In our latest @BlackRock Market Insights commentary we argue that #inflation’s role in the #economic order can be misinterpreted, and therefore that #policy seeking to achieve positive ends can ironically become the means by which those ends are undone: bit.ly/3fyLn4O
Today, policymakers face a set of increasingly critical choices that could end up shaping our quality of life for a generation. Changes to the #Fed’s #inflation framework, without being fully debated, may ironically end up exacerbating the very problems they seek to alleviate.
One might paraphrase the #Fed mandate of full employment and stable prices as being intended “to preserve the purchasing power of as many as possible” – or, to create the best quality of life for the community. So, how do varying levels of #inflation impact that mandate?
On one hand, #prices that are falling too quickly have the potential to hurt purchasing power by raising the real value and servicing cost of #liabilities, and on the other, prices that are rising too quickly can hurt #PurchasingPower by reducing the real value of #income. 

And both these extremes can be detrimental to #psychology and #economic decision making.
Not all #price changes impact purchasing power the same way, but in aggregate, there is a healthy middle ground that allows for a sustainable #debt load while also supporting the quality-of-life-enhancing process of #CreativeDestruction.
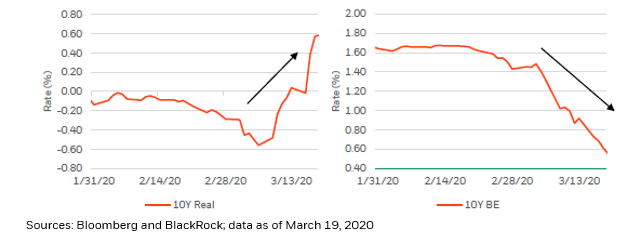
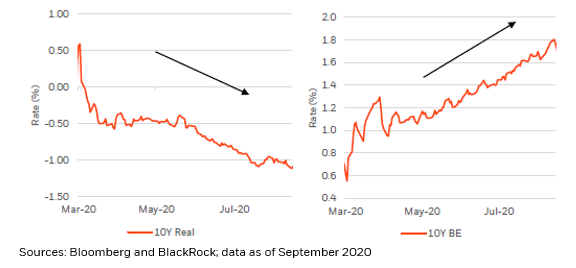
On the back of a blockbuster April #inflation report that hinted at #overheating, the question of what constitutes that healthy middle ground, and whether it needs to be above 2% or not (@federalreserve policymakers tend to believe that it does), has never been more important.
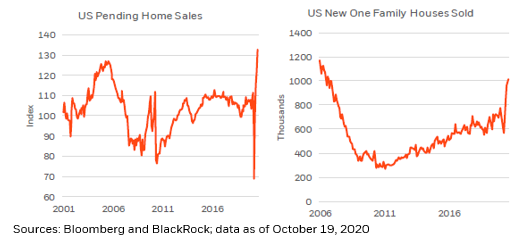
In our view, growing #demand, or expanding #investment, are typically supportive of quality of life improvements, an idea that likely draws little argument.
Considerably more debatable though, is a theory that #inflation proponents often peddle, stating that higher levels of inflation foster #growth and incentivize expansionary investment.
Yet, we think there is a “leap of logic” embedded in that theory; an incredibly important nuance that must be isolated and understood: #inflation is a consequence of demand, not a catalyst for it!
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh