In the early part of the first millennium CE, the #IndoEuropean language known as Proto-#Germanic diverged into an East branch (which included #Gothic) and a Northwest branch.
Northwest then split into West and North branches when Proto-#Norse developed in #Scandinavia.
Northwest then split into West and North branches when Proto-#Norse developed in #Scandinavia.

Until the 8th century, #Germanic #languages, including Proto-#Norse, were written in Elder Futhark, the earliest #runic #alphabet.
The name #Futhark comes from the initial phonemes in the names of the first six #runes:
ᚠ ᚢ ᚦ ᚨ ᚱ ᚲ
F U Þ A R K
The name #Futhark comes from the initial phonemes in the names of the first six #runes:
ᚠ ᚢ ᚦ ᚨ ᚱ ᚲ
F U Þ A R K
https://twitter.com/linglore/status/1114082506431709184
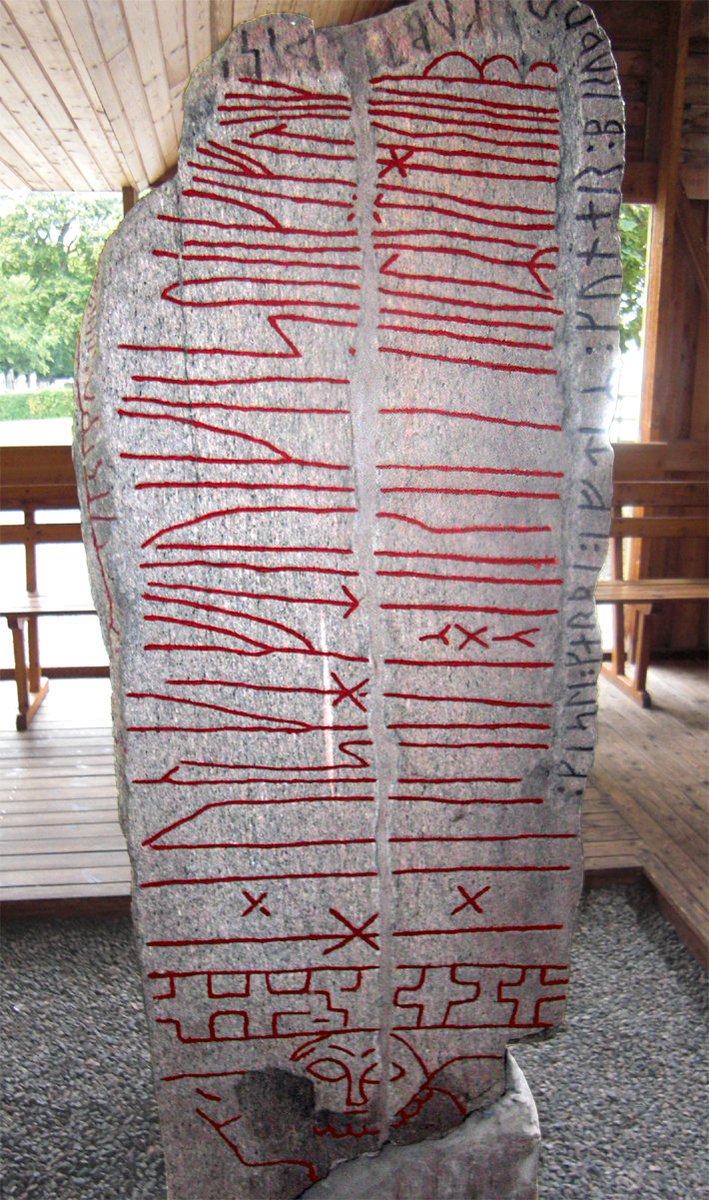
By the beginning of the #Viking Age around 800 CE, Proto-#Norse had evolved into Old Norse, and #Scandinavia's writing system transitioned from the 24 #runes of Elder #Futhark to Younger Futhark's 16 runes.
The #Swedish #Sparlösa #Runestone from ~800 CE features both #alphabets.
The #Swedish #Sparlösa #Runestone from ~800 CE features both #alphabets.

Old #Norse divided into three dialects: Old West Norse, Old East Norse, and Old #Gutnish (Old #Gotlandic).
Old Gutnish formed on the #Baltic island of #Gotland in present-day 🇸🇪#Sweden. It had some similarities with (East #Germanic) #Gothic not found in the other Norse dialects.
Old Gutnish formed on the #Baltic island of #Gotland in present-day 🇸🇪#Sweden. It had some similarities with (East #Germanic) #Gothic not found in the other Norse dialects.

Proto-Norse, and then Old #Norse, were the ancestors of every North #Germanic #language, which today includes #Swedish, #Danish, #Norwegian (#Bokmål and #Nynorsk), #Icelandic and #Faroese. 

The Old East Norse #dialect of Old #Norse was spoken mainly in present-day 🇩🇰#Denmark and 🇸🇪#Sweden. Around the 12th century it began to split into Old #Danish and Old #Swedish as Old Danish in particular changed and developed new features, including stød:
https://twitter.com/linglore/status/1090244439686164480
Old Danish developed into modern #Danish during the 1500s when Danish replaced #Latin as the scholarly #language of religion and writing in 🇩🇰#Denmark. The educated #Copenhagen #dialect began to emerge as the national standard.
Today nearly 6m people speak Danish.
Today nearly 6m people speak Danish.

#Danish is spoken natively by some of the residents of Southern #Schleswig (#Südschleswig or #Sydslesvig), the northernmost part of 🇩🇪#Germany in the #Jutland peninsula. It was part of 🇩🇰#Denmark until 1864. It's now part of the #German state of Schleswig-Holstein. 

🇬🇱#Greenland is a constituent country of the Kingdom of 🇩🇰#Denmark. 12% of its ~56K people are native #Danish speakers. The other 88% speak #Greenlandic, the indigenous #Inuit #language. Most Inuit #Greenlanders also speak Danish, which is widely used in administration. 

#Danes colonised the Danish Virgin Islands (present-day 🇻🇮#USVirginIslands) from 1672 to 1917. The #Danish #language played only a limited role, mainly in administration. #Dutch and #English were the de facto working #languages of the islands. A few Danish place names remain. 

During the colonial era, 🇩🇰#Denmark held several outposts in present-day 🇬🇭#Ghana and 🇮🇳#India. These colonies were sold to the 🇬🇧#UK in the mid 1800s and the #Danish #language had little to no lasting impact in Ghana or India.
1753 depiction of Fort #Dansborg in #TamilNadu.
1753 depiction of Fort #Dansborg in #TamilNadu.

The 13th century Äldre #Västgötalagen (Elder #Westrogothic law) was the first #Swedish text written in the #Latin script. It marks the transition from (#runic) Old #Norse to the Old Swedish #language, spoken from 1225 until 1526. 

Unlike Old #Danish, which diverged considerably from its ancestor, the Old East Norse #dialect of Old #Norse, Old #Swedish underwent only slight changes at first, preserving more of the original features of Old East Norse. In the late 1300s it began to change more significantly. 

The first #Swedish translation of the New Testament in 1526 is considered the beginning of the Modern Swedish #language. The full (king) Gustav Vasa #Bible followed in 1541. It began to standardise Modern Swedish spellings and distinguish them from #Danish spellings. 

With ~10m speakers, #Swedish is the largest of the North #Germanic #languages. It's official in 🇸🇪#Sweden, where most Swedish-speakers live, and in 🇫🇮#Finland, where it's spoken by more than 5% (~290K) of the population.
Map of Swedish #dialects:
Map of Swedish #dialects:

The #Swedish #dialects on the south coast of 🇫🇮#Finland are mostly similar to those in 🇸🇪#Sweden, with some #Finnish loanwords and a few Swedish words that are now considered slightly archaic in Sweden.
The dialects in #Ostrobothnia on the west coast are more divergent.
The dialects in #Ostrobothnia on the west coast are more divergent.

The #Ostrobothnian #Swedish #dialect of #Närpes, 🇫🇮#Finland ("Nerpis" on this 1539 map) is so archaic its mutual intelligibility with other varieties of Swedish is very limited. In many respects it's more similar to #Icelandic and Old #Norse than it is to Modern Swedish. 

