While our February 18th monthly client call argument for rising #RealRates appeared prescient, we were surprised by the magnitude of last week’s #move and would expect a more benign evolution toward #equilibrium going forward.
Taking a stab at periodizing the past year: 1) in Feb/Mar 2020 the Covid crisis was priced into #markets, real #rates spiked higher, #inflation breakevens collapsed and #investors scrambled to raise #cash as the #SPX experienced its fastest 30% drawdown in history. 
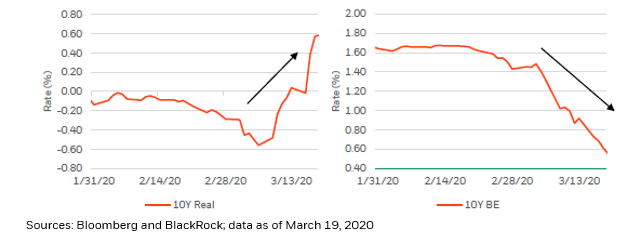
Then, 2) from Apr through Oct 2020 we witnessed the #market impact of monumental #monetary and #fiscal policy responses to the #crisis, as policymakers successfully sought to force #real rates down and restore #inflation expectations. 
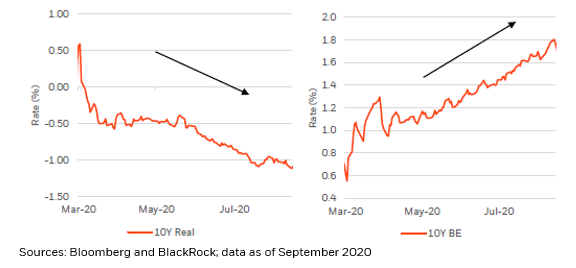
As 3) #investors began to appreciate the sheer magnitude of the #policy response, from roughly mid-2020 through early-2021, news of successful #vaccine trials also began to infiltrate #markets and #price action…
That led real #rates to remain low and stable, while #breakevens continued to recover into above-average territory, reaching highs not seen since 2014 and supporting #risk sentiment. 
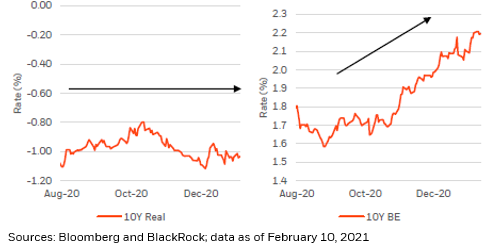
But we appear to be entering into a new regime 4), in which we’re witness rising real #rates and high but stable #breakevens. As such, #AssetAllocation going forward will likely be about determining what drives nominal #interest rates… 

… and it will be about the correlation between #breakevens and real #rates and whether the spread between breakevens and #real rates widens or narrows.
Going forward, changes in the composition of nominal #rates should better reflect changes in the composition of nominal #GDP…
…with real GDP potentially hitting close to 7% by the end of the year, in our estimation, with inflation running at a healthy 2% to 3% clip; 10-Year real rates no longer need to stay at emergency levels of around -1%.
And while 10-Year #breakevens could rise further, substantial #InflationExpectations are already baked into a roughly 2.25% price.
• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh