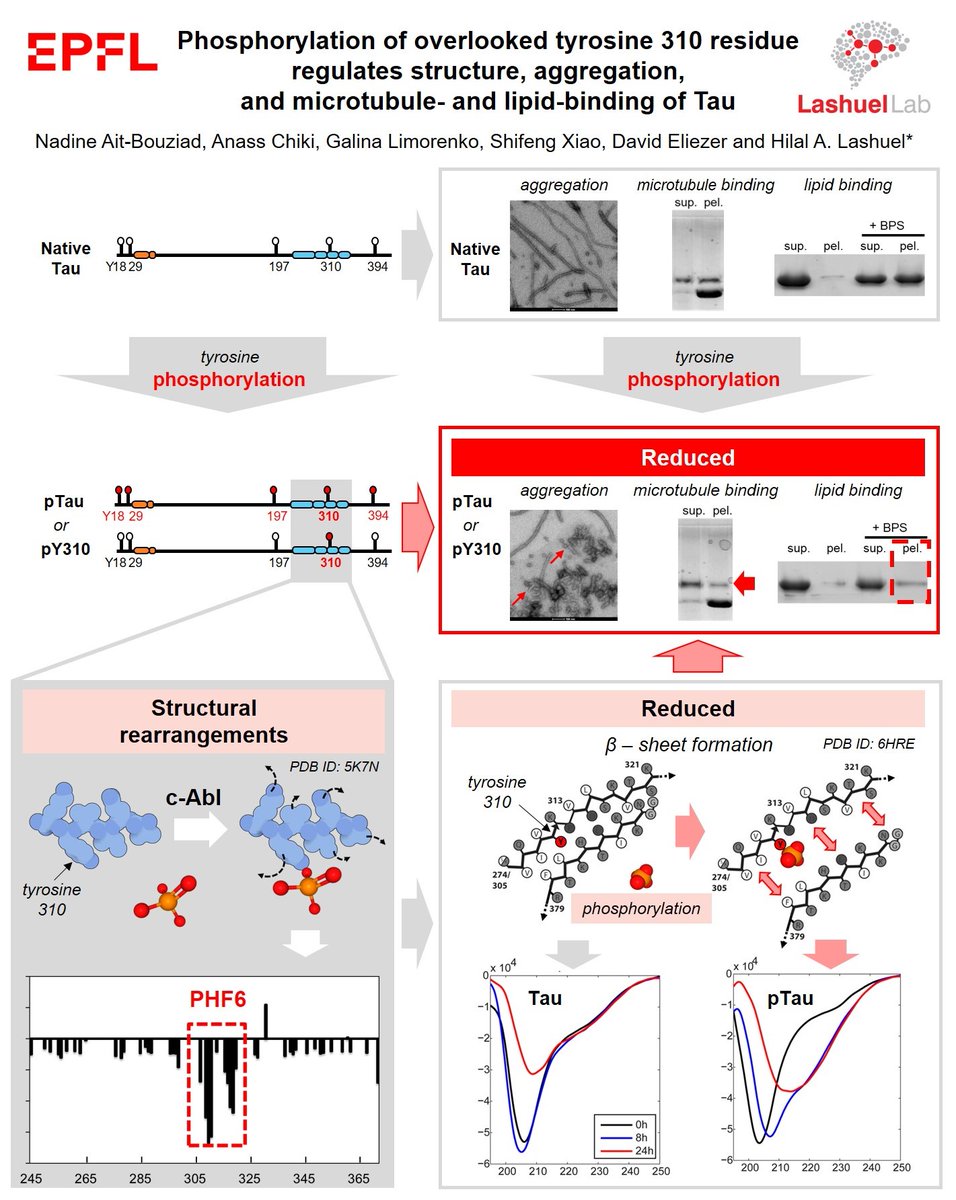
How would addition of bulky negatively charged phosphogroups to tyrosines impact Tau properties?
1. c-Abl is effective tool to produce large quantities (in milligram range, we produced 10mg/protein here) of in vitro phosphorylated Tau.
Tau tyrosine phosphorylation is found in normal and diseased brain. Although Tau phosphorylation predominantly associated with Tau aggregation, we show that site-specificity is crucial, with pY310 leading to MT detachment, but preventing Tau fibrillization