The 🇦🇽#Åland Islands (#Ahvenanmaa in #Finnish) is an autonomous region of 🇫🇮#Finland.
By law Åland (20 on map) is exclusively #Swedish-speaking. Over 90% of its ~29K people are native Swedish speakers. Their #dialect is similar to the #Svealand #Uppländska dialect of 🇸🇪#Sweden.
By law Åland (20 on map) is exclusively #Swedish-speaking. Over 90% of its ~29K people are native Swedish speakers. Their #dialect is similar to the #Svealand #Uppländska dialect of 🇸🇪#Sweden.

Though largely descended from the Old #Gutnish #dialect of Old #Norse, the modern Gutnish (#Gotlandic or #gutamål) dialect of the #Gotland and #Fårö islands has been significantly influenced by Modern #Swedish, and is now considered a Swedish dialect.
https://twitter.com/linglore/status/1135887419440603137
#Swedes inhabited northern and western 🇪🇪#Estonia, an area they called #Aiboland or #Egeland, from at least the 13th century until WWII, when most fled to 🇸🇪#Sweden.
Estonian Swedes spoke a number of eastern #Swedish #dialects. Examples include #rågömål and #nuckömål.
Estonian Swedes spoke a number of eastern #Swedish #dialects. Examples include #rågömål and #nuckömål.

After #Russia gained control of #Estonia in the 18th century, a group of Estonian #Swedes relocated to southern #Ukraine where in 1782 they founded the Swedish-speaking village later known as #Gammalsvenskby (Old #Swedish Village). In 1929 they were transported to #Sweden. 

#Swedish and #Finnish were spoken along the #Delaware River in the 17th century in 🇸🇪#Sweden's colony of Nya #Sverige (New Sweden), which fell to the #Dutch in 1655.
The 🇺🇸#NewJersey towns of #Bridgeport (formerly New Stockholm) and #Swedesboro were established by #Swedes.
The 🇺🇸#NewJersey towns of #Bridgeport (formerly New Stockholm) and #Swedesboro were established by #Swedes.

The 🇫🇷#French #Caribbean island of 🇧🇱#SaintBarthélemy (St Barts) was a 🇸🇪#Swedish colony from 1784 until 1878. Swedish, French and #English were commonly spoken there.
(The island's #indigenous name was #Ouanalao. Christopher Columbus renamed it after his brother Bartolomeo.)
(The island's #indigenous name was #Ouanalao. Christopher Columbus renamed it after his brother Bartolomeo.)

For centuries the southern provinces of present-day 🇸🇪#Sweden were part of 🇩🇰#Denmark.
Many #linguists consider Sweden's #dialects #Hallandian, #Scanian, and #Blekingian (#halländska, #skånska, #blekingemål) to be East #Danish dialects. #Swedes tend to regard them as Swedish.
Many #linguists consider Sweden's #dialects #Hallandian, #Scanian, and #Blekingian (#halländska, #skånska, #blekingemål) to be East #Danish dialects. #Swedes tend to regard them as Swedish.
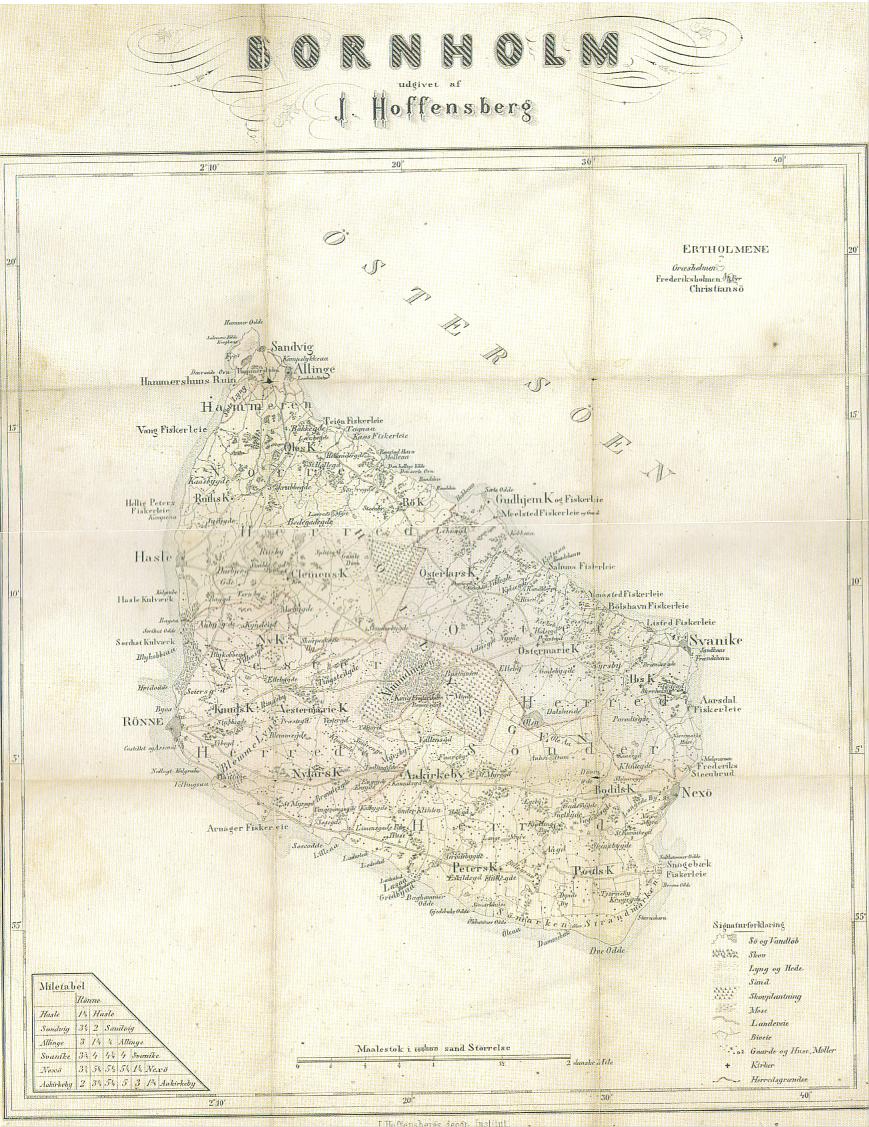
The #Baltic island of #Bornholm was part of #Scania, but broke away to remain in 🇩🇰#Denmark when 🇸🇪#Sweden won Scania.
The endangered #Bornholmsk #dialect is similar to #Scanian and other East #Danish #dialects. Bornholm's ~40K residents are mostly shifting to standard Danish.
The endangered #Bornholmsk #dialect is similar to #Scanian and other East #Danish #dialects. Bornholm's ~40K residents are mostly shifting to standard Danish.
As #Danes and #Swedes spread across northern #Europe during the #Viking Age (793–1066 CE), the Old East Norse #dialect of Old #Norse travelled with them, from #England and #Normandy in the West, to present-day #Russia in the East. 

Originally from #Sweden, the #Rus' #Vikings raided, traded, and settled along the rivers between the #Baltic and Black Seas. They founded and ruled the #Kievan Rus' state.
"#Russia" and "#Belarus" derive from Rus'.
Some #Slavic nationalists reject a #Norse origin of the Rus'.
"#Russia" and "#Belarus" derive from Rus'.
Some #Slavic nationalists reject a #Norse origin of the Rus'.

Though of #Germanic #Viking descent, the #Rus' assimilated into #Slavic culture during their 7 centuries of rule in #Russia.
A few #Russian words and proper names are of Old #Norse origin. Examples:
askr → я́щик (box, chest)
knútr → кнут (whip, knout)
Yngvarr → Игорь (Igor)
A few #Russian words and proper names are of Old #Norse origin. Examples:
askr → я́щик (box, chest)
knútr → кнут (whip, knout)
Yngvarr → Игорь (Igor)

#Danish #Vikings conquered and held large parts of #England, historically known as the #Danelaw, between 865 and 1066.
Many #English words derive from Old East #Norse, including they, them, husband, anger, skill, law, call, and cake. 🍰
Many #English words derive from Old East #Norse, including they, them, husband, anger, skill, law, call, and cake. 🍰

#Hrólfr #Ragnvaldsson, better known as #Rollo, was the first ruler of #Normandy in the 10th century. Sources differ on whether he was from #Denmark or #Norway. #Vikings from both countries settled in Normandy, bringing both the East and West #dialects of Old #Norse. 

The #Normans ("Norse Men" or "North Men") switched from Old #Norse to the Gallo-Romance #Oïl #language of northern #France. However, an injection of Norse loan words helped to shape the local Norman #dialect of #Oïl, aka Norman-French.
More on #Oïl:
More on #Oïl:
https://twitter.com/linglore/status/1108308047649222656
Some #Norse words passed into #Norman, but not into #French:
Norse: hrím
Norman: rimée
French: givre
(hoarfrost / rime)
Norse: lundr
Norman: londe
French: bosquet
(grove)
Other Norse-Norman words were later adopted into French:
Norse: krabbi
Norman: crabe
French: crabe
(crab)
Norse: hrím
Norman: rimée
French: givre
(hoarfrost / rime)
Norse: lundr
Norman: londe
French: bosquet
(grove)
Other Norse-Norman words were later adopted into French:
Norse: krabbi
Norman: crabe
French: crabe
(crab)

The #Normans conquered many places, including parts of present-day #Italy, #Malta, #Tunisia, #Algeria, #Libya, #Syria, #Turkey, #Cyprus, the #UK, #Ireland — even the #CanaryIslands. But the Normans no longer spoke #Norse, so their feats did not expand the use of Norse. 

Recap: Old #Norse divided into three #dialects. Old #Gutnish developed on the #Baltic Sea island of #Gotland. Old East Norse developed in #Sweden and #Denmark.
Old West Norse developed in #Norway and in the North Atlantic settlements of #Norwegian #Vikings and their descendants.
Old West Norse developed in #Norway and in the North Atlantic settlements of #Norwegian #Vikings and their descendants.

#Norwegian #Vikings started raiding the #British-#Irish archipelago in the 8th century and began settling in the 9th, leaving behind many #Norse place names, including:
#Wicklow, 🇮🇪#Ireland
#Swansea, 🏴#Wales
#Sutherland, 🏴#Scotland
#Scafell, 🏴#England
#Laxey, 🇮🇲Isle of #Man
#Wicklow, 🇮🇪#Ireland
#Swansea, 🏴#Wales
#Sutherland, 🏴#Scotland
#Scafell, 🏴#England
#Laxey, 🇮🇲Isle of #Man

Parts of northern and western 🏴#Scotland were under #Norwegian control for centuries.
In #Shetland, #Orkney, and #Caithness, Old West #Norse evolved into #Norn, a North #Germanic #language that still had some speakers well into the 19th century.
In #Shetland, #Orkney, and #Caithness, Old West #Norse evolved into #Norn, a North #Germanic #language that still had some speakers well into the 19th century.
https://twitter.com/linglore/status/1122417385988861958
#Norwegian #Vikings in #Ireland and western #Scotland are known as the "Norse-#Gaels" because they intermarried with the #Celts and adopted #Gaelic culture. Old #Norse place names and family names, and some Norse-derived vocabulary survived the transition to Gaelic. 

In #Ireland the #Vikings established #longphorts (naval fortresses) in #Dublin, #Waterford, #Wexford, #Cork, #Limerick, and Linn Duachaill.
"Waterford" derives from Old #Norse "Veðrafjǫrðr", or "wether fjord". (A wether is a castrated male sheep.)
"Waterford" derives from Old #Norse "Veðrafjǫrðr", or "wether fjord". (A wether is a castrated male sheep.)

#Norwegian #Vikings arrived in the 🇮🇲#IsleOfMan at the end of the 8th century. They established the island's parliament, the #Tynwald, which has held meetings continuously for over 1000 years.
"Tynwald" derives from Old #Norse "Þingvǫllr". [Thing (assembly) + wald (field)].
"Tynwald" derives from Old #Norse "Þingvǫllr". [Thing (assembly) + wald (field)].

The 🇫🇴#FaroeIslands were inhabited as early as the 5th century, perhaps by pre-#Viking #Scandinavians, or perhaps by #Celts from #Ireland or #GreatBritain.
By the 10th century, the #Faroes were dominated by #Norwegian #Vikings, including #Norse-#Gaels from Ireland or #Britain.
By the 10th century, the #Faroes were dominated by #Norwegian #Vikings, including #Norse-#Gaels from Ireland or #Britain.
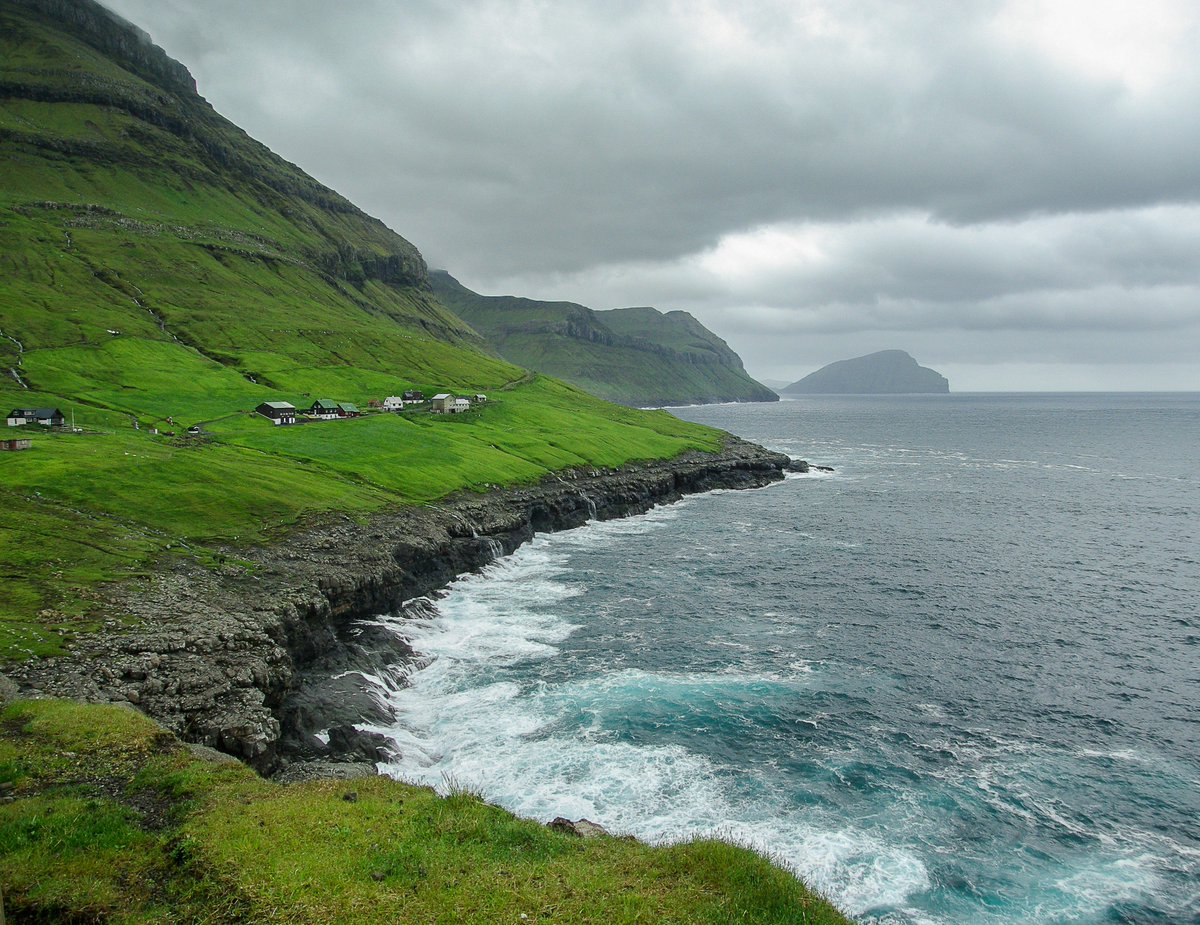

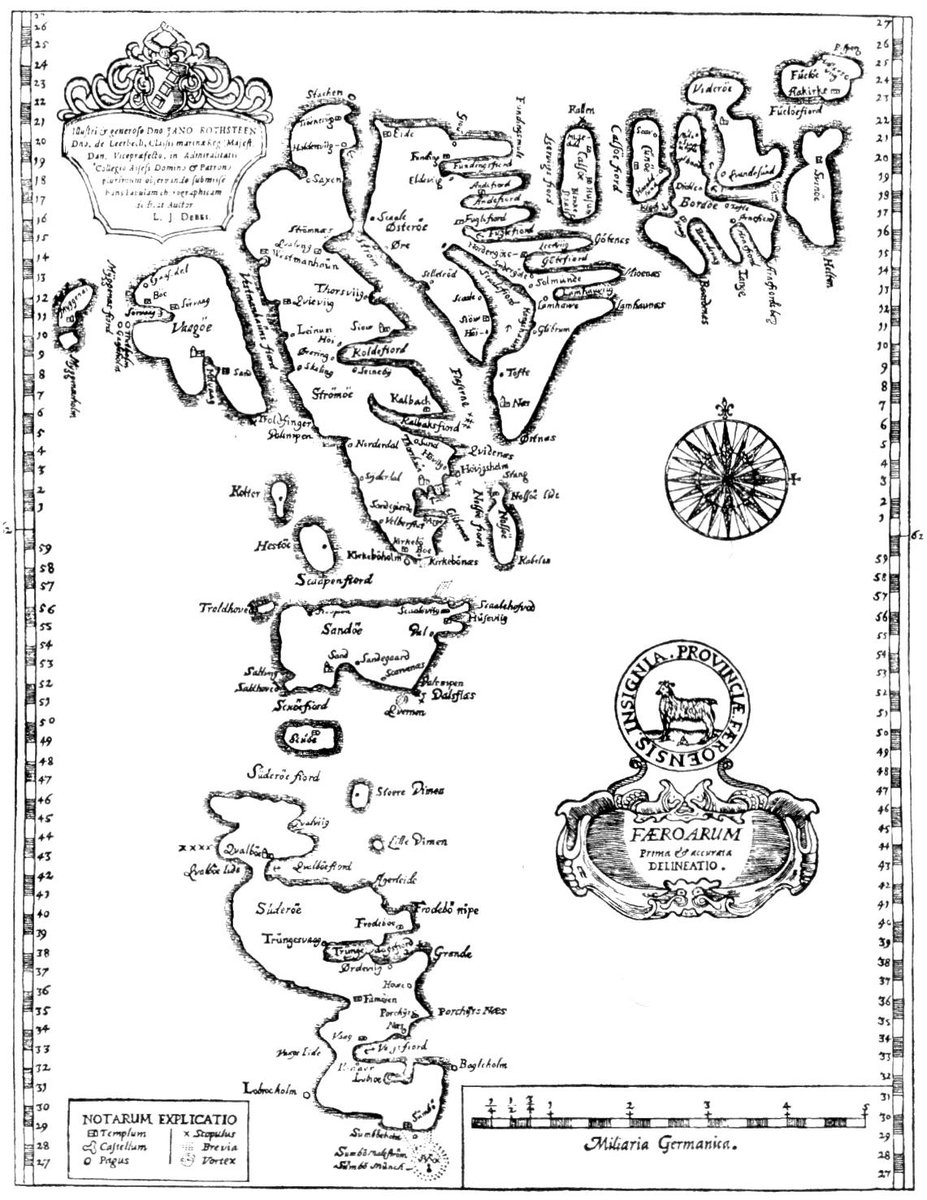
The #runestone pictured in the foreground of this stamp was made in the 13th century in #Sandavágur in the 🇫🇴#FaroeIslands.
The Old #Norse inscription reads:
"Þorkell Ǫnundr's son, man of the east from Rogaland, lived in this place first."
#Rogaland is in western 🇳🇴#Norway.
The Old #Norse inscription reads:
"Þorkell Ǫnundr's son, man of the east from Rogaland, lived in this place first."
#Rogaland is in western 🇳🇴#Norway.

The #sauðabréfit (Sheep Letter) is the oldest surviving document from the 🇫🇴#FaroeIslands. Written in 1298 in Old #Norse, it's a royal decree mostly about sheep husbandry, but also about constitutional matters such as the transfer of administrative power to the king of 🇳🇴#Norway. 

By around the 14th-16th centuries, the variety of Old West #Norse spoken in the 🇫🇴#FaroeIslands had evolved into #Faroese.
Modern Faroese is a North #Germanic #language with ~70K speakers in the #Faroes and in 🇩🇰#Denmark. Today the Faroes are an autonomous country of Denmark.
Modern Faroese is a North #Germanic #language with ~70K speakers in the #Faroes and in 🇩🇰#Denmark. Today the Faroes are an autonomous country of Denmark.

When 🇳🇴#Norway and 🇩🇰#Denmark united in 1380 #Danish became the #language of administration in the 🇫🇴#FaroeIslands. For a few centuries, #Faroese was spoken, but not written.
Today the islanders speak and write Faroese. Danish is taught as a required foreign language at school.
Today the islanders speak and write Faroese. Danish is taught as a required foreign language at school.

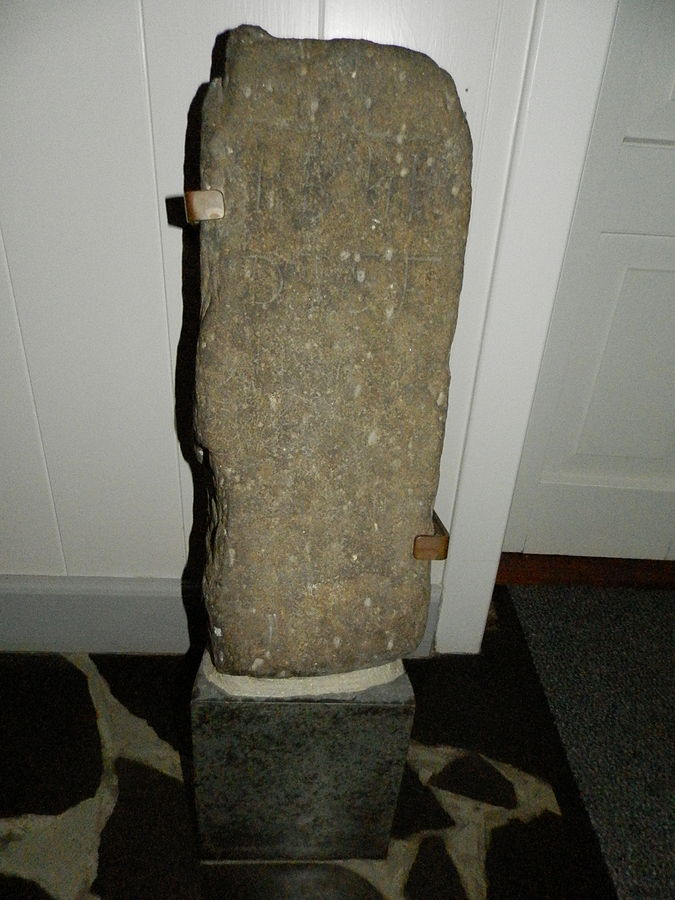
The #Fámjin stone was created around 1538, the youngest known #runestone of the 🇫🇴#FaroeIslands. It proves that #runes were used as late as the 16th century.
The stone bears #Latin letters in addition to the #runic ones.
[Image: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:The_…]
The stone bears #Latin letters in addition to the #runic ones.
[Image: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:The_…]

The #Norse-#Gaels introduced into #Faroese a few #Celtic #Gaelic words that are not found in #Germanic #Norwegian.
[Old #Irish] → [Faroese]
grúac (hair) → grúkur (head of a seal)
tarb (bull) → tarvur
lám (hand) → lámur (paw, left hand, flipper of a seal)
[Old #Irish] → [Faroese]
grúac (hair) → grúkur (head of a seal)
tarb (bull) → tarvur
lám (hand) → lámur (paw, left hand, flipper of a seal)
According to the earliest #Icelandic #sagas (which were recorded in the 12th century) #Irish-speaking Christian monks referred to as the "Papar" inhabited 🇮🇸#Iceland before the first #Vikings arrived in the 870s, and eventually left because they disliked the heathen #Norsemen. 

Ari Þorgilsson (#Thorgilsson) (1067 – 1148 CE) wrote #Íslendingabók (Book of #Icelanders) around 1130, chronicling the early #history of the #Norwegian settlement of 🇮🇸#Iceland.
He wrote in Old #Icelandic, a variety of Old West #Norse.
The original is lost. This is a 1651 copy.
He wrote in Old #Icelandic, a variety of Old West #Norse.
The original is lost. This is a 1651 copy.

Ari Þorgilsson may have also contributed to #Landnámabók (Book of Settlements), which describes the #Norse settlement of 🇮🇸#Iceland in great detail, listing individual #Norwegian settlers and their descendants.
Some brought with them #Gaelic-speaking thralls (slaves or serfs).
Some brought with them #Gaelic-speaking thralls (slaves or serfs).

#Icelander #Snorri Sturluson (1179 - 1241) wrote (or compiled) some of the most important works of Old #Norse literature. The Prose #Edda is the most detailed source of knowledge of #Nordic #mythology.
#Heimskringla is a collection of sagas about #Swedish and #Norwegian kings.
#Heimskringla is a collection of sagas about #Swedish and #Norwegian kings.

Most of the #Viking settlers of 🇮🇸#Iceland came from 🇳🇴#Norway and spoke the Old West #Norse #dialect of #OldNorse.
Old #Icelandic developed as a variety of Old West Norse with minor #Gaelic influence. The Icelandic names Brján and Kormákr come from #Irish Brian and Cormac.
Old #Icelandic developed as a variety of Old West Norse with minor #Gaelic influence. The Icelandic names Brján and Kormákr come from #Irish Brian and Cormac.

Isolated from its continental cousins, #Icelandic changed less than #Danish, #Swedish, or #Norwegian did, and retained more features of Old #Norse, including the [th] sounds (θ, ð) and words starting with hl, hr and hn. #Icelanders can read Old Norse texts with little difficulty. 

Modern #Icelandic is a North #Germanic #language with ~358K speakers.
Its 32-letter #alphabet has no C, Q, or W. It includes ten "#séríslenskur" ("uniquely Icelandic") letters not used in modern #English: Á Ð É Í Ó Ú Ý Þ Æ Ö
Þ (thorn) comes from the #Norse #rune ᚦ (thurs).
Its 32-letter #alphabet has no C, Q, or W. It includes ten "#séríslenskur" ("uniquely Icelandic") letters not used in modern #English: Á Ð É Í Ó Ú Ý Þ Æ Ö
Þ (thorn) comes from the #Norse #rune ᚦ (thurs).

In Old #Norse #Vikings were "Austmenn" (East Men) and #Gaels were "Vestmenn" (West Men).
#Vestmannaeyjar (Westman Islands) are named for #Gaelic slaves who fled there after killing the brother of #Ingólfr Arnarson, 🇮🇸#Iceland's first Norse settler. He killed them in retribution.
#Vestmannaeyjar (Westman Islands) are named for #Gaelic slaves who fled there after killing the brother of #Ingólfr Arnarson, 🇮🇸#Iceland's first Norse settler. He killed them in retribution.
In the 1870s Mormons from #Vestmannaeyjar (Westman Islands) moved to 🇨🇦#Canada.
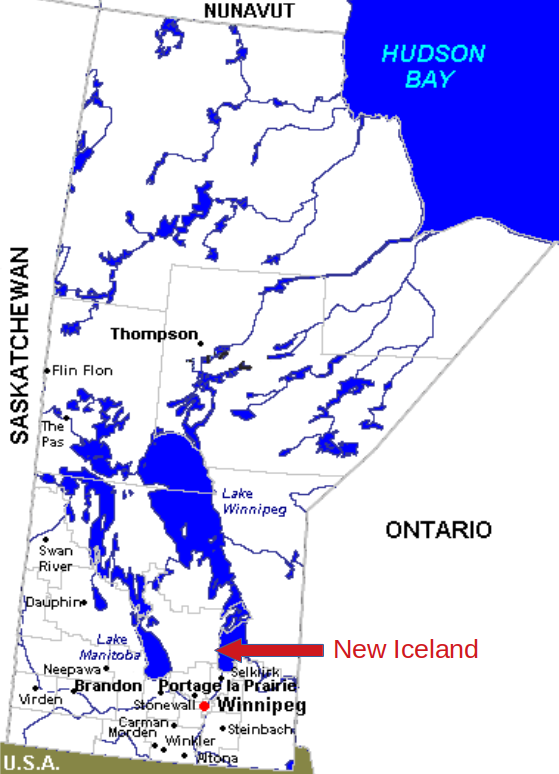
In 1875 they and other #Icelanders fleeing the eruption of 🌋Mount #Askja in 🇮🇸#Iceland established "#NewIceland" on Lake #Winnipeg.
Some residents of #Gimli, #Manitoba still speak #Icelandic today.
In 1875 they and other #Icelanders fleeing the eruption of 🌋Mount #Askja in 🇮🇸#Iceland established "#NewIceland" on Lake #Winnipeg.
Some residents of #Gimli, #Manitoba still speak #Icelandic today.
13th century #Norse #sagas say 🇳🇴#Norway banished Thorvald Asvaldsson around 960 "because of some killings". He moved to 🇮🇸#Iceland with his son, Erik the Red.
In 982 Iceland banished Erik for three years (also for murders). He spent his exile exploring southern 🇬🇱#Greenland.
In 982 Iceland banished Erik for three years (also for murders). He spent his exile exploring southern 🇬🇱#Greenland.

Southern 🇬🇱#Greenland was apparently uninhabited when Erik the Red arrived. Around 985, he returned with #Viking settlers from 🇮🇸#Iceland and established several villages along the southwestern fjords, which at the time were surrounded by forest. 

#Greenlandic #Norse was the variety of Old West Norse spoken in the Norse settlements of 🇬🇱#Greenland.
It used a "t" where most other varieties of #OldNorse used "þ", and retained some features like "hl", "hr", and "œ" that most other varieties lost.
It used a "t" where most other varieties of #OldNorse used "þ", and retained some features like "hl", "hr", and "œ" that most other varieties lost.
The #Kingittorsuaq #Runestone is the longest inscription of #Greenlandic #Norse, showing both "hl" and the "t" substitution for "þ". It was made far north of the #Norse settlements, probably by explorers.
The final signs are unrecognised, not part of any known #runic #alphabet.
The final signs are unrecognised, not part of any known #runic #alphabet.

A #runic "r" with sloping branches is particularly characteristic of #Greenlandic #Norse. Only two such inscriptions have been found outside 🇬🇱#Greenland: one in #Trondheim, 🇳🇴#Norway and one in #Orphir, #Orkney, 🏴#Scotland; perhaps carved by #Greenlanders who sailed to #Europe. 

"#Atlamál in grœnlenzku" is an #OldNorse #Edda (heroic poem) believed to have been composed in 🇬🇱#Greenland in the 12th century. It's a murderous tale about #AttilaTheHun and his wife and inlaws.
Atlamál is included in the #CodexRegius, an #Icelandic collection of #Norse poems.
Atlamál is included in the #CodexRegius, an #Icelandic collection of #Norse poems.

Blown off course in 986, Bjarni Herjólfsson spotted land west of 🇬🇱#Greenland.
Intrigued by the discovery, #Leif Erikson, son of #ErikTheRed, bought Bjarni's ship and led en expedition. He established a #Norse settlement in the land he called #Vinland in present-day 🇨🇦#Canada.
Intrigued by the discovery, #Leif Erikson, son of #ErikTheRed, bought Bjarni's ship and led en expedition. He established a #Norse settlement in the land he called #Vinland in present-day 🇨🇦#Canada.

#Vinland was likely near the Gulf of St Lawrence. #Norse ruins dating to ~1000 have been found at L'Anse aux Meadows in #Newfoundland.
Norse #sagas also refer to #Markland, perhaps #Labrador; and to #Helluland, perhaps #BaffinIsland, where probably-#Viking artefacts were found.
Norse #sagas also refer to #Markland, perhaps #Labrador; and to #Helluland, perhaps #BaffinIsland, where probably-#Viking artefacts were found.
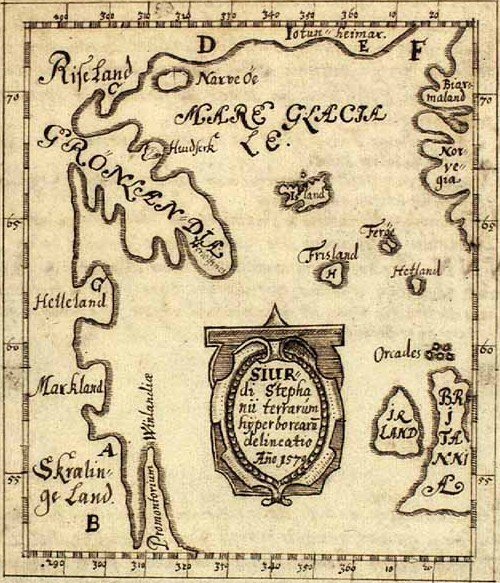
By the mid 15th century, the #Viking colonies of #Greenland and #Vinland — along with the #Greenlandic variety of #OldNorse — were no more, perhaps owing to conflict with #indigenous peoples.
The #Inuit #Kalaallisut #language includes #Norse loan words such as 'kona' ('wife').
The #Inuit #Kalaallisut #language includes #Norse loan words such as 'kona' ('wife').

🇳🇴#Norway is home to important #runestones spanning several centuries.
The Tune stone (200-450 CE) from #Østfold was carved using Elder #Futhark #runes. The Proto-#Norse inscription begins:
'I, Wiwaz, made the runes after Woduridaz, my lord.'
[Image: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Tune…]
The Tune stone (200-450 CE) from #Østfold was carved using Elder #Futhark #runes. The Proto-#Norse inscription begins:
'I, Wiwaz, made the runes after Woduridaz, my lord.'
[Image: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Tune…]

The Proto-#Norse inscription on the 4th century #Einang stone near #Fagernes, 🇳🇴#Norway begins '[I, Go]dagasti painted the #rune', suggesting these Elder #Futhark #runes were originally highlighted with paint.
[Image: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Eina…]
[Image: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Eina…]

The #Hogganvik #runestone is approximately dated to 350 - 500 CE. It was found in #Mandal in southern 🇳🇴#Norway. The Proto-#Norse inscription was carved using the Elder #Futhark #runic #alphabet, and includes a bind-rune (a ligature of more than one #rune). 

The longest known inscription in the Elder #Futhark #runic #alphabet was found on the #Eggja stone in #Sogndal, 🇳🇴#Norway. It dates to 650 - 700 CE. A few of its roughly 200 #runes are transitional toward the Younger Futhark alphabet.
[Image: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Eggj…]
[Image: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Eggj…]

Old #Norwegian diverged from Old West #Norse around the 11th century when 🇳🇴#Norway's conversion to #Christianity introduced #Latin loanwords and the #Roman #alphabet, which gradually replaced #runes.
Around this time hl, hn, and hr clusters lost the h: hringr → ringr (ring).
Around this time hl, hn, and hr clusters lost the h: hringr → ringr (ring).

Near the end of the 14th century 🇳🇴#Norway entered a union with 🇩🇰#Denmark that lasted more than four centuries. #Danish became the #language of the educated elite, the law, and the church. Other #Norwegians, especially in rural areas, spoke #dialects of Middle #Norwegian. 

During the later years of the #Denmark-Norway union, which ended in 1814, the #Danish #language of elite urban areas of 🇳🇴#Norway evolved into 'Dano-Norwegian' as it adopted some #Norwegian vocabulary and pronunciation, and developed minor grammatical differences from Danish. 
In the 19th century competing standards for written #Norwegian developed. #Linguist Knud #Knudsen promoted #Riksmål (national #language), a Norwegianised version of Dano-Norwegian. Riksmål is the basis of #Bokmål (book language), one of 🇳🇴#Norway's two official written standards. 

#Linguist Ivar #Aasen systematically studied #Norwegian #dialects and constructed #Landsmål (country or national #language) as a Norwegian-based alternative to Dano-Norwegian. Landsmål is the basis of #Nynorsk (new or modern Norwegian),🇳🇴#Norway's other official written standard. 

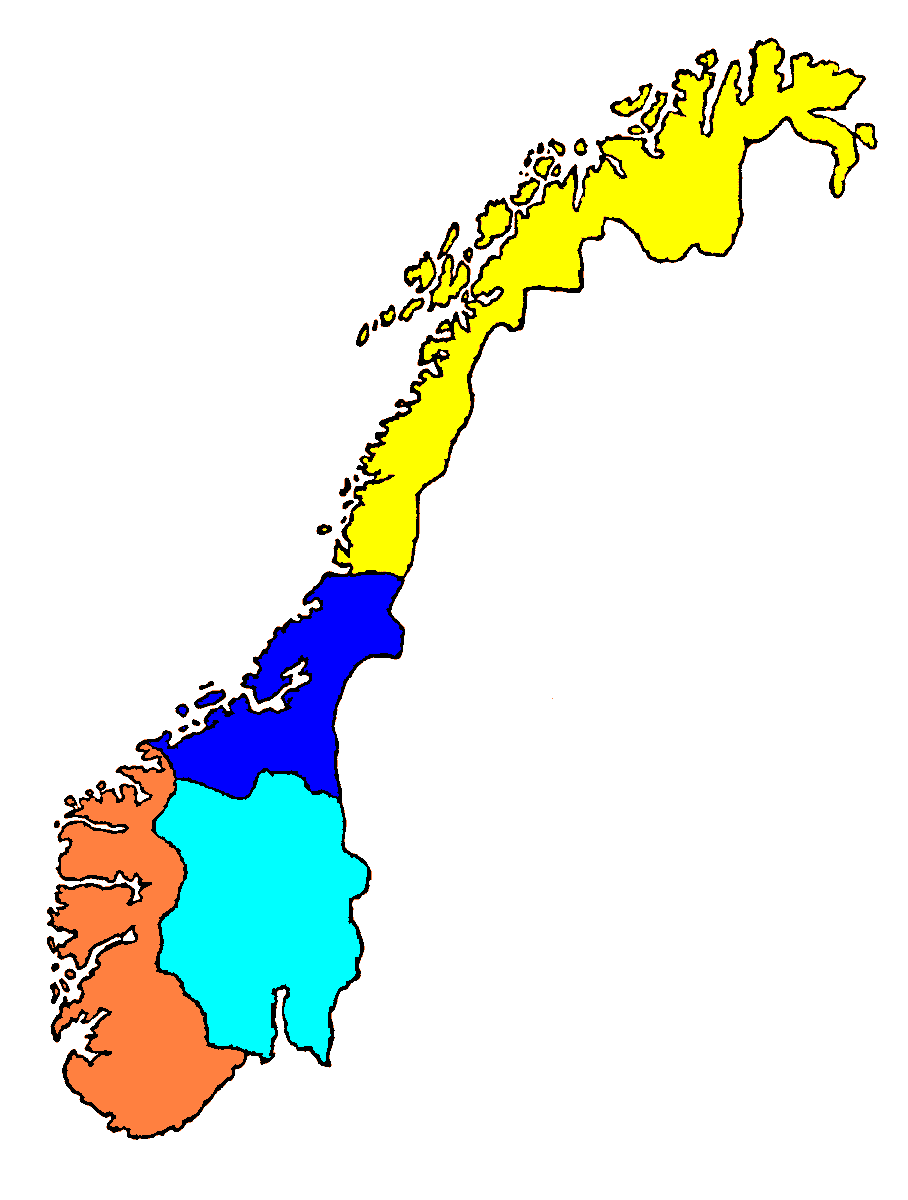
A map of the official #Norwegian #language form (#målform) by municipality:
Red: #Bokmål
Blue: #Nynorsk
Grey: neutral
85% to 90% of 🇳🇴#Norway's population prefers Bokmål as the written standard. Roughly 12% of #Norwegians live in the blue area.
[Image: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:M%C3…]
Red: #Bokmål
Blue: #Nynorsk
Grey: neutral
85% to 90% of 🇳🇴#Norway's population prefers Bokmål as the written standard. Roughly 12% of #Norwegians live in the blue area.
[Image: en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:M%C3…]
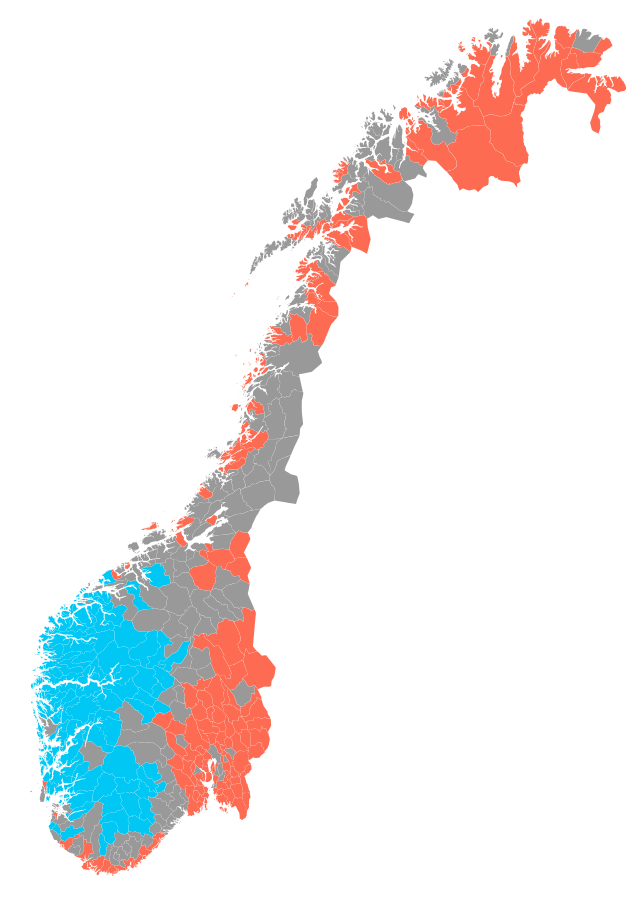
Attempts to merge #Nynorsk and #Bokmål into a unified '#Samnorsk' #Norwegian #language have failed and were abandoned in 2002.
Meanwhile a minority have clung to older forms of their preferred standards. For example, #Høgnorsk is closer to the original #Landsmål than to Nynorsk.
Meanwhile a minority have clung to older forms of their preferred standards. For example, #Høgnorsk is closer to the original #Landsmål than to Nynorsk.

#Norwegian is a North #Germanic #language with ~4.3m native speakers. It's an official language of 🇳🇴#Norway (alongside #Sámi).
Norwegian is part of a #dialect continuum that spans across #Scandinavia. It has a high degree of mutual intelligibility with #Swedish and #Danish.
Norwegian is part of a #dialect continuum that spans across #Scandinavia. It has a high degree of mutual intelligibility with #Swedish and #Danish.
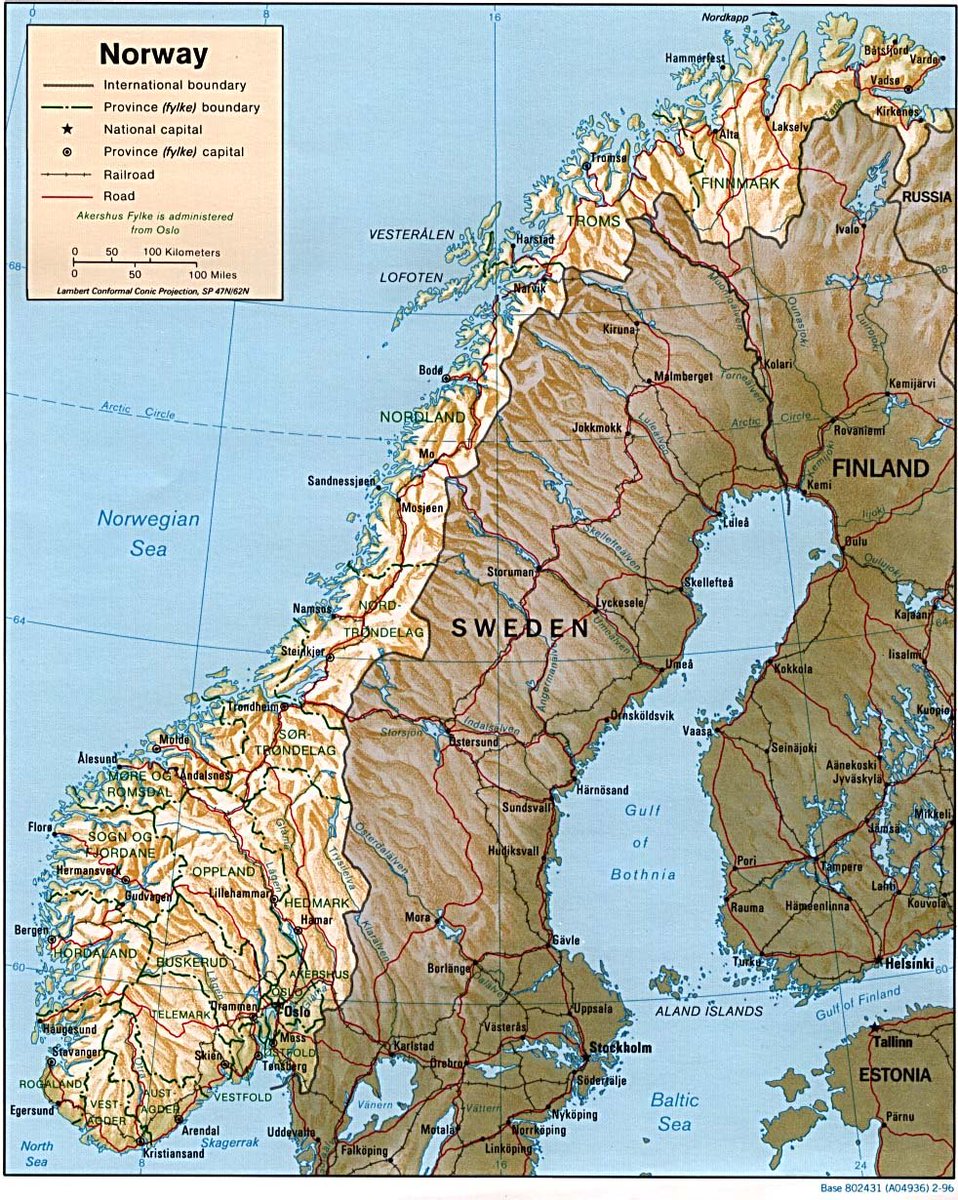
The #Norwegian #alphabet has 29 letters, including æ, ø, and å.
c, q, w, x, and z are used only in loanwords.
#Diacritical marks appear in é, è, ê, ó, ò, and ô. In #Nynorsk, ì, ù and ỳ are occasionally used as well.
Diagram of the Norwegian #SignLanguage alphabet:
c, q, w, x, and z are used only in loanwords.
#Diacritical marks appear in é, è, ê, ó, ò, and ô. In #Nynorsk, ì, ù and ỳ are occasionally used as well.
Diagram of the Norwegian #SignLanguage alphabet:
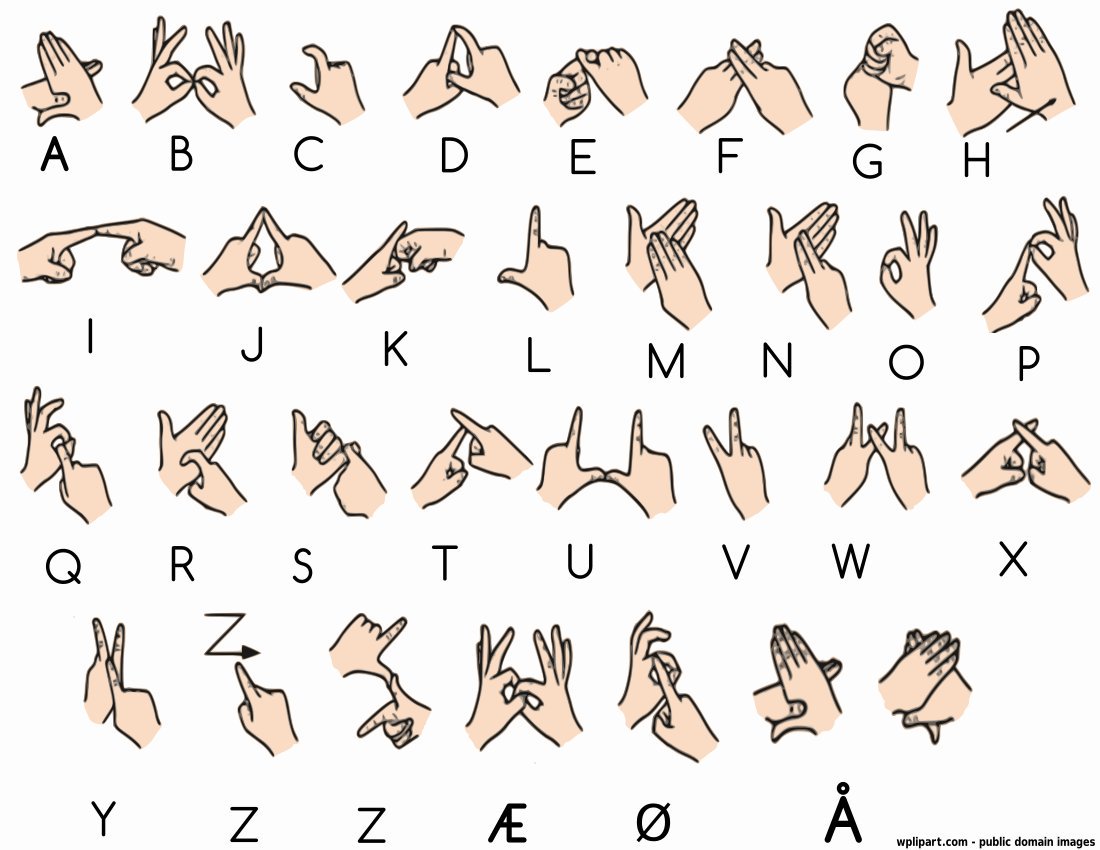
#Norwegian #dialects are often classified into four groups: Northern (#nordnorsk), Central (#trøndersk), Western (#vestlandsk), and Eastern (#østnorsk).
The dialects from #Lyngen (in the north) and #Bergen (in the west) use two grammatical genders. Almost all others use three.
The dialects from #Lyngen (in the north) and #Bergen (in the west) use two grammatical genders. Almost all others use three.
Around ¼ of #Norwegians, including most residents of #Oslo, speak Urban East #Norwegian (#UEN), aka Standard East Norwegian, which doesn't belong to any of the four #dialect groups. It derives from eastern Norwegian elites' pronunciation of #Danish and is written using #Bokmål. 

During the Age of Exploration🇳🇴#Norway was under #Danish rule, and therefore didn't seize oversees colonies. Its far-flung islands of Bouvet, Peter I, and Jan Mayen are uninhabited.
The Arctic archipelago #Svalbard has a population of ~2.7K, of which about 57% speak #Norwegian.
The Arctic archipelago #Svalbard has a population of ~2.7K, of which about 57% speak #Norwegian.

#Norwegians from #Finnmark settled in Russia's #KolaPeninsula around 1870. During WWII, the 'Kola Norwegians' were forcibly resettled in #Soviet #Karelia, where many starved. Some descendants later moved to 🇳🇴#Norway.
In 🇷🇺#Russia roughly 100 people still identify as #Norwegian.
In 🇷🇺#Russia roughly 100 people still identify as #Norwegian.

Before switching to #Russian, Kola #Norwegians spoke a northern #Norwegian #dialect from the #Vardø region.
They likely also used #Russenorsk, a Russian-Norwegian #pidgin #language used between Norwegian fishermen and Russian traders from the 18th century until the #Soviet era.
They likely also used #Russenorsk, a Russian-Norwegian #pidgin #language used between Norwegian fishermen and Russian traders from the 18th century until the #Soviet era.
Hundreds of thousands of 🇳🇴#Norwegians moved to North #America during the 19th and early 20th centuries. Many settled in the Midwestern 🇺🇸#US and the 🇨🇦#Canadian #Prairies.
The Decorah-Posten newspaper in #Iowa was one of several #Norwegian #language publications in the US.
The Decorah-Posten newspaper in #Iowa was one of several #Norwegian #language publications in the US.

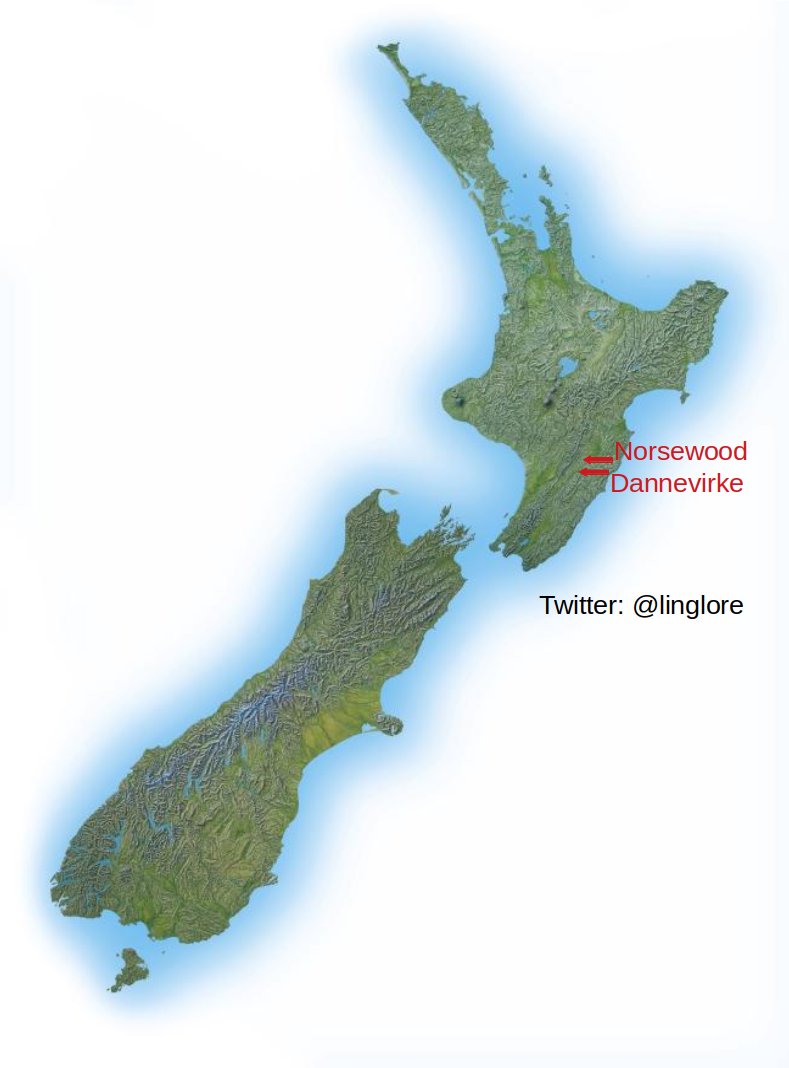
Other #Norwegians journeyed farther, settling in #SouthAmerica, #Africa, #Australia, and elsewhere; occasionally showing up in local place names. Norwegians founded #Norsewood, 🇳🇿#NewZealand in 1872, the year fellow #Scandinavians founded nearby #Dannevirke, 'work of the #Danes'. 
#Elfdalian (#Övdalian) is one of the '#Dalecarlian #dialects' of #Dalarna County, 🇸🇪#Sweden. It's not mutually intelligible with #Swedish or #Norwegian; some therefore consider it a distinct North #Germanic #language with features of Old #Norse.
Listen:
Listen:
#Elfdalian has ~2K speakers, mostly in the #Älvdalen area of #Dalarna County, 🇸🇪#Sweden.
Elfdalian has diverged from #OldNorse less than other varieties of #Dalecarlian have. Its #phonology bears characteristics of both the Old East #Norse and Old West Norse #dialects.
Elfdalian has diverged from #OldNorse less than other varieties of #Dalecarlian have. Its #phonology bears characteristics of both the Old East #Norse and Old West Norse #dialects.

It wasn't only spoken #language that changed slowly in #Dalarna County, 🇸🇪#Sweden. A unique #runic #alphabet known as #Dalecarlian #runes were still used in the 19th century. Samples exist even from the 20th century, but these may have been made after a break in continuous usage. 

After the #Viking era, Younger #Futhark #runes evolved into #mediaeval #runes. These were used throughout #Scandinavia for a few centuries and were the basis of the #Dalecarlian #runic #alphabet (aka #dalrunes), which gradually combined with #Latin letters. 

#Elfdalian now uses the #Latin-based #Dalecarlian #alphabet. Its 32 letters include Ą, Ð, Ę, Į, Ų, Y̨, Å, Ą̊, Ä, and Ö; but not C, Q, X, or Z. The #diacritic hook on vowels like Ų is an #ogonek. It denotes nasality.
A traditional Dalecarlian painted, carved wooden toy horse:
A traditional Dalecarlian painted, carved wooden toy horse:

#Romani people arrived in #Scandinavia around 500 years ago. Their #Indic #language merged with North #Germanic #languages to form #Scandoromani (romani #rakripa). It's mostly extinct in 🇸🇪#Sweden and 🇩🇰#Denmark, but still has roughly 100 speakers in 🇳🇴#Norway, most elderly. 

Some #Romani people travelled alongside indigenous #Norwegian #Traveller communities who speak their own Norwegian #dialect called #Rodi.
Rodi has been influenced by the #languages of other itinerant groups such as #German-derived #Rotwelsch, and more recently, #Scandoromani.
Rodi has been influenced by the #languages of other itinerant groups such as #German-derived #Rotwelsch, and more recently, #Scandoromani.
Newer #immigrants have introduced #Arabic, #Turkish, #Farsi, and other tongues, creating new varieties of the #Nordic #languages commonly known by names that many find offensive: #Kebabnorsk, #Perkerdansk, #Rinkebysvenska.
The #Rinkeby area of #Stockholm: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Rink…
The #Rinkeby area of #Stockholm: commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Rink…

• • •
Missing some Tweet in this thread? You can try to
force a refresh